Peter D. Mitchell
Encyclopedia
Peter Dennis Mitchell, FRS (29 September 1920–10 April 1992) was a British
biochemist
who was awarded the 1978 Nobel Prize for Chemistry for his discovery of the chemiosmotic mechanism of ATP
synthesis.
Mitchell was born in Mitcham
, Surrey
, England
.
, Surrey
on 29 September 1920. His parents were Christopher Gibbs Mitchell, a civil servant, and Kate Beatrice Dorothy (née) Taplin. His Uncle was Sir Godfrey Way Mitchell, chairman of George Wimpey
. He was educated at Queen's College
, Taunton
, and at Jesus College, Cambridge
where he studied the Natural Sciences Tripos specialising in biochemistry
.
He accepted a research post in the Department of Biochemistry, Cambridge, in 1942, and received the degree of Ph.D.
in early 1951 for work on the mode of action of penicillin
. In 1955 he was invited by Professor Michael Swann
to set up a biochemical research unit, called the Chemical Biology Unit, in the Department of Zoology, Edinburgh University, where he was appointed to a Senior Lectureship in 1961, to a Readership in 1962, although ill health led to his resignation in 1963.
-fronted Mansion, known as Glynn House, near Bodmin
, Cornwall
- adapting a major part of it for use as a research laboratory. He and his former research colleague, Jennifer Moyle
founded a charitable company, known as Glynn Research Ltd., to promote fundamental biological research at Glynn House and they embarked on a programme of research on chemiosmotic reactions and reaction systems.
In 1978 he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
"for his contribution to the understanding of biological energy transfer through the formulation of the chemiosmotic theory
."
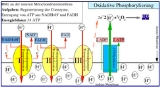
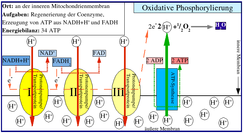 In the 1960s, ATP
In the 1960s, ATP
was known to be the energy currency of life, but the mechanism by which ATP was created in the mitochondria was assumed to be by substrate-level phosphorylation
. Mitchell's chemiosmotic hypothesis
was the basis for understanding the actual process of oxidative phosphorylation
. At the time, the biochemical mechanism of ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation was unknown.
Mitchell realised that the movement of ions across an electrochemical membrane potential could provide the energy needed to produce ATP. His hypothesis was derived from information that was well known in the 1960s. He knew that living cells had a membrane potential
; interior negative to the environment. The movement of charged ions across a membrane is thus affected by the electrical forces (the attraction of plus to minus charges). Their movement is also affected by thermodynamic forces
, the tendency of substances to diffuse
from regions of higher concentration. He went on to show that ATP synthesis was coupled to this electrochemical gradient
.
His hypothesis was confirmed by the discovery of ATP synthase
, a membrane-bound protein that uses the potential energy of the electrochemical gradient to make ATP.
English people
The English are a nation and ethnic group native to England, who speak English. The English identity is of early mediaeval origin, when they were known in Old English as the Anglecynn. England is now a country of the United Kingdom, and the majority of English people in England are British Citizens...
biochemist
Biochemist
Biochemists are scientists who are trained in biochemistry. Typical biochemists study chemical processes and chemical transformations in living organisms. The prefix of "bio" in "biochemist" can be understood as a fusion of "biological chemist."-Role:...
who was awarded the 1978 Nobel Prize for Chemistry for his discovery of the chemiosmotic mechanism of ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
synthesis.
Mitchell was born in Mitcham
Mitcham
Mitcham is a district in the south west area of London, in the London Borough of Merton. A suburban area, Mitcham is located on the border of Inner London and Outer London. It is both residentially and financially developed, well served by Transport for London, and home to Mitcham Town Centre,...
, Surrey
Surrey
Surrey is a county in the South East of England and is one of the Home Counties. The county borders Greater London, Kent, East Sussex, West Sussex, Hampshire and Berkshire. The historic county town is Guildford. Surrey County Council sits at Kingston upon Thames, although this has been part of...
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
.
Biography
Peter D. Mitchell was born in MitchamMitcham
Mitcham is a district in the south west area of London, in the London Borough of Merton. A suburban area, Mitcham is located on the border of Inner London and Outer London. It is both residentially and financially developed, well served by Transport for London, and home to Mitcham Town Centre,...
, Surrey
Surrey
Surrey is a county in the South East of England and is one of the Home Counties. The county borders Greater London, Kent, East Sussex, West Sussex, Hampshire and Berkshire. The historic county town is Guildford. Surrey County Council sits at Kingston upon Thames, although this has been part of...
on 29 September 1920. His parents were Christopher Gibbs Mitchell, a civil servant, and Kate Beatrice Dorothy (née) Taplin. His Uncle was Sir Godfrey Way Mitchell, chairman of George Wimpey
George Wimpey
George Wimpey was formed in 1880 and, based in Hammersmith, operated largely as a road surfacing contractor. The business was acquired by Godfrey Mitchell in 1919 and he developed it into the UK’s pre-eminent construction and housebuilding firm. In 2007, Wimpey merged with Taylor Woodrow to create...
. He was educated at Queen's College
Queen's College, Taunton
Queen's College is a co-educational independent school located in Taunton, the county town of Somerset, England. It is a day/boarding school for children aged 2–18. The school incorporates Nursery, Pre-Prep, Junior and Senior schools. The current headmaster of the Senior School is Chris Alcock...
, Taunton
Taunton
Taunton is the county town of Somerset, England. The town, including its suburbs, had an estimated population of 61,400 in 2001. It is the largest town in the shire county of Somerset....
, and at Jesus College, Cambridge
Jesus College, Cambridge
Jesus College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge, England.The College was founded in 1496 on the site of a Benedictine nunnery by John Alcock, then Bishop of Ely...
where he studied the Natural Sciences Tripos specialising in biochemistry
Biochemistry
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes in living organisms, including, but not limited to, living matter. Biochemistry governs all living organisms and living processes...
.
He accepted a research post in the Department of Biochemistry, Cambridge, in 1942, and received the degree of Ph.D.
Doctor of Philosophy
Doctor of Philosophy, abbreviated as Ph.D., PhD, D.Phil., or DPhil , in English-speaking countries, is a postgraduate academic degree awarded by universities...
in early 1951 for work on the mode of action of penicillin
Penicillin
Penicillin is a group of antibiotics derived from Penicillium fungi. They include penicillin G, procaine penicillin, benzathine penicillin, and penicillin V....
. In 1955 he was invited by Professor Michael Swann
Michael Swann
Michael Meredith Swann, Baron Swann, FRS was a distinguished molecular and cell biologist working on the mechanisms of cell division and fertilisation. He used cell polarisation methods to understand the changes in molecular organisation of the mitotic spindle...
to set up a biochemical research unit, called the Chemical Biology Unit, in the Department of Zoology, Edinburgh University, where he was appointed to a Senior Lectureship in 1961, to a Readership in 1962, although ill health led to his resignation in 1963.
Independent researcher
From then to 1965, he supervised the restoration of a RegencyRegency architecture
The Regency style of architecture refers primarily to buildings built in Britain during the period in the early 19th century when George IV was Prince Regent, and also to later buildings following the same style...
-fronted Mansion, known as Glynn House, near Bodmin
Bodmin
Bodmin is a civil parish and major town in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated in the centre of the county southwest of Bodmin Moor.The extent of the civil parish corresponds fairly closely to that of the town so is mostly urban in character...
, Cornwall
Cornwall
Cornwall is a unitary authority and ceremonial county of England, within the United Kingdom. It is bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Cornwall has a population of , and covers an area of...
- adapting a major part of it for use as a research laboratory. He and his former research colleague, Jennifer Moyle
Jennifer Moyle
Jennifer Moyle is a biochemist who worked alongside Peter D. Mitchell and helped discover the chemiosmotic mechanism of ATP synthesis. She also did work on the properties of purified isocitric enzymes.She was born in Norwich, England.- Biography :...
founded a charitable company, known as Glynn Research Ltd., to promote fundamental biological research at Glynn House and they embarked on a programme of research on chemiosmotic reactions and reaction systems.
In 1978 he won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of chemistry. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895, awarded for outstanding contributions in chemistry, physics, literature,...
"for his contribution to the understanding of biological energy transfer through the formulation of the chemiosmotic theory
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a selectively permeable membrane, down their electrochemical gradient. More specifically, it relates to the generation of ATP by the movement of hydrogen ions across a membrane during cellular respiration....
."
Chemiosmotic hypothesis

Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
was known to be the energy currency of life, but the mechanism by which ATP was created in the mitochondria was assumed to be by substrate-level phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Substrate-level phosphorylation is a type of metabolism that results in the formation and creation of adenosine triphosphate or guanosine triphosphate by the direct transfer and donation of a phosphoryl group to adenosine diphosphate or guanosine diphosphate from a phosphorylated reactive...
. Mitchell's chemiosmotic hypothesis
Chemiosmosis
Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a selectively permeable membrane, down their electrochemical gradient. More specifically, it relates to the generation of ATP by the movement of hydrogen ions across a membrane during cellular respiration....
was the basis for understanding the actual process of oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate . Although the many forms of life on earth use a range of different nutrients, almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP,...
. At the time, the biochemical mechanism of ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation was unknown.
Mitchell realised that the movement of ions across an electrochemical membrane potential could provide the energy needed to produce ATP. His hypothesis was derived from information that was well known in the 1960s. He knew that living cells had a membrane potential
Membrane potential
Membrane potential is the difference in electrical potential between the interior and exterior of a biological cell. All animal cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with a variety of types of proteins embedded in it...
; interior negative to the environment. The movement of charged ions across a membrane is thus affected by the electrical forces (the attraction of plus to minus charges). Their movement is also affected by thermodynamic forces
Chemical thermodynamics
Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics...
, the tendency of substances to diffuse
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
from regions of higher concentration. He went on to show that ATP synthesis was coupled to this electrochemical gradient
Electrochemical gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a spatial variation of both electrical potential and chemical concentration across a membrane; that is, a combination of the membrane potential and the pH gradient...
.
His hypothesis was confirmed by the discovery of ATP synthase
ATP synthase
right|thumb|300px|Molecular model of ATP synthase by X-ray diffraction methodATP synthase is an important enzyme that provides energy for the cell to use through the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate . ATP is the most commonly used "energy currency" of cells from most organisms...
, a membrane-bound protein that uses the potential energy of the electrochemical gradient to make ATP.

