
Perpetuity
Encyclopedia
A perpetuity is an annuity
that has no end, or a stream of cash payments that continues forever. There are few actual perpetuities in existence (the United Kingdom
(UK) government has issued them in the past; these are known and still trade as consols
). A number of types of investments are effectively perpetuities, such as real estate and preferred stock
, and techniques for valuing a perpetuity can be applied to establish price. Perpetuities are but one of the time value of money
methods for valuing financial assets. Perpetuities are a form of ordinary annuities.
The concept is closely linked to terminal value
and terminal growth rate in valuation
.
in which the periodic payments begin on a fixed date and continue indefinitely. It is sometimes referred to as a perpetual annuity. Fixed coupon payments on permanently invested (irredeemable) sums of money are prime examples of perpetuities. Scholarships paid perpetually from an endowment fit the definition of perpetuity.
The value of the perpetuity is finite because receipts that are anticipated far in the future have extremely low present value (present value
of the future cash flows). Unlike a typical bond, because the principal is never repaid, there is no present value for the principal. Assuming that payments begin at the end of the current period, the price of a perpetuity is simply the coupon amount over the appropriate discount rate or yield, that is
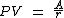
Where PV = Present Value of the Perpetuity, A = the Amount of the periodic payment, and r = yield , discount rate
or interest rate
.
To give a numerical example, a 3% UK government War Loan will trade at 50 pence per pound in a yield environment of 6%, while at 3% yield it is trading at par. That is, if the face value of the Loan is £100 and the annual payment £3, the value of the Loan is £50 when market interest rates are 6%, and £100 when they are 3%.
, that are undated and irredeemable (e.g. war loan) pay fixed coupons (interest payments) and trade actively in the bond market. Very long dated bonds have financial characteristics that can appeal to some investors and in some circumstances, e.g. long-dated bonds have prices that change rapidly (either up or down) when yields change (fall or rise) in the financial markets.
A more current example is the convention used in real estate finance for valuing real estate with a cap rate. Using a cap rate, the value of a particular real estate asset is either the net income
or the net cash flow of the property, divided by the cap rate. Effectively, the use of a cap rate to value a piece of real estate assumes that the current income from the property continues in perpetuity. Underlying this valuation is the assumption that rents will rise at the same rate as inflation
. Although the property may be sold in future (or even the very near future), the assumption is that other investors will apply the same valuation approach to the property.
Another example is the constant growth Dividend Discount Model
for the valuation of the common stock of a corporation, which assumes that the market price per share is equal to the discounted stream of all future dividends, which is assumed to be perpetual. If the discount rate for stocks (shares) with this level of systematic risk
is 12.50%, then a constant perpetuity of per dollar of dividend income is eight dollars. However if the future dividends represent a perpetuity increasing at 5.00% per year, then the dividend discount model, in effect, subtracts 5.00% off the discount rate of 12.50% for 7.50% implying that the price per dollar of income is $13.33.
Annuity (finance theory)
The term annuity is used in finance theory to refer to any terminating stream of fixed payments over a specified period of time. This usage is most commonly seen in discussions of finance, usually in connection with the valuation of the stream of payments, taking into account time value of money...
that has no end, or a stream of cash payments that continues forever. There are few actual perpetuities in existence (the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
(UK) government has issued them in the past; these are known and still trade as consols
Consols
Consol is a form of British government bond , dating originally from the 18th century. The first consols were originally issued in 1751...
). A number of types of investments are effectively perpetuities, such as real estate and preferred stock
Preferred stock
Preferred stock, also called preferred shares, preference shares, or simply preferreds, is a special equity security that has properties of both an equity and a debt instrument and is generally considered a hybrid instrument...
, and techniques for valuing a perpetuity can be applied to establish price. Perpetuities are but one of the time value of money
Time value of money
The time value of money is the value of money figuring in a given amount of interest earned over a given amount of time. The time value of money is the central concept in finance theory....
methods for valuing financial assets. Perpetuities are a form of ordinary annuities.
The concept is closely linked to terminal value
Terminal value (finance)
In finance, the terminal value of a security is the present value at a future point in time of all future cash flows when we expect stable growth rate forever. It is most often used in multi-stage discounted cash flow analysis, and allows for the limitation of cash flow projections to a...
and terminal growth rate in valuation
Valuation (finance)
In finance, valuation is the process of estimating what something is worth. Items that are usually valued are a financial asset or liability. Valuations can be done on assets or on liabilities...
.
Detailed description
A perpetuity is an annuityAnnuity (finance theory)
The term annuity is used in finance theory to refer to any terminating stream of fixed payments over a specified period of time. This usage is most commonly seen in discussions of finance, usually in connection with the valuation of the stream of payments, taking into account time value of money...
in which the periodic payments begin on a fixed date and continue indefinitely. It is sometimes referred to as a perpetual annuity. Fixed coupon payments on permanently invested (irredeemable) sums of money are prime examples of perpetuities. Scholarships paid perpetually from an endowment fit the definition of perpetuity.
The value of the perpetuity is finite because receipts that are anticipated far in the future have extremely low present value (present value
Present value
Present value, also known as present discounted value, is the value on a given date of a future payment or series of future payments, discounted to reflect the time value of money and other factors such as investment risk...
of the future cash flows). Unlike a typical bond, because the principal is never repaid, there is no present value for the principal. Assuming that payments begin at the end of the current period, the price of a perpetuity is simply the coupon amount over the appropriate discount rate or yield, that is
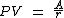
Where PV = Present Value of the Perpetuity, A = the Amount of the periodic payment, and r = yield , discount rate
Discount rate
The discount rate can mean*an interest rate a central bank charges depository institutions that borrow reserves from it, for example for the use of the Federal Reserve's discount window....
or interest rate
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by a borrower for the use of money that they borrow from a lender. For example, a small company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for their business, and in return the lender receives interest at a predetermined interest rate for...
.
To give a numerical example, a 3% UK government War Loan will trade at 50 pence per pound in a yield environment of 6%, while at 3% yield it is trading at par. That is, if the face value of the Loan is £100 and the annual payment £3, the value of the Loan is £50 when market interest rates are 6%, and £100 when they are 3%.
Real-life examples
For example, UK government bonds, called consolsConsols
Consol is a form of British government bond , dating originally from the 18th century. The first consols were originally issued in 1751...
, that are undated and irredeemable (e.g. war loan) pay fixed coupons (interest payments) and trade actively in the bond market. Very long dated bonds have financial characteristics that can appeal to some investors and in some circumstances, e.g. long-dated bonds have prices that change rapidly (either up or down) when yields change (fall or rise) in the financial markets.
A more current example is the convention used in real estate finance for valuing real estate with a cap rate. Using a cap rate, the value of a particular real estate asset is either the net income
Net income
Net income is the residual income of a firm after adding total revenue and gains and subtracting all expenses and losses for the reporting period. Net income can be distributed among holders of common stock as a dividend or held by the firm as an addition to retained earnings...
or the net cash flow of the property, divided by the cap rate. Effectively, the use of a cap rate to value a piece of real estate assumes that the current income from the property continues in perpetuity. Underlying this valuation is the assumption that rents will rise at the same rate as inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
. Although the property may be sold in future (or even the very near future), the assumption is that other investors will apply the same valuation approach to the property.
Another example is the constant growth Dividend Discount Model
Dividend Discount Model
The dividend discount model is a way of valuing a company based on the theory that a stock is worth the discounted sum of all of its future dividend payments. In other words, it is used to evaluate stocks based on the net present value of the future dividends. Dividend discount model is a tool...
for the valuation of the common stock of a corporation, which assumes that the market price per share is equal to the discounted stream of all future dividends, which is assumed to be perpetual. If the discount rate for stocks (shares) with this level of systematic risk
Systematic risk
In finance, systematic risk, sometimes called market risk, aggregate risk, or undiversifiable risk, is the risk associated with aggregate market returns....
is 12.50%, then a constant perpetuity of per dollar of dividend income is eight dollars. However if the future dividends represent a perpetuity increasing at 5.00% per year, then the dividend discount model, in effect, subtracts 5.00% off the discount rate of 12.50% for 7.50% implying that the price per dollar of income is $13.33.

