
Permeance
Encyclopedia
Permeance, in general, is the degree to which a material admits a flow of matter
or energy
. Permeance is usually represented by a curly (calligraphic) capital P: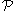 , or capital lambda Λ.
, or capital lambda Λ.
, permeance is the inverse of reluctance. Permeance is a measure of the quantity of flux
for a number of current-turns in magnetic circuit. A magnetic circuit
almost acts as though the flux
is 'conducted', therefore permeance is larger for large cross sections of a material and smaller for longer lengths. This concept is analogous to electrical conductance in the electric circuit.
Magnetic permeance is defined as the reciprocal of magnetic reluctance
is defined as the reciprocal of magnetic reluctance 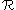 (in analogy with the reciprocity between electric conductance and resistance):
(in analogy with the reciprocity between electric conductance and resistance):

which can also be re-written:
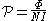
using Hopkinson's law (magnetic circuit analogue of Ohm's law
for electric circuits) and the definition of magnetomotive force
(magnetic analogue of electromotive force
):

Where:
ΦB = Magnetic flux
NI = Current-turns, (current) × (number of turns of conductor to make a coil).
Alternatively in terms of magnetic permeability
(analogous to electric conductance):
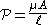
Where:
μ = Permeability of material
A = Cross-sectional area
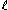 = Length of conductor in circuit
= Length of conductor in circuit
The SI unit of magnetic permeance is "webers per ampere-turn", that is Wb A-1.
, permeance is the degree to which a material transmits another substance.
Matter
Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects consist. Typically, matter includes atoms and other particles which have mass. A common way of defining matter is as anything that has mass and occupies volume...
or energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
. Permeance is usually represented by a curly (calligraphic) capital P:
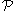 , or capital lambda Λ.
, or capital lambda Λ.Electromagnetism
In ElectromagnetismElectromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
, permeance is the inverse of reluctance. Permeance is a measure of the quantity of flux
Flux
In the various subfields of physics, there exist two common usages of the term flux, both with rigorous mathematical frameworks.* In the study of transport phenomena , flux is defined as flow per unit area, where flow is the movement of some quantity per time...
for a number of current-turns in magnetic circuit. A magnetic circuit
Magnetic circuit
A magnetic circuit is made up of one or more closed loop paths containing a magnetic flux. The flux is usually generated by permanent magnets or electromagnets and confined to the path by magnetic cores consisting of ferromagnetic materials like iron, although there may be air gaps or other...
almost acts as though the flux
Flux
In the various subfields of physics, there exist two common usages of the term flux, both with rigorous mathematical frameworks.* In the study of transport phenomena , flux is defined as flow per unit area, where flow is the movement of some quantity per time...
is 'conducted', therefore permeance is larger for large cross sections of a material and smaller for longer lengths. This concept is analogous to electrical conductance in the electric circuit.
Magnetic permeance
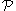 is defined as the reciprocal of magnetic reluctance
is defined as the reciprocal of magnetic reluctance 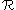 (in analogy with the reciprocity between electric conductance and resistance):
(in analogy with the reciprocity between electric conductance and resistance):
which can also be re-written:
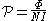
using Hopkinson's law (magnetic circuit analogue of Ohm's law
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
for electric circuits) and the definition of magnetomotive force
Magnetomotive force
Magnetomotive force is any physical driving force that produces magnetic flux. In this context, the expression "driving force" is used in a general sense of "work potential", and is analogous, but distinct from force measured in newtons...
(magnetic analogue of electromotive force
Electromotive force
In physics, electromotive force, emf , or electromotance refers to voltage generated by a battery or by the magnetic force according to Faraday's Law, which states that a time varying magnetic field will induce an electric current.It is important to note that the electromotive "force" is not a...
):

Where:
ΦB = Magnetic flux
Magnetic flux
Magnetic flux , is a measure of the amount of magnetic B field passing through a given surface . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber...
NI = Current-turns, (current) × (number of turns of conductor to make a coil).
Alternatively in terms of magnetic permeability
Permeability (electromagnetism)
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...
(analogous to electric conductance):
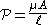
Where:
μ = Permeability of material
A = Cross-sectional area
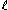 = Length of conductor in circuit
= Length of conductor in circuitThe SI unit of magnetic permeance is "webers per ampere-turn", that is Wb A-1.
Materials science
In Materials scienceMaterials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field applying the properties of matter to various areas of science and engineering. This scientific field investigates the relationship between the structure of materials at atomic or molecular scales and their macroscopic properties. It incorporates...
, permeance is the degree to which a material transmits another substance.
Electromagnetism
- Properties of Magnetic Materials (units of magnetic permeance)
Material science
- Bombaru, D., Jutras, R., and Patenaude, A., "Air Permeance of Building Materials". Summary report prepared by, AIR-INS Inc. for Canada Mortgage and Housing CorporationCanada Mortgage and Housing CorporationCanada Mortgage and Housing Corporation is a Crown corporation, owned by the Government of Canada, founded after World War II to provide housing for returning soldiers...
, Ottawa, 1988.

