Peptide sequence tag
Encyclopedia
A peptide sequence tag is a piece of information about a peptide
obtained by tandem mass spectrometry
that can be used to identify this peptide in a protein database
.
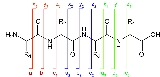
peptides collide with a gas within the mass spectrometer and break into pieces at their peptide bond
s. The resulting fragment ion
s (called b-ions and y-ions) have mass differences corresponding to the residue
masses of the respective amino acid
s. Thus, a tandem mass spectrum contains partial information about the amino acid sequence of the peptide. The peptide sequence tag approach, developed by Matthias Wilm and Matthias Mann
at the EMBL, uses this information to identify the peptide in a database. Briefly, a couple of masses are extracted from the spectrum in order to obtain the peptide sequence tag. This peptide sequence tag is a unique identifier of a specific peptide and can be used to find it in a database containing all possible peptide sequences.
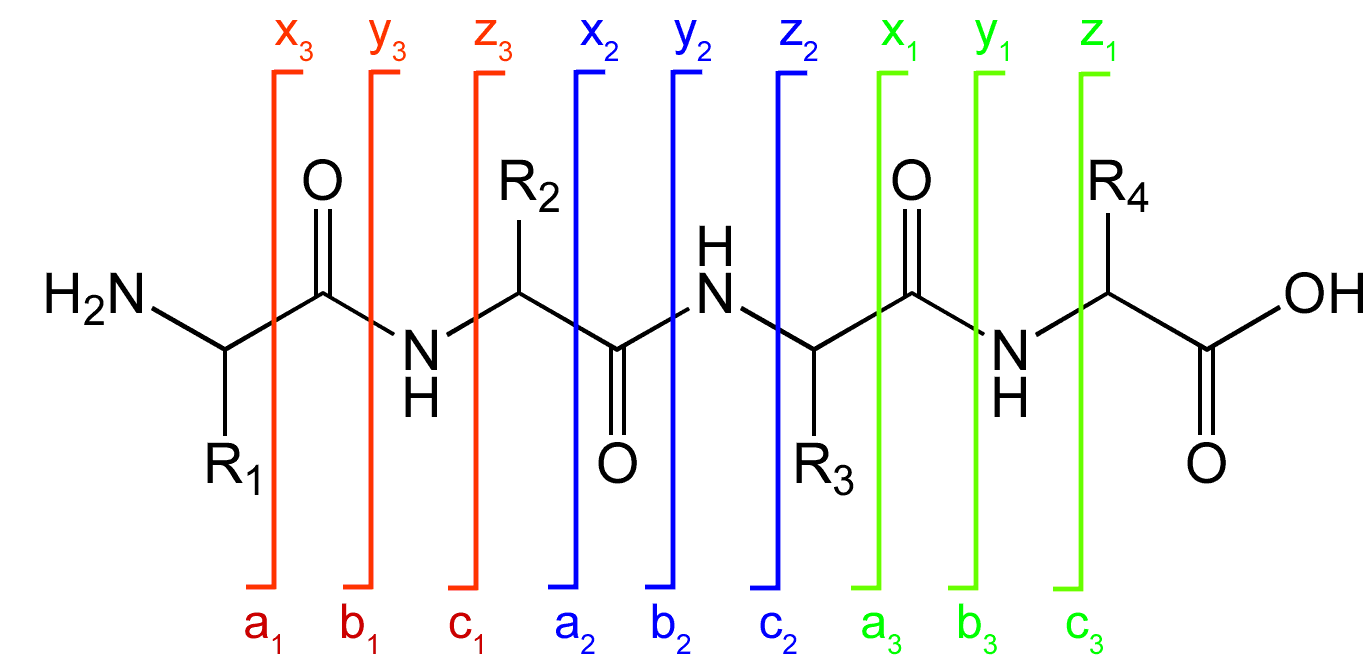 A notation has been developed for indicating peptide fragments that arise from a tandem mass spectrum. Peptide fragment ions are indicated by a, b, or c if the charge is retained on the N-terminus and by x, y or z if the charge is maintained on the C-terminus. The subscript indicates the number of amino acid residues in the fragment. Prime
A notation has been developed for indicating peptide fragments that arise from a tandem mass spectrum. Peptide fragment ions are indicated by a, b, or c if the charge is retained on the N-terminus and by x, y or z if the charge is maintained on the C-terminus. The subscript indicates the number of amino acid residues in the fragment. Prime
symbols indicate the number of protons or hydrogens added to the fragment to form the observed ion. For example, y
Peptide
Peptides are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing less than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond...
obtained by tandem mass spectrometry
Tandem mass spectrometry
Tandem mass spectrometry, also known as MS/MS or MS2, involves multiple steps of mass spectrometry selection, with some form of fragmentation occurring in between the stages.-Tandem MS instruments:...
that can be used to identify this peptide in a protein database
Sequence database
In the field of bioinformatics, a sequence database is a large collection of computerized nucleic acid sequences, protein sequences, or other sequences stored on a computer...
.
Mass spectrometry
In general, peptides can be identified by fragmenting them in a mass spectrometer. For example, during collision-induced dissociationCollision-induced dissociation
In Mass spectrometry, Collision-induced dissociation , referred to by some as collisionally activated dissociation , is a mechanism by which to fragment molecular ions in the gas phase. The molecular ions are usually accelerated by some electrical potential to high kinetic energy and then allowed...
peptides collide with a gas within the mass spectrometer and break into pieces at their peptide bond
Peptide bond
This article is about the peptide link found within biological molecules, such as proteins. A similar article for synthetic molecules is being created...
s. The resulting fragment ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s (called b-ions and y-ions) have mass differences corresponding to the residue
Residue (chemistry)
In chemistry, residue is the material remaining after a distillation or an evaporation, or to a portion of a larger molecule, such as a methyl group. It may also refer to the undesired byproducts of a reaction....
masses of the respective amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s. Thus, a tandem mass spectrum contains partial information about the amino acid sequence of the peptide. The peptide sequence tag approach, developed by Matthias Wilm and Matthias Mann
Matthias Mann
Matthias Mann is a scientist in the area of mass spectrometry and proteomics. Born 1959 in Germany he studied mathematics and physics at the University of Göttingen. He received his Ph.D. in 1988 at Yale University where he worked in the group of John Fenn, who was later awarded the Nobel Prize in...
at the EMBL, uses this information to identify the peptide in a database. Briefly, a couple of masses are extracted from the spectrum in order to obtain the peptide sequence tag. This peptide sequence tag is a unique identifier of a specific peptide and can be used to find it in a database containing all possible peptide sequences.
Peptide fragment notation

Prime (symbol)
The prime symbol , double prime symbol , and triple prime symbol , etc., are used to designate several different units, and for various other purposes in mathematics, the sciences and linguistics...
symbols indicate the number of protons or hydrogens added to the fragment to form the observed ion. For example, y

