
Parapneumonic effusion
Encyclopedia
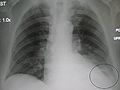
Pleural effusion
Pleural effusion is excess fluid that accumulates between the two pleural layers, the fluid-filled space that surrounds the lungs. Excessive amounts of such fluid can impair breathing by limiting the expansion of the lungs during ventilation.-Pathophysiology:...
that arises as a result of a pneumonia
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung—especially affecting the microscopic air sacs —associated with fever, chest symptoms, and a lack of air space on a chest X-ray. Pneumonia is typically caused by an infection but there are a number of other causes...
, lung abscess, or bronchiectasis. There are three types of parapneumonic effusions: uncomplicated effusions, complicated effusions, and empyema
Empyema
Pleural empyema is an accumulation of pus in the pleural cavity. Most pleural empyemas arise from an infection within the lung , often associated with parapneumonic effusions. There are three stages: exudative, fibrinopurulent and organizing. In the exudative stage, the pus accumulates...
. Uncomplicated effusions generally respond well to appropriate antibiotic treatment. The criteria for a complicated parapneumonic effusion include the presence of pus or Gram stain–positive pleural fluid or a pleural fluid pH <7.0. Appropriate management includes chest tube drainage (tube thoracostomy). Treatment of empyemas includes antibiotics, complete pleural fluid drainage, and reexpansion of the lung.
Other treatments include the use of decortication.
Diagnostic techniques available include plain film chest x-ray, computed tomography (CT), and ultrasound. Ultrasound can be useful in differentiating between empyema and other transudative and exudative effusions due in part to relative echogenicity of different organs such as the liver (often isoechogenic with empyema).

