
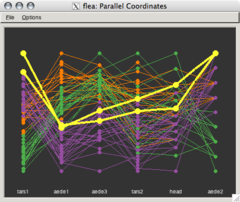
Parallel coordinates
Encyclopedia
Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
and analyzing multivariate data.
To show a set of points
Point (geometry)
In geometry, topology and related branches of mathematics a spatial point is a primitive notion upon which other concepts may be defined. In geometry, points are zero-dimensional; i.e., they do not have volume, area, length, or any other higher-dimensional analogue. In branches of mathematics...
in an n-dimensional space, a backdrop is drawn consisting of n parallel
Parallel (geometry)
Parallelism is a term in geometry and in everyday life that refers to a property in Euclidean space of two or more lines or planes, or a combination of these. The assumed existence and properties of parallel lines are the basis of Euclid's parallel postulate. Two lines in a plane that do not...
lines, typically vertical and equally spaced. A point in n-dimensional space is represented as a polyline with vertices
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex is a special kind of point that describes the corners or intersections of geometric shapes.-Of an angle:...
on the parallel axes; the position of the vertex on the ith axis corresponds to the ith coordinate of the point.
History
Parallel coordinates were invented by Maurice d'Ocagne in 1885, and were independently re-discovered and popularised by Al Inselbergin 1959 and systematically developed as a coordinate system starting from 1977. Some important
applications are in Collision Avoidance Algorithms for Air Traffic Control (1987—3 USA patents), Data Mining (USA patent), Computer Vision (USA patent), Optimization, Process Control,
more recently in Intrusion Detection and elsewhere (see discussion). It is worth mentioning that most of these applications of parallel coordinates and their success are due to the landmark paper entitled "Hyperdimensional Data Analysis Using
Parallel Coordinates" (Wegman 1990). Generalized parallel coordinates system is proposed by Moustafa and Wegman (2002,2006), at which the Cartesian coordinates system is transformed into a parameter space (parallel coordinates) using basis functions. The relationships between generalized parallel coordinates and Andrews plots, as well as the Grand tour are explored by Moustafa and Wegman (2002,2006).
Higher dimensions
Adding more dimensionsDimensions
Dimensions is a French project that makes educational movies about mathematics, focusing on spatial geometry. It uses POV-Ray to render some of the animations, and the films are release under a Creative Commons licence....
in the parallel coordinates (often abbreviated ||-coords or PCs) involves adding more axes. The value of parallel coordinates is that certain geometrical properties in high dimensions transform into easily seen 2D patterns. For example, a set of points on a line in n-space transforms to a set of polylines(or curves) in parallel coordinates all intersecting at n − 1 points. For n = 2 this yields a point <---> line duality pointing out why the mathematical foundations of parallel coordinates are developed in the Projective rather than Euclidean space. Also known are the patterns corresponding to (hyper)planes, curves, several smooth (hyper)surfaces, proximities, convexity and recently non-orientability. It is worth mentioning that since the process maps a k-dimensional data onto a lower 2D space, some loss of information is expected. The loss of information can be measured using the Parseval's identity
Parseval's identity
In mathematical analysis, Parseval's identity is a fundamental result on the summability of the Fourier series of a function. Geometrically, it is thePythagorean theorem for inner-product spaces....
(or energy norm).
Statistical considerations
When used for statistical data visualisation there are three important considerations: the order, the rotation, and the scaling of the axes.The order of the axes is critical for finding features, and in typical data analysis many reorderings will need to be tried. Some authors have come up with ordering heuristics which may create illuminating orderings.
The rotation of the axes is a translation in the parallel coordinates and if the lines intersected outside the parallel axes it can be translated between them by rotations. The simplest example of this is rotating the axis by 180 degrees. More details can be found at.
The necessity of scaling stems from the fact that the plot is based on interpolation (linear combination) of consecutive pairs of variables. Therefore, the variables must be in common scale, and there are many scaling methods to be considered as part of data preparation process that can reveal more informative views.
Generalized parallel coordinates
The generalized parallel coordinate plot (GPCP) has been proposed as a generalization of parallel coordinates plots, based on parameter transformation. In this design, instead of plotting the raw data, it is transformed in some way first. If the interpolation function is piecewise Lagrange, this corresponds to the traditional PCP. If splines are used as the interpolation function, then the smooth parallel coordinate plot (SPCP) is achieved. In the smooth plot, every observation is mapped into a parametric line (or curve), which is smooth, continuous on the axes, and orthogonal to each parallel axis.This SPCP design gives a clear quantization level of each data attribute, that can best describe its distribution in complex situations, even with large data sets. Finally, if one uses the Fourier interpolation of degree equals to the data dimensionality, then an Andrews plot is achieved. The GPCP design gives opportunities to researchers to explore alternative interpolation functions that best suited for particular application, and statistical dualities between the data space and GPC space that are important for visual pattern recognition using GPCP
.
External links
- Alfred Inselberg's Homepage, with Visual Tutorial, History, Selected Publications and Applications
- Parallel Coordinates: Visual Multidimensional Geometry and Its Applications by Alfred Inselberg, Springer, 2009.
- An Investigation of Methods for Visualising Highly Multivariate Datasets by C.Brunsdon, A.S.Fotheringham & M.E.Charlton, University of NewcastleUniversity of Newcastle upon TyneNewcastle University is a major research-intensive university located in Newcastle upon Tyne in the north-east of England. It was established as a School of Medicine and Surgery in 1834 and became the University of Newcastle upon Tyne by an Act of Parliament in August 1963. Newcastle University is...
, UK - Parallel coordinates plot in GGobi
- Parallel coordinates plot in the public-domain software package XmdvTool
- Using Curves to Enhance Parallel Coordinate Visualisations by Martin Graham & Jessie Kennedy, Napier UniversityNapier UniversityEdinburgh Napier is one of the largest higher education institutions in Scotland with over 17,000 students, including nearly 5,000 international students, from more than 100 nations worldwide.-History:...
, EdinburghEdinburghEdinburgh is the capital city of Scotland, the second largest city in Scotland, and the eighth most populous in the United Kingdom. The City of Edinburgh Council governs one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas. The council area includes urban Edinburgh and a rural area...
, UK - On Some Generalization of Parallel Coordinate Plots by Rida E. Moustafa and Edward J. Wegman (2002), George Mason UniversityGeorge Mason UniversityGeorge Mason University is a public university based in unincorporated Fairfax County, Virginia, United States, south of and adjacent to the city of Fairfax. Additional campuses are located nearby in Arlington County, Prince William County, and Loudoun County...
, Fairfax, VA - picviz — the graphviz of parallel coordinates licensed under the GNU GPL v3 – implemented in CC (programming language)C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....
, with PythonPython (programming language)Python is a general-purpose, high-level programming language whose design philosophy emphasizes code readability. Python claims to "[combine] remarkable power with very clear syntax", and its standard library is large and comprehensive...
bindings used for the GUIGuiGui or guee is a generic term to refer to grilled dishes in Korean cuisine. These most commonly have meat or fish as their primary ingredient, but may in some cases also comprise grilled vegetables or other vegetarian ingredients. The term derives from the verb, "gupda" in Korean, which literally...
. - Clustergram: A graph for visualizing cluster analyses based on the Parallel Coordinates of each observations cluster mean over the number of potential clusters (implemented in RR (programming language)R is a programming language and software environment for statistical computing and graphics. The R language is widely used among statisticians for developing statistical software, and R is widely used for statistical software development and data analysis....
). - XDAT – a free GPL JAVA-based software for plotting parallel coordinates.

