
Paleomagnetic secular variation
Encyclopedia
Geomagnetic secular variation refers to changes in the Earth's magnetic field
on time scales of about a year or more. These changes mostly reflect changes in the Earth's interior, while more rapid changes mostly originate in the ionosphere
or magnetosphere
.
and magnetosphere
, and some changes can be traced to geomagnetic storms or daily variations in currents. Changes over time scales of a year or more mostly reflect changes in the Earth's interior, particularly the iron-rich core. These changes are referred to as secular variation.
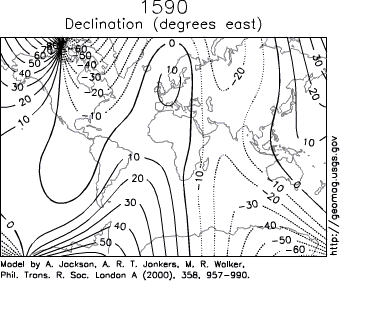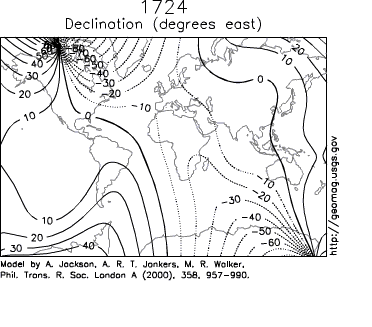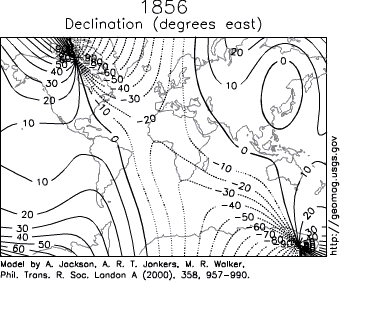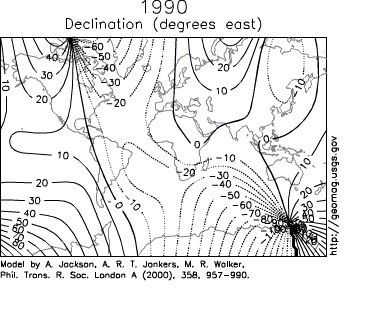 Secular variation can be observed in measurements at magnetic observatories, some of which have been around for hundreds of years (the Kew Observatory
Secular variation can be observed in measurements at magnetic observatories, some of which have been around for hundreds of years (the Kew Observatory
, for example). Over such a time scale, magnetic declination
is observed to vary over tens of degrees. A movie on the right shows how global declinations have changed over the last few centuries.
To analyze global patterns of change in the geomagnetic field, geophysicists fit the field data to a spherical harmonic
expansion (see International Geomagnetic Reference Field). The terms in this expansion can be divided into a dipolar
part, like the field around a bar magnet, and a nondipolar part. The dipolar part dominates the geomagnetic field and determines the direction of the geomagnetic poles. The direction and intensity of the dipole change over time. Over the last two centuries the dipole strength has been decreasing at a rate of about 6.3% per century. At this rate of decrease, the field would reach zero in about 1600 years. However, this strength is about average for the last 7 thousand years, and the current rate of change is not unusual.
A prominent feature in the non-dipolar part of the secular variation is a westward drift at a rate of about 0.2 degrees per year. This drift is not the same everywhere and has varied over time. The globally averaged drift has been westward since about 1400 AD but eastward between about 1000 AD and 1400 AD.
s and geomagnetic reversal
s.
Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's inner core to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of energetic particles emanating from the Sun...
on time scales of about a year or more. These changes mostly reflect changes in the Earth's interior, while more rapid changes mostly originate in the ionosphere
Ionosphere
The ionosphere is a part of the upper atmosphere, comprising portions of the mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere, distinguished because it is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important part in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere...
or magnetosphere
Magnetosphere
A magnetosphere is formed when a stream of charged particles, such as the solar wind, interacts with and is deflected by the intrinsic magnetic field of a planet or similar body. Earth is surrounded by a magnetosphere, as are the other planets with intrinsic magnetic fields: Mercury, Jupiter,...
.
Introduction
The geomagnetic field changes on time scales from milliseconds to millions of years. Shorter time scales mostly arise from currents in the ionosphereIonosphere
The ionosphere is a part of the upper atmosphere, comprising portions of the mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere, distinguished because it is ionized by solar radiation. It plays an important part in atmospheric electricity and forms the inner edge of the magnetosphere...
and magnetosphere
Magnetosphere
A magnetosphere is formed when a stream of charged particles, such as the solar wind, interacts with and is deflected by the intrinsic magnetic field of a planet or similar body. Earth is surrounded by a magnetosphere, as are the other planets with intrinsic magnetic fields: Mercury, Jupiter,...
, and some changes can be traced to geomagnetic storms or daily variations in currents. Changes over time scales of a year or more mostly reflect changes in the Earth's interior, particularly the iron-rich core. These changes are referred to as secular variation.
Recent change

Kew Observatory
Kew Observatory was an astronomical and terrestrial magnetic observatoryfounded by King George III , located within the Old Deer Park of the former Richmond Palace in Richmond, Surrey, now within Greater London. The former royal manor of Kew lies to the immediate north...
, for example). Over such a time scale, magnetic declination
Magnetic declination
Magnetic declination is the angle between magnetic north and true north. The declination is positive when the magnetic north is east of true north. The term magnetic variation is a synonym, and is more often used in navigation...
is observed to vary over tens of degrees. A movie on the right shows how global declinations have changed over the last few centuries.
To analyze global patterns of change in the geomagnetic field, geophysicists fit the field data to a spherical harmonic
Spherical harmonics
In mathematics, spherical harmonics are the angular portion of a set of solutions to Laplace's equation. Represented in a system of spherical coordinates, Laplace's spherical harmonics Y_\ell^m are a specific set of spherical harmonics that forms an orthogonal system, first introduced by Pierre...
expansion (see International Geomagnetic Reference Field). The terms in this expansion can be divided into a dipolar
Dipole
In physics, there are several kinds of dipoles:*An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.*A...
part, like the field around a bar magnet, and a nondipolar part. The dipolar part dominates the geomagnetic field and determines the direction of the geomagnetic poles. The direction and intensity of the dipole change over time. Over the last two centuries the dipole strength has been decreasing at a rate of about 6.3% per century. At this rate of decrease, the field would reach zero in about 1600 years. However, this strength is about average for the last 7 thousand years, and the current rate of change is not unusual.
A prominent feature in the non-dipolar part of the secular variation is a westward drift at a rate of about 0.2 degrees per year. This drift is not the same everywhere and has varied over time. The globally averaged drift has been westward since about 1400 AD but eastward between about 1000 AD and 1400 AD.
Paleomagnetic secular variation
Changes that predate magnetic observatories are recorded in archaeological and geological materials. Such changes are referred to as paleomagnetic secular variation or paleosecular variation (PSV). The records typically include long periods of small change with occasional large changes reflecting geomagnetic excursionGeomagnetic excursion
A geomagnetic excursion, like a geomagnetic reversal, is a significant change in the Earth's magnetic field. Unlike reversals however, an excursion does not permanently change the large scale orientation of the field, but rather represents a dramatic, typically short-lived decrease in field...
s and geomagnetic reversal
Geomagnetic reversal
A geomagnetic reversal is a change in the Earth's magnetic field such that the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south are interchanged. The Earth's field has alternated between periods of normal polarity, in which the direction of the field was the same as the present direction, and reverse...
s.

