
Oxalate CoA-transferase
Encyclopedia
In enzymology, an oxalate CoA-transferase is an enzyme
that catalyzes
the chemical reaction
Thus, the two substrates
of this enzyme are succinyl-CoA
and oxalate
, whereas its two products
are succinate and oxalyl-CoA.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
s, specifically the CoA-transferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is succinyl-CoA:oxalate CoA-transferase. Other names in common use include succinyl-beta-ketoacyl-CoA transferase, and oxalate coenzyme A-transferase. This enzyme participates in glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism
.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that catalyzes
Catalysis
Catalysis is the change in rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of a substance called a catalyst. Unlike other reagents that participate in the chemical reaction, a catalyst is not consumed by the reaction itself. A catalyst may participate in multiple chemical transformations....
the chemical reaction
Chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Chemical reactions can be either spontaneous, requiring no input of energy, or non-spontaneous, typically following the input of some type of energy, such as heat, light or electricity...
- succinyl-CoA + oxalate
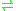 succinate + oxalyl-CoA
succinate + oxalyl-CoA
Thus, the two substrates
Substrate (biochemistry)
In biochemistry, a substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate. In the case of a single substrate, the substrate binds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed. The substrate is transformed into one or...
of this enzyme are succinyl-CoA
Succinyl-CoA
Succinyl-Coenzyme A, abbreviated as Succinyl-CoA or SucCoA, is a combination of succinic acid and coenzyme A.-Source:It is an important intermediate in the citric acid cycle, where it is synthesized from α-Ketoglutarate by α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase through decarboxylation...
and oxalate
Oxalate
Oxalate , is the dianion with formula C2O42− also written 22−. Either name is often used for derivatives, such as disodium oxalate, 2C2O42−, or an ester of oxalic acid Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate), is the dianion with formula C2O42− also written (COO)22−. Either...
, whereas its two products
Product (chemistry)
Product are formed during chemical reactions as reagents are consumed. Products have lower energy than the reagents and are produced during the reaction according to the second law of thermodynamics. The released energy comes from changes in chemical bonds between atoms in reagent molecules and...
are succinate and oxalyl-CoA.
This enzyme belongs to the family of transferase
Transferase
In biochemistry, a transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another . For example, an enzyme that catalyzed this reaction would be a transferase:In this example, A would be the donor, and B would be the acceptor...
s, specifically the CoA-transferases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is succinyl-CoA:oxalate CoA-transferase. Other names in common use include succinyl-beta-ketoacyl-CoA transferase, and oxalate coenzyme A-transferase. This enzyme participates in glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism
Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism
Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism describes a variety of reactions involving glyoxylate or dicarboxylates. Glyoxylate is the conjugate base of glyoxylic acid, and within a buffered environment of known pH such as the cell cytoplasm these terms can be used almost interchangeably, as the gain...
.

