
Otoacoustic emission
Encyclopedia
An otoacoustic emission is a sound
which is generated from within the inner ear
. Having been predicted by Thomas Gold
in 1948, its existence was first demonstrated experimentally by David Kemp in 1978 and otoacoustic emissions have since been shown to arise by a number of different cellular mechanisms within the inner ear
. Studies have shown that OAEs disappear after the inner ear has been damaged, so OAEs are often used in the laboratory and the clinic as a measure of inner ear health.
Broadly speaking, there are two types of otoacoustic emissions: spontaneous otoacoustic emissions (SOAEs), which can occur without external stimulation, and evoked otoacoustic emissions (EOAEs), which require an evoking stimulus
.
. In the absence of external stimulation, the activity of the cochlear amplifier
increases, leading to the production of sound. Several lines of evidence suggest that, in mammals, outer hair cells are the elements that enhance cochlear sensitivity and frequency selectivity and hence act as the energy sources for amplification. One theory is that they act to increase the discriminability of signal variations in continuous noise by lowering the masking effect of its cochlear amplification.
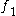 and
and 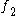 with particular intensity (usually either 65 - 55 dBSPL or 65 for both) and ratio (
with particular intensity (usually either 65 - 55 dBSPL or 65 for both) and ratio (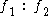 ). The evoked responses from these stimuli occur at frequencies (
). The evoked responses from these stimuli occur at frequencies (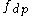 ) mathematically related to the primary frequencies, with the two most prominent being
) mathematically related to the primary frequencies, with the two most prominent being 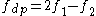 (the "cubic" distortion tone, most commonly used for hearing screening) and
(the "cubic" distortion tone, most commonly used for hearing screening) and 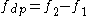 (the "quadratic" distortion tone, or simple difference tone).
(the "quadratic" distortion tone, or simple difference tone).
).
identification. Devices equipped with a microphone could detect these subsonic emissions and potentially identify an individual, thereby providing access to the device, without the need of a traditional password. (Telegraph.co.uk, April 25, 2009, "Ear noise can be used as identification", http://www.telegraph.co.uk/scienceandtechnology/science/sciencenews/5219233/Ear-noise-can-be-used-as-identification.html). It is speculated, however, that colds, medication, trimming one's ear hair, or recording and playing back a signal to the microphone could subvert the identification process. (IEEE Spectrum Online, April 29, 2009, "Your Ear Noise as Computer Password", http://blogs.spectrum.ieee.org/riskfactor/2009/04/your_ear_noise_as_computer_pas.html)
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
which is generated from within the inner ear
Inner ear
The inner ear is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:...
. Having been predicted by Thomas Gold
Thomas Gold
Thomas Gold was an Austrian-born astrophysicist, a professor of astronomy at Cornell University, a member of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences, and a Fellow of the Royal Society . Gold was one of three young Cambridge scientists who in the 1950s proposed the now mostly abandoned 'steady...
in 1948, its existence was first demonstrated experimentally by David Kemp in 1978 and otoacoustic emissions have since been shown to arise by a number of different cellular mechanisms within the inner ear
Inner ear
The inner ear is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts:...
. Studies have shown that OAEs disappear after the inner ear has been damaged, so OAEs are often used in the laboratory and the clinic as a measure of inner ear health.
Broadly speaking, there are two types of otoacoustic emissions: spontaneous otoacoustic emissions (SOAEs), which can occur without external stimulation, and evoked otoacoustic emissions (EOAEs), which require an evoking stimulus
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity....
.
Mechanism of occurrence
OAEs are considered to be related to the amplification function of the cochleaCochlea
The cochlea is the auditory portion of the inner ear. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, making 2.5 turns around its axis, the modiolus....
. In the absence of external stimulation, the activity of the cochlear amplifier
Cochlear amplifier
The cochlear amplifier was first proposed in 1948 by T. Gold. This was around the time when Georg von Békésy was publishing articles observing the propagation of passive travelling waves in the dead Cochlea....
increases, leading to the production of sound. Several lines of evidence suggest that, in mammals, outer hair cells are the elements that enhance cochlear sensitivity and frequency selectivity and hence act as the energy sources for amplification. One theory is that they act to increase the discriminability of signal variations in continuous noise by lowering the masking effect of its cochlear amplification.
Evoked OAEs
OAEs are currently evoked using three different methodologies. Stimulus Frequency OAEs (SFOAEs) are measured during the application of a pure-tone stimulus, and are detected by the vectorial difference between the stimulus waveform and the recorded waveform (which consists of the sum of the stimulus and the OAE). Transient-evoked OAEs (TEOAEs or TrOAEs) are evoked using a click (broad frequency range) or toneburst (brief duration pure tone) stimulus. The evoked response from a click covers the frequency range up to around 4 kHz, while a toneburst will elicit a response from the region that has the same frequency as the pure tone. Distortion product OAEs (DPOAEs) are evoked using a pair of primary tones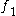 and
and 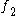 with particular intensity (usually either 65 - 55 dBSPL or 65 for both) and ratio (
with particular intensity (usually either 65 - 55 dBSPL or 65 for both) and ratio (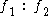 ). The evoked responses from these stimuli occur at frequencies (
). The evoked responses from these stimuli occur at frequencies (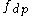 ) mathematically related to the primary frequencies, with the two most prominent being
) mathematically related to the primary frequencies, with the two most prominent being 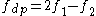 (the "cubic" distortion tone, most commonly used for hearing screening) and
(the "cubic" distortion tone, most commonly used for hearing screening) and 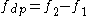 (the "quadratic" distortion tone, or simple difference tone).
(the "quadratic" distortion tone, or simple difference tone).Clinical importance
Otoacoustic emissions are clinically important because they are the basis of a simple, non-invasive, test for hearing defects in newborn babies and in children who are too young to cooperate in conventional hearing tests. Many western countries now have national programmes for the universal hearing screening of newborn babies. Periodic early childhood hearing screenings program are also utilizing OAE technology. One excellent example has been demonstrated by the Early Childhood Hearing Outreach (ECHO) Initiative at the National Center for Hearing Assessment and Management (NCHAM), Utah State University which has helped hundreds of Early Head Start programs across the United States implement OAE screening and follow-up practices in those early childhood educational settings. The primary screening tool is a test for the presence of a click-evoked OAE. Otoacoustic emissions also assist in differential diagnosis of cochlear and higher level hearing losses (e.g., auditory neuropathyAuditory neuropathy
Auditory neuropathy is a variety of hearing loss in which the outer hair cells within the cochlea are present and functional, but sound information is not faithfully transmitted to the auditory nerve and brain properly....
).
Biometric importance
In 2009, Dr Stephen Beeby of The University of Southampton, led research into utilizing otoacoustic emissions for biometricBiometrics
Biometrics As Jain & Ross point out, "the term biometric authentication is perhaps more appropriate than biometrics since the latter has been historically used in the field of statistics to refer to the analysis of biological data [36]" . consists of methods...
identification. Devices equipped with a microphone could detect these subsonic emissions and potentially identify an individual, thereby providing access to the device, without the need of a traditional password. (Telegraph.co.uk, April 25, 2009, "Ear noise can be used as identification", http://www.telegraph.co.uk/scienceandtechnology/science/sciencenews/5219233/Ear-noise-can-be-used-as-identification.html). It is speculated, however, that colds, medication, trimming one's ear hair, or recording and playing back a signal to the microphone could subvert the identification process. (IEEE Spectrum Online, April 29, 2009, "Your Ear Noise as Computer Password", http://blogs.spectrum.ieee.org/riskfactor/2009/04/your_ear_noise_as_computer_pas.html)
See also
- Auditory brainstem responseAuditory Brainstem ResponseThe auditory brainstem response is an auditory evoked potential extracted from ongoing electrical activity in the brain and recorded via electrodes placed on the scalp. The resulting recording is a series of vertex positive waves of which I through V are evaluated...
- Pure tone audiometryPure tone audiometryPure tone audiometry is the key hearing test used to identify hearing threshold levels of an individual, enabling determination of the degree, type and configuration of a hearing loss. Thus, providing the basis for diagnosis and management. PTA is a subjective, behavioural measurement of hearing...
- Entoptic phenomenonEntoptic phenomenonEntoptic phenomena are visual effects whose source is within the eye itself. In Helmholtz's words:...
- Maryanne AmacherMaryanne AmacherMaryanne Amacher was an American composer and installation artist.-Biography:Amacher was born in Kane, Pennsylvania, to an American nurse and a Swiss freight train worker. As the only child, she grew up playing the piano. Amacher left Kane to attend the University of Pennsylvania on a full...
, a composer who used this phenomenon in her music

