
Optical unit
Encyclopedia
The Optical Unit is a dimensionless units of length used in optical microscopy. Because every diffraction limited system have their resolution proportional to wavelength / NA
, it is convenient for comparison to use this unit.
There are actually 2 units, one "axial" (along the optical axis of the objective) and one "radial".
In radial optical unit, the radius of the first Airy minimum (radius) is 3,77. It is also approximatively the same for the FWHM
of Airy function.
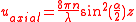
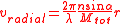
where :
Note : n * sin α = numerical aperture
Numerical aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...
, it is convenient for comparison to use this unit.
There are actually 2 units, one "axial" (along the optical axis of the objective) and one "radial".
In radial optical unit, the radius of the first Airy minimum (radius) is 3,77. It is also approximatively the same for the FWHM
Full width at half maximum
Full width at half maximum is an expression of the extent of a function, given by the difference between the two extreme values of the independent variable at which the dependent variable is equal to half of its maximum value....
of Airy function.
Equation
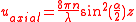
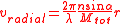
where :
- n is the refractive indexRefractive indexIn optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
- λ is the wavelength
- α the beam conus angle
- M_tot is the total magnification (M is 1 if you want the size in the sample)
Note : n * sin α = numerical aperture
Numerical aperture
In optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...

