
Optical parametric oscillator
Encyclopedia

Parametric oscillator
A parametric oscillator is a harmonic oscillator whose parameters oscillate in time. For example, a well known parametric oscillator is a child pumping a swing by periodically standing and squatting to increase the size of the swing's oscillations. The varying of the parameters drives the system...
which oscillates at optical frequencies. It converts an input laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
wave (called "pump") into two output waves of lower frequency (
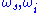 ) by means of second order nonlinear optical interaction
) by means of second order nonlinear optical interactionNonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
. The sum of the output waves frequencies is equal to the input wave frequency:
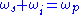 . For historic reasons, the two output waves are called "signal" and "idler", where the wave with higher frequency is called signal. A special case is the degenerate OPO, when the output frequency is one-half the pump frequency,
. For historic reasons, the two output waves are called "signal" and "idler", where the wave with higher frequency is called signal. A special case is the degenerate OPO, when the output frequency is one-half the pump frequency, 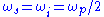 .
.Overview
The OPO consists essentially of an optical resonatorOptical cavity
An optical cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors that forms a standing wave cavity resonator for light waves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and providing feedback of the laser light. They are also used in optical parametric...
and a nonlinear optical
Nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
crystal. The optical resonator serves to resonate at least one of signal and idler waves. In the nonlinear optical crystal, the pump, signal and idler waves overlap. The interaction between these three waves leads to amplitude gain for signal and idler waves (parametric amplification) and a corresponding deamplification of the pump wave. The gain allows the resonating wave(s) (signal or idler or both) to oscillate in the resonator, compensating the loss that the resonating wave(s) experience(s) at each round-trip. This loss includes the loss due to outcoupling by one of the resonator mirrors, which provides the desired output wave. Since the (relative) loss is independent of the pump power, but the gain is dependent on pump power, at low pump power there is insufficient gain to support oscillation. Only when the pump power reaches a particular threshold level, oscillation occurs. Above threshold, the gain depends also on the amplitude of the resonated wave. Thus, in steady-state operation, the amplitude of the resonated wave is determined by the condition that this gain equals the (constant) loss. The circulating amplitude increases with increasing pump power, and so does the output power.
The photon conversion efficiency, the number of output photons per unit time in the output signal or idler wave relative to number of pump photons incident per unit time into the OPO can be high, in the range of tens of percent. Typical threshold pump power is between tens of milliwatts to several watts, depending on losses of the resonator, the frequencies of the interacting light, the intensity in the nonlinear material, and its nonlinearity. Output powers of several watts can be achieved.
There exist both continuous-wave and pulsed
Pulsed power
Pulsed power is the term used to describe the science and technology of accumulating energy over a relatively long period of time and releasing it very quickly thus increasing the instantaneous power.-Overview:...
OPOs. The latter are easier to build, since the high intensity lasts only for a tiny fraction of a second, which damages the nonlinear optical material and the mirrors less than a continuous high intensity.
In the optical parametric oscillator the initial idler and signal waves are taken from background waves, which are always present. If the idler wave is given from the outside along with the pump beam, then the process is called difference frequency generation (DFG). This is a more efficient process than optical parametric oscillation, so that also the threshold intensity is lower.
In order to change the output wave frequencies, one can change the pump frequency or the phasematching
Nonlinear optics
Nonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
properties of the nonlinear optical crystal. This latter is accomplished by changing its temperature or orientation or quasi-phasematching period (see below). For fine-tuning one can also change the optical path length of the resonator. In addition, the resonator may contain elements to suppress mode-hops of the resonating wave. This often requires active control of some element of the OPO system.
If the nonlinear optical crystal cannot be phase-matched, quasi-phase-matching
Quasi-phase-matching
Quasi-phase-matching is a technique in nonlinear optics which allows a positive net flow of energy from the pump frequency to the signal and idler frequencies by creating a periodic structure in the nonlinear medium. Momentum is conserved, as is necessary for phase-matching, through an additional...
(QPM) can be employed. This is accomplished by periodically changing the nonlinear optical properties of the crystal, mostly by periodical poling. With a suitable range of periods, output wavelengths from 700 nm to 5000 nm can be generated in periodically poled lithium niobate
Lithium niobate
Lithium niobate is a compound of niobium, lithium, and oxygen. Its single crystals are an important material for optical waveguides, mobile phones, optical modulators and various other linear and non-linear optical applications.-Properties:...
(PPLN). Common pump sources are neodymium lasers at 1.064 µm or 0.532 µm.
An important feature of the OPO is the coherence and the spectral width of the generated radiation.
When the pump power is significantly above threshold, the two output waves are, to a very good approximation, coherent state
Coherent state
In quantum mechanics a coherent state is a specific kind of quantum state of the quantum harmonic oscillator whose dynamics most closely resembles the oscillating behaviour of a classical harmonic oscillator...
s (laser-like waves). The linewidth of the resonated wave is very narrow (as low as several kHz). The nonresonated generated wave also exhibits narrow linewidth if a pump wave of narrow linewidth is employed. Narrow-linewidth OPOs are widely used in spectroscopy.
Quantum properties of the generated light beams

Quantum entanglement
Quantum entanglement occurs when electrons, molecules even as large as "buckyballs", photons, etc., interact physically and then become separated; the type of interaction is such that each resulting member of a pair is properly described by the same quantum mechanical description , which is...
states of light in the continuous variables regime. Many demonstrations of quantum information protocols for continuous variables were realized using OPOs.
The downconversion
Spontaneous parametric down conversion
Spontaneous parametric down-conversion is an important process in quantum optics, used especially as a source of entangled photon pairs, and of single photons.-Basic process:...
process really occurs in the single photon regime: each pump photon that is annihilated inside the cavity gives rise to a pair of photons in the signal and idler intracavity modes. This leads to a quantum correlation between the intensities of signal and idler fields, so that there is squeezing in the subtraction of intensities, which motivated the name "twin beams" for the downconverted fields. The highest squeezing level attained was 10.12 ± 0.15 dB.
It turns out that the phases of the twin beams are quantum correlated as well, leading to entanglement
Quantum entanglement
Quantum entanglement occurs when electrons, molecules even as large as "buckyballs", photons, etc., interact physically and then become separated; the type of interaction is such that each resulting member of a pair is properly described by the same quantum mechanical description , which is...
, theoretically predicted in 1988. Below threshold, entanglement was measured for the first time in 1992, and in 2005 above threshold.
Above threshold, the pump beam depletion makes it sensitive to the quantum phenomena happening inside the crystal. The first measurement of squeezing in the pump field after parametric interaction was done in 1997. It has been recently predicted that all three fields (pump, signal and idler) must be entangled.
Not only intensity and phase of the twin beams share quantum correlations, but also do their spatial modes. This feature could be used to enhance signal to noise ratio in image systems.
The OPO is being employed nowadays as a source of squeezed light tuned to atomic transitions, in order to study how the atoms interact with squeezed light.
External links
Articles on OPOs- http://www.rp-photonics.com/optical_parametric_oscillators.html Encyclopedia of Laser Physics and Technology
Companies commercialising OPOs
- http://www.radiantis.com Radiantis
See also
- Nonlinear opticsNonlinear opticsNonlinear optics is the branch of optics that describes the behavior of light in nonlinear media, that is, media in which the dielectric polarization P responds nonlinearly to the electric field E of the light...
- Optical parametric amplifierOptical parametric amplifierAn optical parametric amplifier, abbreviated OPA, is a laser light source that emits light of variable wavelengths by an optical parametric amplification process.-Optical parametric generation :...

