
Opaque context
Encyclopedia
An opaque context is a linguistic context in which it is not always possible to substitute co-referential expressions (usually grammatically singular terms) salva veritate
. In other words, substitution of co-referential expressions into an opaque context does not always preserve truth. For example, "Lois believes x is a hero" is an opaque context because "Louis believes Superman is a hero" is true while "Lois believes Clark Kent is a hero" is false, even though 'Superman' and 'Clark Kent' are co-referential expressions.
The term is used in philosophical
theories of reference, and is to be contrasted with "transparent context". In rough outline:
Similar usage of the term applies for artificial languages such as programming language
s and logic
s. The Cicero-Tully example above can be easily adapted. Let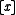 be interpreted as a function symbol returning a "name" of the value of the variable
be interpreted as a function symbol returning a "name" of the value of the variable
 on a language
on a language 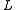 with domain
with domain 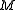 . Define a
. Define a 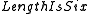 predicate with the property that
predicate with the property that 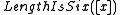 is true if and only if
is true if and only if 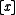 has
has 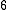 characters. Then
characters. Then 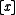 induces an opaque context, or is referentially opaque, because
induces an opaque context, or is referentially opaque, because 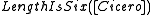 is true while
is true while 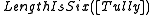 is false. Programming languages often have richer semantics than logics' semantics of truth and falsity, and so an operator
is false. Programming languages often have richer semantics than logics' semantics of truth and falsity, and so an operator
such as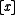 may fail to be referentially transparent for other reasons if it is not a pure function
may fail to be referentially transparent for other reasons if it is not a pure function
.
Salva veritate
Salva veritate is the logical condition in virtue of which interchanging two expressions may be done without changing the truth-value of statements in which the expressions occur. The phrase occurs in two fragments from Gottfried Leibniz's General Science...
. In other words, substitution of co-referential expressions into an opaque context does not always preserve truth. For example, "Lois believes x is a hero" is an opaque context because "Louis believes Superman is a hero" is true while "Lois believes Clark Kent is a hero" is false, even though 'Superman' and 'Clark Kent' are co-referential expressions.
The term is used in philosophical
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
theories of reference, and is to be contrasted with "transparent context". In rough outline:
- Opacity: "Mary believes that CiceroCiceroMarcus Tullius Cicero , was a Roman philosopher, statesman, lawyer, political theorist, and Roman constitutionalist. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the equestrian order, and is widely considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists.He introduced the Romans to the chief...
is a great orator" gives rise to an opaque context; although Cicero was also called 'Tully', we can't simply substitute 'Tully' for 'Cicero' in this context ("Mary believes that Tully is a great orator") and guarantee the same truth value, for Mary might not know that the names 'Tully' and 'Cicero' refer to one and the same thing. Of course, if Mary does believe that Cicero is a great orator, then there is a sense in which Mary believes that Tully is a great orator, even if she does not know that 'Tully' and 'Cicero' corefer. It is the sense forced on us by "direct reference" theories of proper names, i.e. those that maintain that the meaning of a proper name just is its referent.
- Transparency: "Cicero was a Roman orator" gives rise to a transparent context; there is no problem substituting 'Tully' for 'Cicero' here: "Tully was a Roman orator". Both sentences necessarily express the same thing if 'Cicero' and 'Tully' refer to the same person. Note that this element is missing in the opaque contexts, where a shift in the name can result in a sentence that expresses something different from the original.
Similar usage of the term applies for artificial languages such as programming language
Programming language
A programming language is an artificial language designed to communicate instructions to a machine, particularly a computer. Programming languages can be used to create programs that control the behavior of a machine and/or to express algorithms precisely....
s and logic
Logic
In philosophy, Logic is the formal systematic study of the principles of valid inference and correct reasoning. Logic is used in most intellectual activities, but is studied primarily in the disciplines of philosophy, mathematics, semantics, and computer science...
s. The Cicero-Tully example above can be easily adapted. Let
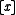 be interpreted as a function symbol returning a "name" of the value of the variable
be interpreted as a function symbol returning a "name" of the value of the variableVariable (mathematics)
In mathematics, a variable is a value that may change within the scope of a given problem or set of operations. In contrast, a constant is a value that remains unchanged, though often unknown or undetermined. The concepts of constants and variables are fundamental to many areas of mathematics and...
 on a language
on a language 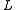 with domain
with domain 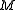 . Define a
. Define a 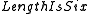 predicate with the property that
predicate with the property that 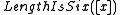 is true if and only if
is true if and only if 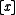 has
has 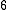 characters. Then
characters. Then 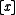 induces an opaque context, or is referentially opaque, because
induces an opaque context, or is referentially opaque, because 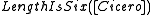 is true while
is true while 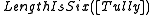 is false. Programming languages often have richer semantics than logics' semantics of truth and falsity, and so an operator
is false. Programming languages often have richer semantics than logics' semantics of truth and falsity, and so an operatorOperator (programming)
Programming languages typically support a set of operators: operations which differ from the language's functions in calling syntax and/or argument passing mode. Common examples that differ by syntax are mathematical arithmetic operations, e.g...
such as
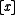 may fail to be referentially transparent for other reasons if it is not a pure function
may fail to be referentially transparent for other reasons if it is not a pure functionPure function
In computer programming, a function may be described as pure if both these statements about the function hold:# The function always evaluates the same result value given the same argument value...
.
See also
- Masked man fallacyMasked man fallacyThe masked man fallacy is a fallacy of formal logic in which substitution of identical designators in a true statement can lead to a false one.One form of the fallacy may be summarized as follows:* Premise 1: I know who X is....
- Transitivity of identity
- W.V.O. Quine
- Pure functionPure functionIn computer programming, a function may be described as pure if both these statements about the function hold:# The function always evaluates the same result value given the same argument value...
s - Fuzzy conceptFuzzy conceptA fuzzy concept is a concept of which the content, value, or boundaries of application can vary according to context or conditions, instead of being fixed once and for all....
- Saul KripkeSaul KripkeSaul Aaron Kripke is an American philosopher and logician. He is a professor emeritus at Princeton and teaches as a Distinguished Professor of Philosophy at the CUNY Graduate Center...

