Olympian spirits
Encyclopedia
Olympian spirits refers to seven (or sometimes fourteen) spirits mentioned in several renaissance and post-renaissance books of ritual magic/ceremonial magic
, such as the Arbatel de magia veterum
, The Secret Grimoire of Turiel and The Complete Book of Magic Science. The Arbatel of Magick (1655, London) writes of the Olympian spirits: "They are called Olympick spirits, which do inhabit in the firmament, and in the stars of the firmament: and the office of these spirits is to declare Destinies, and to administer fatal Charms, so far forth as God pleaseth to permit them."
In this magic system, the universe is divided into 196 provinces (a number which in numerology
adds up to 7: 1+9+6=16; 1+6=7) with each of the seven Olympian spirits ruling a set number of provinces (see below). Aratron rules the most provinces (49), while each succeeding Olympian rules seven fewer than the former, down to Phul who rules seven provinces. Each Olympian spirit is also associated with one of the seven luminaries which figure in ancient and medieval Western magic.
(usually the Sun), Anael (Venus), Raphael
(usually Mercury), Gabriel
(the Moon), Cassiel
(Saturn), Samael
(Mars), and Zadkiel
(Jupiter), or a variation thereof.
The seven Olympian spirits are often invoked in conjunction with the seven classic archangels, and magic seals often associate one of the classic seven with one of the Olympian spirits.
For example, a magic seal from The Complete Book of Magic Science (1573) shows the form of a seal which binds a spirit of Jupiter, Pabiel, to the magician: Pabiel's name appears in a band stretched between two circles: the circle on the left bearing the name and sigil of Bethor, the circle on the right bearing the name and sigil of Sachiel
(equivalent to Zadkiel).
Ceremonial magic
Ceremonial magic, also referred to as high magic and as learned magic, is a broad term used in the context of Hermeticism or Western esotericism to encompass a wide variety of long, elaborate, and complex rituals of magic. It is named as such because the works included are characterized by...
, such as the Arbatel de magia veterum
Arbatel de magia veterum
Arbatel de magia veterum is a treatise on ceremonial magic written in Latin, first published in 1575 in Basel, Switzerland...
, The Secret Grimoire of Turiel and The Complete Book of Magic Science. The Arbatel of Magick (1655, London) writes of the Olympian spirits: "They are called Olympick spirits, which do inhabit in the firmament, and in the stars of the firmament: and the office of these spirits is to declare Destinies, and to administer fatal Charms, so far forth as God pleaseth to permit them."
In this magic system, the universe is divided into 196 provinces (a number which in numerology
Numerology
Numerology is any study of the purported mystical relationship between a count or measurement and life. It has many systems and traditions and beliefs...
adds up to 7: 1+9+6=16; 1+6=7) with each of the seven Olympian spirits ruling a set number of provinces (see below). Aratron rules the most provinces (49), while each succeeding Olympian rules seven fewer than the former, down to Phul who rules seven provinces. Each Olympian spirit is also associated with one of the seven luminaries which figure in ancient and medieval Western magic.
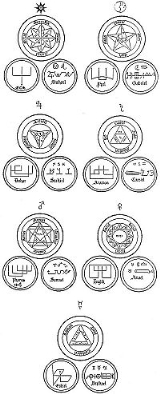
The seven Olympian spirits
- AratronAratronAratron is an Olympian spirit in the grimoire known as the Arbatel de magia veterum. He rules over Saturn....
(or Arathron), "the alchemistAlchemistAn alchemist is a person who practices alchemy. Alchemist may also refer to:-People and groups:*The Alchemist , a hip hop music producer and rapper*Alchemist , an Australian progressive metal band...
who commanded seventeen million six hundred and forty thousand spirits". He rules 49 provinces. His planet is Saturn. - BethorBethorBethor is an Olympian spirit in the Grimoire known as the Arbatel de magia veterum. He rules over Jupiter....
, "who commanded twenty-nine thousand legions of spirits". He rules 42 provinces. His planet is Jupiter. - PhalegPhaleg (spirit)Phaleg is an Olympian spirit in the grimoire known as the Arbatel de magia veterum who rules over Mars....
(or Phalec, Pharos), "the War-Lord". His planet is Mars. He rules 35 provinces. - OchOch (spirit)Och is believed to be an Olympian spirit in the grimoire Arbatel de magia veterum who rules the Sun....
, "the alchemist, physicianPhysicianA physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
, and magician". He rules 28 provinces. His "planet" is the Sun. - HagithHagith (spirit)Hagith is an Olympian spirit in the grimoire known as the Arbatel de magia veterum. He rules over Venus....
, "transmuter of metals, and commander of four thousand legions of spirits". He rules 21 provinces. His planet is Venus. - OphielOphielOphiel is an Olympian spirit in the grimoire known as the Arbatel de magia veterum. He rules over Mercury....
, "who commanded one hundred thousand legions of spirits". He rules 14 provinces. His planet is Mercury. - PhulPhulPhul is an Olympian spirit in the grimoire known as the Arbatel de magia veterum. He rules over the Moon....
, "lord of the powers of the moon and supreme lord of the waters". He rules 7 provinces. His "planet" is the Moon.
The seven Archangels and the seven Olympian spirits
In ritual magic, the seven Olympian spirits are not confused with the seven traditional archangels, which usually are MichaelMichael (archangel)
Michael , Micha'el or Mîkhā'ēl; , Mikhaḗl; or Míchaël; , Mīkhā'īl) is an archangel in Jewish, Christian, and Islamic teachings. Roman Catholics, Anglicans, and Lutherans refer to him as Saint Michael the Archangel and also simply as Saint Michael...
(usually the Sun), Anael (Venus), Raphael
Raphael (archangel)
Raphael is an archangel of Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, who in the Judeo-Christian tradition performs all manners of healing....
(usually Mercury), Gabriel
Gabriel
In Abrahamic religions, Gabriel is an Archangel who typically serves as a messenger to humans from God.He first appears in the Book of Daniel, delivering explanations of Daniel's visions. In the Gospel of Luke Gabriel foretells the births of both John the Baptist and of Jesus...
(the Moon), Cassiel
Cassiel
Cassiel is the Latin name of an archangel in post-biblical Judeo-Christian religion, particularly that of the Kabbalah. Unlike many other angels, Cassiel is known for simply watching the events of the cosmos unfold with little interference...
(Saturn), Samael
Samael
Samael is an important archangel in Talmudic and post-Talmudic lore, a figure who is accuser, seducer and destroyer, and has been regarded as both good and evil...
(Mars), and Zadkiel
Zadkiel
Zadkiel or Hesediel is the archangel of freedom, benevolence, mercy, and the Patron Angel of all who forgive. Also known as Sachiel, Zedekiel, Zadakiel, Tzadkiel, Zedekul and Hesediel...
(Jupiter), or a variation thereof.
The seven Olympian spirits are often invoked in conjunction with the seven classic archangels, and magic seals often associate one of the classic seven with one of the Olympian spirits.
For example, a magic seal from The Complete Book of Magic Science (1573) shows the form of a seal which binds a spirit of Jupiter, Pabiel, to the magician: Pabiel's name appears in a band stretched between two circles: the circle on the left bearing the name and sigil of Bethor, the circle on the right bearing the name and sigil of Sachiel
Sachiel
In kabbalistic and Christian angelology, Sachiel is an archangel of the order of Cherubim. The meaning of his name is given as "the covering of God" and he is associated with the Zodiacal sign Sagittarius, the weekday Thursday, wealth and charity. While in most sources Sachiel presides over...
(equivalent to Zadkiel).

