
OZI Rule
Encyclopedia
The OZI rule is part of QCD
which explains why certain decay mode
s appear less frequently than otherwise might be expected. It was independently proposed by Susumu Okubo
, George Zweig
and Jugoro Iizuka in the 1960s. It states that any strongly
occurring process with a Feynman Diagram
that can be split in two by cutting only internal gluon
lines will be suppressed.
An example of such a suppressed decay is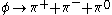 . It would be expected that this decay mode would dominate over other decay modes such as φ → K+ + K-, which have much lower Q values. In actuality, it is seen that φ
. It would be expected that this decay mode would dominate over other decay modes such as φ → K+ + K-, which have much lower Q values. In actuality, it is seen that φ
decays to kaon
s 84% of the time, suggesting the decay path to pion
s is suppressed.
An explanation of the OZI rule can be seen from the fact that the coupling constant in QCD decreases with increasing energy (or momentum transfer). For the OZI suppressed channels the gluons must have high q2 (at least as much as the rest mass energies of the quarks into which they decay) and so the coupling constant will appear small to these gluons.
Quantum chromodynamics
In theoretical physics, quantum chromodynamics is a theory of the strong interaction , a fundamental force describing the interactions of the quarks and gluons making up hadrons . It is the study of the SU Yang–Mills theory of color-charged fermions...
which explains why certain decay mode
Particle decay
Particle decay is the spontaneous process of one elementary particle transforming into other elementary particles. During this process, an elementary particle becomes a different particle with less mass and an intermediate particle such as W boson in muon decay. The intermediate particle then...
s appear less frequently than otherwise might be expected. It was independently proposed by Susumu Okubo
Susumu Okubo
is a Japanese theoretical physicist at the University of Rochester.Ōkubo began study at the University of Tokyo in 1949 and received his bachelor's degree there in 1952. He became a graduate student at the University of Rochester in 1954, where he earned his PhD in 1958 with Robert Marshak as...
, George Zweig
George Zweig
George Zweig was originally trained as a particle physicist under Richard Feynman and later turned his attention to neurobiology...
and Jugoro Iizuka in the 1960s. It states that any strongly
Strong interaction
In particle physics, the strong interaction is one of the four fundamental interactions of nature, the others being electromagnetism, the weak interaction and gravitation. As with the other fundamental interactions, it is a non-contact force...
occurring process with a Feynman Diagram
Feynman diagram
Feynman diagrams are a pictorial representation scheme for the mathematical expressions governing the behavior of subatomic particles, first developed by the Nobel Prize-winning American physicist Richard Feynman, and first introduced in 1948...
that can be split in two by cutting only internal gluon
Gluon
Gluons are elementary particles which act as the exchange particles for the color force between quarks, analogous to the exchange of photons in the electromagnetic force between two charged particles....
lines will be suppressed.
An example of such a suppressed decay is
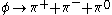 . It would be expected that this decay mode would dominate over other decay modes such as φ → K+ + K-, which have much lower Q values. In actuality, it is seen that φ
. It would be expected that this decay mode would dominate over other decay modes such as φ → K+ + K-, which have much lower Q values. In actuality, it is seen that φPhi meson
In particle physics, the phi meson is a vector meson formed of a strange quark and a strange antiquark. It has a mass of .-Overview:-See also:*Charmonium*List of mesons*List of particles*Quark model...
decays to kaon
Kaon
In particle physics, a kaon is any one of a group of four mesons distinguished by the fact that they carry a quantum number called strangeness...
s 84% of the time, suggesting the decay path to pion
Pion
In particle physics, a pion is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Pions are the lightest mesons and they play an important role in explaining the low-energy properties of the strong nuclear force....
s is suppressed.
An explanation of the OZI rule can be seen from the fact that the coupling constant in QCD decreases with increasing energy (or momentum transfer). For the OZI suppressed channels the gluons must have high q2 (at least as much as the rest mass energies of the quarks into which they decay) and so the coupling constant will appear small to these gluons.

