
OFDMA
Encyclopedia
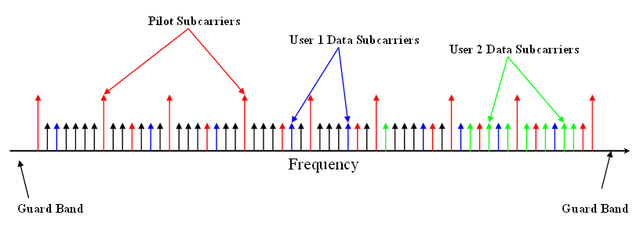
Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) is a multi-user version of the popular Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM)
digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarriers to individual users as shown in the illustration below. This allows simultaneous low data rate transmission from several users.
and narrow-band cochannel interference, and makes it possible to achieve even better system spectral efficiency.
Different number of sub-carriers can be assigned to different users, in view to support differentiated Quality of Service
(QoS), i.e. to control the data rate and error probability individually for each user.
OFDMA resembles code division multiple access
(CDMA) spread spectrum, where users can achieve different data rates by assigning a different code spreading factor or a different number of spreading codes to each user.
OFDMA can be seen as an alternative to combining OFDM with time division multiple access
(TDMA) or time-domain statistical multiplexing
, i.e. packet mode communication. Low-data-rate users can send continuously with low transmission power instead of using a "pulsed" high-power carrier. Constant delay, and shorter delay, can be achieved.
OFDMA can also be described as a combination of frequency domain and time domain multiple access, where the resources are partitioned in the time-frequency space, and slots are assigned along the OFDM symbol index as well as OFDM sub-carrier index.
OFDMA is considered as highly suitable for broadband wireless networks, due to advantages including scalability and MIMO
-friendliness, and ability to take advantage of channel frequency selectivity.
In spectrum sensing cognitive radio
, OFDMA
is a possible approach to filling free radio frequency
bands adaptively. Timo A. Weiss and Friedrich K. Jondral of the University of Karlsruhe proposed a spectrum pooling
system in which free bands sensed by nodes were immediately filled by OFDMA
subbands.
OFDMA is also a candidate access method for the IEEE 802.22
Wireless Regional Area Networks (WRAN). The project aims at designing the first cognitive radio
based standard operating in the VHF-low UHF spectrum (TV spectrum).
The term "OFDMA" is claimed to be a registered trademark by Runcom Technologies Ltd.http://www.runcom.com/, with various other claimants to the underlying technologies through patents.
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing is a method of encoding digital data on multiple carrier frequencies. OFDM has developed into a popular scheme for wideband digital communication, whether wireless or over copper wires, used in applications such as digital television and audio...
digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarriers to individual users as shown in the illustration below. This allows simultaneous low data rate transmission from several users.

Key features
The advantages and disadvantages summarized below are further discussed in the Characteristics and principles of operation section. See also the list of OFDM Key features.Claimed advantages over CDMA
- OFDM can combat multipath interferenceMultipath interferenceMultipath interference is a phenomenon in the physics of waves whereby a wave from a source travels to a detector via two or more paths and, under the right condition, the two components of the wave interfere...
with more robustness and less complexity. - OFDMA can achieve a higher MIMOMIMOIn radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO , is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna technology...
spectral efficiencySpectral efficiencySpectral efficiency, spectrum efficiency or bandwidth efficiency refers to the information rate that can be transmitted over a given bandwidth in a specific communication system...
due to providing flatter frequency channels than a CDMA rake receiverRake receiverA rake receiver is a radio receiver designed to counter the effects of multipath fading. It does this by using several "sub-receivers" called fingers, that is, several correlators each assigned to a different multipath component...
can. - No cell size breathing as more users connect.
Claimed advantages over OFDM with time-domain statistical multiplexing
- Allows simultaneous low-data-rate transmission from several users.
- Pulsed carrier can be avoided.
- Lower maximum transmission power for low data rate users.
- Shorter delay, and constant delay.
- Contention-based multiple access (collision avoidance) is simplified.
- Further improves OFDM robustness to fading and interference.
Claimed OFDMA Advantages
- Flexibility of deployment across various frequency bands with little needed modification to the air interface.
- Averaging interferences from neighboring cells, by using different basic carrier permutations between users in different cells.
- Interferences within the cell are averaged by using allocation with cyclic permutations.
- Enables Single Frequency Network coverage, where coverage problem exists and gives excellent coverage.
- Offers Frequency diversity by spreading the carriers all over the used spectrum.
- Allows per channel or per subchannel power control.
Recognized disadvantages of OFDMA
- Higher sensitivity to frequency offsets and phase noise.
- Asynchronous data communication services such as web access are characterized by short communication bursts at high data rate. Few users in a base station cell are transferring data simultaneously at low constant data rate.
- The complex OFDM electronics, including the FFT algorithm and forward error correctionForward error correctionIn telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, forward error correction or channel coding is a technique used for controlling errors in data transmission over unreliable or noisy communication channels....
, is constantly active independent of the data rate, which is inefficient from power consumption point of view, while OFDM combined with data packet scheduling may allow FFT algorithm to hibernate during certain time intervals. - The OFDM diversity gain, and resistance to frequency-selective fading, may partly be lost if very few sub-carriers are assigned to each user, and if the same carrier is used in every OFDM symbol. Adaptive sub-carrier assignment based on fast feedback information about the channel, or sub-carrier frequency hopping, is therefore desirable.
- Dealing with co-channel interference from nearby cells is more complex in OFDM than in CDMA. It would require dynamic channel allocation with advanced coordination among adjacent base stations.
- The fast channel feedback information and adaptive sub-carrier assignment is more complex than CDMA fast power control.
Characteristics and principles of operation
Based on feedback information about the channel conditions, adaptive user-to-subcarrier assignment can be achieved. If the assignment is done sufficiently fast, this further improves the OFDM robustness to fast fadingFading
In wireless communications, fading is deviation of the attenuation that a carrier-modulated telecommunication signal experiences over certain propagation media. The fading may vary with time, geographical position and/or radio frequency, and is often modelled as a random process. A fading channel...
and narrow-band cochannel interference, and makes it possible to achieve even better system spectral efficiency.
Different number of sub-carriers can be assigned to different users, in view to support differentiated Quality of Service
Quality of service
The quality of service refers to several related aspects of telephony and computer networks that allow the transport of traffic with special requirements...
(QoS), i.e. to control the data rate and error probability individually for each user.
OFDMA resembles code division multiple access
Code division multiple access
Code division multiple access is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. It should not be confused with the mobile phone standards called cdmaOne, CDMA2000 and WCDMA , which are often referred to as simply CDMA, and use CDMA as an underlying channel access...
(CDMA) spread spectrum, where users can achieve different data rates by assigning a different code spreading factor or a different number of spreading codes to each user.
OFDMA can be seen as an alternative to combining OFDM with time division multiple access
Time division multiple access
Time division multiple access is a channel access method for shared medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession, one after the other, each using its own time slot. This...
(TDMA) or time-domain statistical multiplexing
Statistical multiplexing
Statistical multiplexing is a type of communication link sharing, very similar to dynamic bandwidth allocation . In statistical multiplexing, a communication channel is divided into an arbitrary number of variable bit-rate digital channels or data streams. The link sharing is adapted to the...
, i.e. packet mode communication. Low-data-rate users can send continuously with low transmission power instead of using a "pulsed" high-power carrier. Constant delay, and shorter delay, can be achieved.
OFDMA can also be described as a combination of frequency domain and time domain multiple access, where the resources are partitioned in the time-frequency space, and slots are assigned along the OFDM symbol index as well as OFDM sub-carrier index.
OFDMA is considered as highly suitable for broadband wireless networks, due to advantages including scalability and MIMO
MIMO
In radio, multiple-input and multiple-output, or MIMO , is the use of multiple antennas at both the transmitter and receiver to improve communication performance. It is one of several forms of smart antenna technology...
-friendliness, and ability to take advantage of channel frequency selectivity.
In spectrum sensing cognitive radio
Cognitive radio
A cognitive radio is a kind of two-way radio that automatically changes its transmission or reception parameters, in a way where the entire wireless communication network -- of which it is a node -- communicates efficiently, while avoiding interference with licensed or licensed exempt users...
, OFDMA
OFDMA
Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access is a multi-user version of the popular Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarriers to individual users as shown in the illustration below...
is a possible approach to filling free radio frequency
Radio frequency
Radio frequency is a rate of oscillation in the range of about 3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating currents which carry radio signals...
bands adaptively. Timo A. Weiss and Friedrich K. Jondral of the University of Karlsruhe proposed a spectrum pooling
Spectrum pooling
Spectrum pooling is a spectrum management strategy in which multiple radio spectrum users can coexist within a single allocation of radio spectrum space. One use of this technique is for primary users of a spectrum allocation to be able to rent out use of unused parts of their allocation to...
system in which free bands sensed by nodes were immediately filled by OFDMA
OFDMA
Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access is a multi-user version of the popular Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing digital modulation scheme. Multiple access is achieved in OFDMA by assigning subsets of subcarriers to individual users as shown in the illustration below...
subbands.
Usage
OFDMA is used in:- the mobility mode of the IEEE 802.16IEEE 802.16IEEE 802.16 is a series of Wireless Broadband standards authored by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers . The IEEE Standards Board in established a working group in 1999 to develop standards for broadband Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks...
Wireless MAN standard, commonly referred to as WiMAX, - the IEEE 802.20IEEE 802.20IEEE 802.20 or Mobile Broadband Wireless Access was a specification by the standard association of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers for mobile wireless Internet access networks...
mobile Wireless MAN standard, commonly referred to as MBWA, - the downlink of the 3GPP3GPPThe 3rd Generation Partnership Project is a collaboration between groups of telecommunications associations, known as the Organizational Partners...
Long Term Evolution (LTE) fourth generation mobile broadband standard. The radio interface was formerly named High Speed OFDM Packet Access (HSOPA), now named Evolved UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA). - the Qualcomm Flarion Technologies Mobile Flash-OFDM
- the now defunct QualcommQualcommQualcomm is an American global telecommunication corporation that designs, manufactures and markets digital wireless telecommunications products and services based on its code division multiple access technology and other technologies. Headquartered in San Diego, CA, USA...
/3GPP2 Ultra Mobile BroadbandUltra Mobile BroadbandUMB was the brand name for a project within 3GPP2 to improve the CDMA2000 mobile phone standard for next generation applications and requirements...
(UMB) project, intended as a successor of CDMA2000CDMA2000CDMA2000 is a family of 3G mobile technology standards, which use CDMA channel access, to send voice, data, and signaling data between mobile phones and cell sites. The set of standards includes: CDMA2000 1X, CDMA2000 EV-DO Rev. 0, CDMA2000 EV-DO Rev. A, and CDMA2000 EV-DO Rev. B...
, but replaced by LTE.
OFDMA is also a candidate access method for the IEEE 802.22
IEEE 802.22
IEEE 802.22 is a standard for Wireless Regional Area Network using white spaces in the TV frequency spectrum. The development of the IEEE 802.22 WRAN standard is aimed at using cognitive radio techniques to allow sharing of geographically unused spectrum allocated to the Television Broadcast...
Wireless Regional Area Networks (WRAN). The project aims at designing the first cognitive radio
Cognitive radio
A cognitive radio is a kind of two-way radio that automatically changes its transmission or reception parameters, in a way where the entire wireless communication network -- of which it is a node -- communicates efficiently, while avoiding interference with licensed or licensed exempt users...
based standard operating in the VHF-low UHF spectrum (TV spectrum).
The term "OFDMA" is claimed to be a registered trademark by Runcom Technologies Ltd.http://www.runcom.com/, with various other claimants to the underlying technologies through patents.
Literature
- K. Fazel and S. Kaiser, Multi-Carrier and Spread Spectrum Systems: From OFDM and MC-CDMA to LTE and WiMAX, 2nd Edition, John Wiley & Sons, 2008, ISBN 978-0-470-99821-2.
See also
- Code division multiple accessCode division multiple accessCode division multiple access is a channel access method used by various radio communication technologies. It should not be confused with the mobile phone standards called cdmaOne, CDMA2000 and WCDMA , which are often referred to as simply CDMA, and use CDMA as an underlying channel access...
- Frequency division multiple access
- Time division multiple accessTime division multiple accessTime division multiple access is a channel access method for shared medium networks. It allows several users to share the same frequency channel by dividing the signal into different time slots. The users transmit in rapid succession, one after the other, each using its own time slot. This...
- Single-carrier FDMASingle-carrier FDMASingle-carrier FDMA is a frequency-division multiple access scheme. Like other multiple access schemes , it deals with the assignment of multiple users to a shared communication resource...
(SC-FDMA), a.k.a Linearly precoded OFDMA (LP-OFDMA) - 3GPP Long Term Evolution3GPP Long Term Evolution3GPP Long Term Evolution, usually referred to as LTE, is a standard for wireless communication of high-speed data for mobile phones and data terminals. It is based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA network technologies, increasing the capacity and speed using new modulation techniques...
- WiMAXWiMAXWiMAX is a communication technology for wirelessly delivering high-speed Internet service to large geographical areas. The 2005 WiMAX revision provided bit rates up to 40 Mbit/s with the 2011 update up to 1 Gbit/s for fixed stations...
- WiBroWiBroWiBro is a wireless broadband Internet technology developed by the South Korean telecoms industry. WiBro is the South Korean service name for IEEE 802.16e international standard...
External links
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access: is it the multiple access system of the future?, S. Srikanth, V. Kumaran, C. Manikandan et al., AU-KBC Research Center, Anna University, India.
- Short Introduction to OFDM - Tutorial written by Prof. Debbah, head of the Alcatel-Lucent Chair on flexible radio.

