
Nuclear Polynesian languages
Encyclopedia
Samoic languages
The Samoic–Outlier languages, also known as Samoic languages, are a purported group of Polynesian languages, encompassing the Polynesian languages of Samoa, Tuvalu, American Samoa, Tokelau, Wallis and Futuna, and Polynesian outlier languages in New Caledonia, the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Papua New...
and the Eastern Polynesian
Eastern Polynesian languages
The dozen Eastern Polynesian languages are found on Pacific Islands from Hawaii in the north, to New Zealand in the southwest, to Easter Island in the southeast...
branches of the Polynesian
Polynesian languages
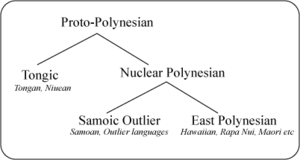
The Polynesian languages are a language family spoken in the region known as Polynesia. They are classified as part of the Austronesian family, belonging to the Oceanic branch of that family. They fall into two branches: Tongic and Nuclear Polynesian. Polynesians share many cultural traits...
group of Austronesian languages
Austronesian languages
The Austronesian languages are a language family widely dispersed throughout the islands of Southeast Asia and the Pacific, with a few members spoken on continental Asia that are spoken by about 386 million people. It is on par with Indo-European, Niger-Congo, Afroasiatic and Uralic as one of the...
.
The Eastern Polynesian group comprises two major subgroups: Rapa Nui
Rapa Nui language
Rapa Nui , also known as Pascuan or Pascuense, is an Eastern Polynesian language spoken on the island of Rapa Nui, also known as Easter Island....
, spoken on Easter Island
Easter Island
Easter Island is a Polynesian island in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian triangle. A special territory of Chile that was annexed in 1888, Easter Island is famous for its 887 extant monumental statues, called moai, created by the early Rapanui people...
, and Central Eastern, which is itself composed of Rapan
Rapan language
Rapan is the language of Rapa, in the Austral Islands of French Polynesia. It is classified as an East Central Polynesian language, along with the Marquesic and Tahitic languages....
, and the Marquesic
Marquesic languages
Marquesic languages are a small but historically important subgroup of Central Eastern Polynesian languages:# Marquesan languages of the Marquesas Islands in French Polynesia...
and Tahitic languages
Tahitic languages
The Tahitic languages are a group of Eastern Polynesian languages in the Central Eastern branch. ....
.
Nuclear Polynesian is differentiated, among Polynesian languages, by its distinguishing characteristics from the Tongic languages
Tongic languages
The family of Tongic languages is a small group of the Polynesian languages. It consists of at least two languages, Tongan and Niuean, and possibly a third, Niuafoʻouan.-External links:*...
spoken in most of Tonga
Tonga
Tonga, officially the Kingdom of Tonga , is a state and an archipelago in the South Pacific Ocean, comprising 176 islands scattered over of ocean in the South Pacific...
and in Niue
Niue
Niue , is an island country in the South Pacific Ocean. It is commonly known as the "Rock of Polynesia", and inhabitants of the island call it "the Rock" for short. Niue is northeast of New Zealand in a triangle between Tonga to the southwest, the Samoas to the northwest, and the Cook Islands to...
.
Components
Eastern PolynesianEastern Polynesian languages
The dozen Eastern Polynesian languages are found on Pacific Islands from Hawaii in the north, to New Zealand in the southwest, to Easter Island in the southeast...
- Central Eastern Polynesian
- RapaRapan languageRapan is the language of Rapa, in the Austral Islands of French Polynesia. It is classified as an East Central Polynesian language, along with the Marquesic and Tahitic languages....
- Marquesic languagesMarquesic languagesMarquesic languages are a small but historically important subgroup of Central Eastern Polynesian languages:# Marquesan languages of the Marquesas Islands in French Polynesia...
- HawaiianHawaiian languageThe Hawaiian language is a Polynesian language that takes its name from Hawaii, the largest island in the tropical North Pacific archipelago where it developed. Hawaiian, along with English, is an official language of the state of Hawaii...
- MarquesanMarquesan languageMarquesan is a collection of East-Central Polynesian dialects, of the Marquesic group, spoken in the Marquesas Islands of French Polynesia. They are usually classified into two groups, North Marquesan and South Marquesan, roughly along geographic lines....
- Northern
- Southern
- Mangerevan
- Hawaiian
- Tahitic languagesTahitic languagesThe Tahitic languages are a group of Eastern Polynesian languages in the Central Eastern branch. ....
- AustralAustral languageAustral is a Polynesian language spoken by about 8000 people on the Austral Islands of French Polynesia. It is being supplanted by Tahitian....
- MaoriMaori languageMāori or te reo Māori , commonly te reo , is the language of the indigenous population of New Zealand, the Māori. It has the status of an official language in New Zealand...
- TuamotuanTuamotuan languageThe Tuamotuan language or Paumotuan is a Tahitic language spoken by about 6700 people in the Tuamotu Islands with an additional 2000 speakers in Tahiti...
- PenrhynPenrhyn languageThe Penrhyn language is a Polynesian language spoken by about 600 people on Penrhyn Island and other islands of the Cook Islands. It is considered to be an endangered language....
- Rarotongan
- Rakahanga-ManihikiRakahanga-Manihiki languageRakahanga-Manihiki is a Cook Islands Maori dialectal variant belonging to the Polynesian languages family, spoken by about 2500 people on Rakahanga and Manihiki Islands and another 2500 in other countries, mostly New Zealand and Australia...
- TahitianTahitian languageTahitian is an indigenous language spoken mainly in the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is an Eastern Polynesian language closely related to the other indigenous languages spoken in French Polynesia: Marquesan, Tuamotuan, Mangarevan, and Austral Islands languages...
- Austral
- Rapa NuiRapa Nui languageRapa Nui , also known as Pascuan or Pascuense, is an Eastern Polynesian language spoken on the island of Rapa Nui, also known as Easter Island....
- Rapa
Samoic
Samoic languages
The Samoic–Outlier languages, also known as Samoic languages, are a purported group of Polynesian languages, encompassing the Polynesian languages of Samoa, Tuvalu, American Samoa, Tokelau, Wallis and Futuna, and Polynesian outlier languages in New Caledonia, the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Papua New...
- East Uvean–Niuafo'ou languages
- Ellicean languagesEllicean languagesThe Ellicean or Ellicean–Outlier languages are a group languages spoken in Polynesian outliers in Micronesia, Papua New Guinea, and the northern Solomon Islands, as well as the languages of Tuvalu...
- Futunic languagesFutunic languages-External links:*...
- PukapukaPukapukan languagePukapukan is a Polynesian language that developed in isolation on the island of Pukapuka in the northern group of the Cook Islands...
- SamoanSamoan languageSamoan Samoan Samoan (Gagana Sāmoa, is the language of the Samoan Islands, comprising the independent country of Samoa and the United States territory of American Samoa. It is an official language—alongside English—in both jurisdictions. Samoan, a Polynesian language, is the first language for most...
- TokelauanTokelauan languageTokelauan is a Polynesian language closely related to Tuvaluan.-Speakers:It is spoken by about 1,500 people on the atolls of Tokelau, and by the few inhabitants of Swains Island in neighbouring American Samoa. It is a member of the Samoic family of Polynesian languages. It is, alongside English,...

