Nitrogen-13
Encyclopedia
Nitrogen-13 is a radioisotope of nitrogen
used in positron emission tomography
(PET). It has a half life of a little under ten minutes, so it must be made at the PET site. A cyclotron
may be used for this purpose.
Nitrogen-13 is used to tag ammonia
molecules for PET.
The proton must be accelerated to a kinetic energy
of about 5.55 Mev or a little more.
The reaction is endothermic
(i.e. the mass of the products is greater than the reactants, so energy needs to be supplied which is converted to mass).This is one reason why the proton needs to carry extra energy
to produce the nuclear reaction
.
The energy difference is actually 5.22 MeV, but if the proton only supplied this energy the reactants would be formed with no kinetic energy. As momentum
must be conserved, the true energy that needs to be supplied by the proton is given by:
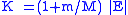
 Nitrogen-13 plays a significant role in the CNO cycle
Nitrogen-13 plays a significant role in the CNO cycle
, which is the dominant source of energy in stars heavier than the sun
.
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
used in positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography is nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide , which is introduced into the body on a...
(PET). It has a half life of a little under ten minutes, so it must be made at the PET site. A cyclotron
Cyclotron
In technology, a cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator. In physics, the cyclotron frequency or gyrofrequency is the frequency of a charged particle moving perpendicularly to the direction of a uniform magnetic field, i.e. a magnetic field of constant magnitude and direction...
may be used for this purpose.
Nitrogen-13 is used to tag ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
molecules for PET.
Production
- H1 + O16 → N13 + He4
The proton must be accelerated to a kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
of about 5.55 Mev or a little more.
The reaction is endothermic
Endothermic
In thermodynamics, the word endothermic describes a process or reaction in which the system absorbs energy from the surroundings in the form of heat. Its etymology stems from the prefix endo- and the Greek word thermasi,...
(i.e. the mass of the products is greater than the reactants, so energy needs to be supplied which is converted to mass).This is one reason why the proton needs to carry extra energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
to produce the nuclear reaction
Nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is semantically considered to be the process in which two nuclei, or else a nucleus of an atom and a subatomic particle from outside the atom, collide to produce products different from the initial particles...
.
The energy difference is actually 5.22 MeV, but if the proton only supplied this energy the reactants would be formed with no kinetic energy. As momentum
Momentum
In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object...
must be conserved, the true energy that needs to be supplied by the proton is given by:
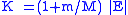
Role in stellar fusion

CNO cycle
The CNO cycle is one of two sets of fusion reactions by which stars convert hydrogen to helium, the other being the proton–proton chain. Unlike the proton–proton chain reaction, the CNO cycle is a catalytic cycle. Theoretical models show that the CNO cycle is the dominant source of energy in stars...
, which is the dominant source of energy in stars heavier than the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
.
| → | 1.95 MeV | ||||||
| → | 2.22 MeV | ||||||
| → | 7.54 MeV | ||||||
| → | 7.35 MeV | ||||||
| → | 2.75 MeV | ||||||
| → | 4.96 MeV |
External links
- PET site of the University of MelbourneUniversity of MelbourneThe University of Melbourne is a public university located in Melbourne, Victoria. Founded in 1853, it is the second oldest university in Australia and the oldest in Victoria...

