Nierenstein reaction
Encyclopedia
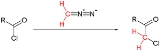
The Nierenstein reaction is an organic reaction
describing the conversion of an acid chloride into an haloketone
with diazomethane
. It is an insertion reaction
in that the methylene
from the diazomethane is inserted into the carbon-chlorine bond of the acid chloride.
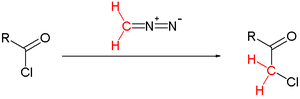
 The synthesis of benzyl chloromethyl ketone from phenylacetyl chloride in fact requires the addition of HCl gas to the diazoketone intermediate for it to succeed. The unassisted reaction failed.
The synthesis of benzyl chloromethyl ketone from phenylacetyl chloride in fact requires the addition of HCl gas to the diazoketone intermediate for it to succeed. The unassisted reaction failed.
 and a reaction starting from benzoyl bromide
and a reaction starting from benzoyl bromide
going haywire with formation of the dioxane dimer:

Organic reaction
Organic reactions are chemical reactions involving organic compounds. The basic organic chemistry reaction types are addition reactions, elimination reactions, substitution reactions, pericyclic reactions, rearrangement reactions, photochemical reactions and redox reactions. In organic synthesis,...
describing the conversion of an acid chloride into an haloketone
Haloketone
A haloketone in organic chemistry is a functional group consisting of a ketone group or more general a carbonyl group with a α-halogen substituent. The general structure is RR'CCR where R is an alkyl or aryl residue and X any one of the halogens...
with diazomethane
Diazomethane
Diazomethane is the chemical compound CH2N2. It is the simplest of diazo compounds. In the pure form at room temperature, it is a extremely sensitive explosive yellow gas, thus it is almost universally used as a solution in diethyl ether...
. It is an insertion reaction
Insertion reaction
An insertion reaction is a chemical reaction where one chemical entity interposes itself into an existing bond of typically a second chemical entity e.g.:...
in that the methylene
Methylene
Methylene is a chemical species in which a carbon atom is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. Three different possibilities present themselves:* the -CH2- substituent group: e.g., dichloromethane ....
from the diazomethane is inserted into the carbon-chlorine bond of the acid chloride.

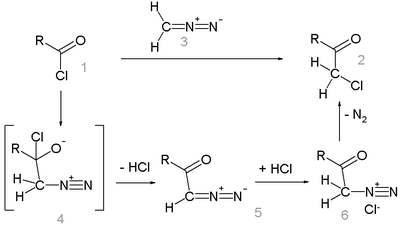
Reaction mechanism
Like the related Arndt-Eistert reaction, this reactions proceeds through a diazoketone intermediate (5). The loss of nitrogen to gives the desired haloketone (2).
Scope
One original 1924 Nierenstein reaction:
Benzoyl
In organic chemistry, benzoyl is the acyl of benzoic acid, with structure C6H5CO-. It should not be confused with benzyl, which is the radical or ion formed from the removal of one of the methyl hydrogens of toluene...
going haywire with formation of the dioxane dimer:


