
Newmark-beta method
Encyclopedia
The Newmark-beta method is a method of numerical integration
used to solve differential equations. It is widely used in numerical evaluation of the dynamic response of structures and solids such as in finite element analysis to model dynamic systems. The method is named after Nathan M. Newmark
, former Professor of Civil Engineering at the University of Illinois, who developed it in 1959 for use in Structural dynamics
.
Using the extended mean value theorem, The Newmark-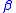 method states that the first time derivative (velocity in the equation of motion
method states that the first time derivative (velocity in the equation of motion
) can be solved as,
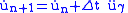
where

therefore
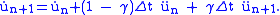
Because acceleration also varies with time, however, the extended mean value theorem must also be extended to the second time derivative to obtain the correct displacement. Thus,
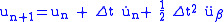
where again

Newmark showed that a reasonable value of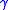 is 0.5, therefore the update rules are,
is 0.5, therefore the update rules are,
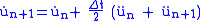
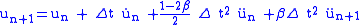
Setting β to various values between 0 and 1 can give a wide range of results. Typically β = 1/4, which yields the constant average acceleration method, is used.
Numerical integration
In numerical analysis, numerical integration constitutes a broad family of algorithms for calculating the numerical value of a definite integral, and by extension, the term is also sometimes used to describe the numerical solution of differential equations. This article focuses on calculation of...
used to solve differential equations. It is widely used in numerical evaluation of the dynamic response of structures and solids such as in finite element analysis to model dynamic systems. The method is named after Nathan M. Newmark
Nathan M. Newmark
Nathan Mortimore Newmark was an American structural engineer and academic. He was awarded the National Medal of Science for engineering.-Early life:...
, former Professor of Civil Engineering at the University of Illinois, who developed it in 1959 for use in Structural dynamics
Structural Dynamics
Structural dynamics is a subset of structural analysis which covers the behaviour of structures subjected to dynamic loading. Dynamic loads include people, wind, waves, traffic, earthquakes, and blasts. Any structure can be subject to dynamic loading. Dynamic analysis can be used to find dynamic...
.
Using the extended mean value theorem, The Newmark-
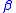 method states that the first time derivative (velocity in the equation of motion
method states that the first time derivative (velocity in the equation of motionEquation of motion
Equations of motion are equations that describe the behavior of a system in terms of its motion as a function of time...
) can be solved as,
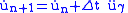
where

therefore
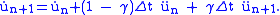
Because acceleration also varies with time, however, the extended mean value theorem must also be extended to the second time derivative to obtain the correct displacement. Thus,
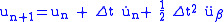
where again

Newmark showed that a reasonable value of
 is 0.5, therefore the update rules are,
is 0.5, therefore the update rules are,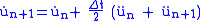
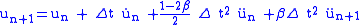
Setting β to various values between 0 and 1 can give a wide range of results. Typically β = 1/4, which yields the constant average acceleration method, is used.

