
Neutral density filter
Encyclopedia
In photography
and optics
, a neutral density filter or ND filter can be a colorless (clear) or grey filter
. An ideal neutral density filter reduces and/or modifies intensity of all wavelength
s or color
s of light equally, giving no changes in hue
of color rendition.
The purpose of standard photographic neutral density filters is to allow the photographer greater flexibility to change the aperture
, exposure time and/or motion blur
of subject in different situations and atmospheric conditions.
of the ratio of the measurable intensity (I) after the filter to the incident intensity (I0), shown as the following:
For example, on a very bright day, one might wish to photograph a waterfall at a slow shutter speed
to create a deliberate motion blur
effect. In order to do this, one would need a shutter speed on the order of tenths of a second. There might be so much light that even at minimum film speed
and a minimum aperture such as f/32, the desired shutter speed would still let in too much light and the photo would be overexposed – or, if shooting at aperture priority, the camera would select a shutter speed that would be too fast to achieve the desired effect. In this situation, applying an appropriate neutral density filter is the equivalent of stopping down one or more additional stops, allowing for the slower shutter speed and the desired motion-blur effect.
Instead of reducing the aperture to limit light, the photographer can add a ND filter to limit light, and can then set the shutter speed according to the particular motion desired (blur of water movement, for example) and the aperture set as needed (small aperture for maximum sharpness or large aperture for narrow depth of field (subject in focus and background out of focus). Using a digital camera, the photographer can see the image right away, and can choose the best ND filter to use for the scene being captured by first knowing the best aperture to use for maximum sharpness desired. The shutter speed would be selected by finding the desired blur from subject movement. The camera would be set up for these in manual mode, and then the overall exposure then adjusted darker by adjusting either aperture or shutter speed, noting the number of stops needed to bring the exposure to that which is desired. That offset would then be the amount of stop needed in the ND filter to use for that scene.
Examples of this use include:
Neutral density filters are used to control exposure with photographic catadioptric lenses, since the use of a traditional iris diaphragm
increases the ratio of the central obstruction found in those systems leading to poor performance.
ND filters find applications in several high-precision laser
experiments because the power
of a laser cannot be adjusted without changing other properties of the laser light
(e.g. collimation of the beam). Moreover, most lasers have a minimum power setting at which they can be operated. To achieve the desired light attenuation, one or more neutral density filters can be placed in the path of the beam.
Large telescopes can cause the moon and planets to become too bright and lose contrast. A neutral density filter can increase the contrast and cut down the brightness, making the moon easier to view.
is similar except the intensity varies across the surface of the filter. This is useful when one region of the image is bright and the rest is not, as in a picture of a sunset.
The transition area, or edge, is available in different variations (soft, hard, attenuator). The most common is a soft edge and provides a smooth transition from the ND side and the clear side. Hard edge grads have a sharp transition from ND to clear and the attenuator edge changes gradually over most of the filter so the transition is less noticeable.
Another type of ND filter configuration is the ND Filter-wheel. It consists of two perforated glass disks which have progressively denser coating applied around the perforation on the face of each disk. When the two disks are counter-rotated in front of each other they gradually and evenly go from 100% transmission to 0% transmission. These are used on catadioptric telescopes mentioned above and in any system that is required to work at 100% of its aperture (usually because the system is required to work at its maximum angular resolution).
Practical ND filters are not perfect, as they do not reduce the intensity of all wavelengths equally. This can sometimes create color casts in recorded images, particularly with inexpensive filters. More significantly, most ND filters are only specified over the visible
region of the spectrum, and do not proportionally block all wavelengths of ultraviolet
or infrared
radiation. This can be dangerous if using ND filters to view sources (such as the sun
or white-hot metal or glass) which emit intense non-visible radiation, since the eye may be damaged even though the source does not look bright when viewed through the filter. Special filters must be used if such sources are to be safely viewed.
Photography
Photography is the art, science and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film...
and optics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
, a neutral density filter or ND filter can be a colorless (clear) or grey filter
Photographic filter
In photography and videography, a filter is a camera accessory consisting of an optical filter that can be inserted in the optical path. The filter can be a square or oblong shape mounted in a holder accessory, or, more commonly, a glass or plastic disk with a metal or plastic ring frame, which...
. An ideal neutral density filter reduces and/or modifies intensity of all wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
s or color
Color
Color or colour is the visual perceptual property corresponding in humans to the categories called red, green, blue and others. Color derives from the spectrum of light interacting in the eye with the spectral sensitivities of the light receptors...
s of light equally, giving no changes in hue
Hue
Hue is one of the main properties of a color, defined technically , as "the degree to which a stimulus can be describedas similar to or different from stimuli that are described as red, green, blue, and yellow,"...
of color rendition.
The purpose of standard photographic neutral density filters is to allow the photographer greater flexibility to change the aperture
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture of an optical system is the opening that determines the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. The aperture determines how collimated the admitted rays are,...
, exposure time and/or motion blur
Motion blur
Motion blur is the apparent streaking of rapidly moving objects in a still image or a sequence of images such as a movie or animation. It results when the image being recorded changes during the recording of a single frame, either due to rapid movement or long exposure.- Photography :When a camera...
of subject in different situations and atmospheric conditions.
Mechanism
For a ND filter with optical density d the amount of optical power transmitted through the filter, which can be calculated from the logarithmLogarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
of the ratio of the measurable intensity (I) after the filter to the incident intensity (I0), shown as the following:
- , or
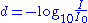
For example, on a very bright day, one might wish to photograph a waterfall at a slow shutter speed
Shutter speed
In photography, shutter speed is a common term used to discuss exposure time, the effective length of time a camera's shutter is open....
to create a deliberate motion blur
Motion blur
Motion blur is the apparent streaking of rapidly moving objects in a still image or a sequence of images such as a movie or animation. It results when the image being recorded changes during the recording of a single frame, either due to rapid movement or long exposure.- Photography :When a camera...
effect. In order to do this, one would need a shutter speed on the order of tenths of a second. There might be so much light that even at minimum film speed
Film speed
Film speed is the measure of a photographic film's sensitivity to light, determined by sensitometry and measured on various numerical scales, the most recent being the ISO system....
and a minimum aperture such as f/32, the desired shutter speed would still let in too much light and the photo would be overexposed – or, if shooting at aperture priority, the camera would select a shutter speed that would be too fast to achieve the desired effect. In this situation, applying an appropriate neutral density filter is the equivalent of stopping down one or more additional stops, allowing for the slower shutter speed and the desired motion-blur effect.
Uses
The use of an ND filter allows the photographer to utilize a larger aperture that is at or below the diffraction limit, which varies depending on the size of the sensory medium (film or digital) and for many cameras, is between f/8 and f/11, with smaller sensory medium sizes needing larger sized apertures, and larger ones able to use smaller apertures.Instead of reducing the aperture to limit light, the photographer can add a ND filter to limit light, and can then set the shutter speed according to the particular motion desired (blur of water movement, for example) and the aperture set as needed (small aperture for maximum sharpness or large aperture for narrow depth of field (subject in focus and background out of focus). Using a digital camera, the photographer can see the image right away, and can choose the best ND filter to use for the scene being captured by first knowing the best aperture to use for maximum sharpness desired. The shutter speed would be selected by finding the desired blur from subject movement. The camera would be set up for these in manual mode, and then the overall exposure then adjusted darker by adjusting either aperture or shutter speed, noting the number of stops needed to bring the exposure to that which is desired. That offset would then be the amount of stop needed in the ND filter to use for that scene.
Examples of this use include:
- Blurring water motion (e.g. waterfalls, rivers, oceans).
- Reducing depth of field in very bright light (e.g. daylight).
- When using a flash on a camera with a focal-plane shutter, exposure time is limited to the maximum speed -often 1/250th of a second, at best- at which the entire film or sensor is exposed to light at one instant. Without an ND filter this can result in the need to use f8 or higher.
- Using a wider aperture to stay below the diffraction limit.
- Reduce the visibility of moving objects
- Add motion blur to subjects
Neutral density filters are used to control exposure with photographic catadioptric lenses, since the use of a traditional iris diaphragm
Diaphragm (optics)
In optics, a diaphragm is a thin opaque structure with an opening at its center. The role of the diaphragm is to stop the passage of light, except for the light passing through the aperture...
increases the ratio of the central obstruction found in those systems leading to poor performance.
ND filters find applications in several high-precision laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
experiments because the power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
of a laser cannot be adjusted without changing other properties of the laser light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
(e.g. collimation of the beam). Moreover, most lasers have a minimum power setting at which they can be operated. To achieve the desired light attenuation, one or more neutral density filters can be placed in the path of the beam.
Large telescopes can cause the moon and planets to become too bright and lose contrast. A neutral density filter can increase the contrast and cut down the brightness, making the moon easier to view.
Varieties
A graduated ND filterGraduated neutral density filter
A graduated neutral density filter, also known as a graduated ND filter, split neutral density filter, or just a graduated filter, is an optical filter that has a variable light transmission. Typically half of the filter is of neutral density which transitions, either abruptly or gradually, into...
is similar except the intensity varies across the surface of the filter. This is useful when one region of the image is bright and the rest is not, as in a picture of a sunset.
The transition area, or edge, is available in different variations (soft, hard, attenuator). The most common is a soft edge and provides a smooth transition from the ND side and the clear side. Hard edge grads have a sharp transition from ND to clear and the attenuator edge changes gradually over most of the filter so the transition is less noticeable.
Another type of ND filter configuration is the ND Filter-wheel. It consists of two perforated glass disks which have progressively denser coating applied around the perforation on the face of each disk. When the two disks are counter-rotated in front of each other they gradually and evenly go from 100% transmission to 0% transmission. These are used on catadioptric telescopes mentioned above and in any system that is required to work at 100% of its aperture (usually because the system is required to work at its maximum angular resolution).
Practical ND filters are not perfect, as they do not reduce the intensity of all wavelengths equally. This can sometimes create color casts in recorded images, particularly with inexpensive filters. More significantly, most ND filters are only specified over the visible
Visible spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called visible light or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 390 to 750 nm. In terms of...
region of the spectrum, and do not proportionally block all wavelengths of ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
or infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
radiation. This can be dangerous if using ND filters to view sources (such as the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
or white-hot metal or glass) which emit intense non-visible radiation, since the eye may be damaged even though the source does not look bright when viewed through the filter. Special filters must be used if such sources are to be safely viewed.
ND filter types
In photography, ND filters are quantified by their optical density or equivalently their f-stop reduction. In microscopy, the 'transmittance' value is sometimes used.| lens area opening, as fraction of the complete lens | optical density | f-stop reduction | % transmittance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0 | 100% | ||
| ND2 | 1/2 | 0.3 | 1 | 50% |
| ND4 | 1/4 | 0.6 | 2 | 25% |
| ND8 | 1/8 | 0.9 | 3 | 12.5% |
| ND16 | 1/16 | 1.2 | 4 | 6.25% |
| ND32 | 1/32 | 1.5 | 5 | 3.125% |
| ND64 | 1/64 | 1.8 | 6 | 1.563% |
| ND128 | 1/128 | 2.1 | 7 | 0.781% |
| ND256 | 1/256 | 2.4 | 8 | 0.391% |
| ND512 | 1/512 | 2.7 | 9 | 0.195% |
| ND1024 | 1/1024 | 3.0 | 10 | 0.098% |
| ND2048 | 1/2048 | 3.3 | 11 | 0.049% |
| ND4096 | 1/4096 | 3.6 | 12 | 0.024% |
| ND8192 | 1/8192 | 3.9 | 13 | 0.012% |

