Neuroactive steroid
Encyclopedia
Neuroactive steroid
s (or neurosteroids) rapidly alter neuron
al excitability through interaction with neurotransmitter
-gated ion channel
s. In addition, these steroids may also exert effects on gene expression
via intracellular steroid hormone receptor
s. Neurosteroids have a wide range of potential clinical applications from sedation
to treatment of epilepsy
and traumatic brain injury
. Ganaxolone
, an analog of the endogenous neurosteroid allopregnanolone
, is under investigation for the treatment of epilepsy.
(PREG) and dehydroepiandrosterone
(DHEA), their sulfates, and reduced metabolites such as the tetrahydroderivative of progesterone 3α-hydroxy-5α-pregnane-20-one (3α,5α-THPROG).
, and sigma receptor
s. Progesterone
(PROG) is also a neurosteroid which activates progesterone receptor
s expressed in peripheral and central glial cells. The 3α-hydroxy ring A-reduced pregnane steroids allopregnanolone
and tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone
have been surmised to enhance GABA
-mediated chloride currents, whereas pregnenolone
sulfate and dehydroepiandrosterone
(DHEA) sulfate display functional antagonistic properties at GABAA receptors.
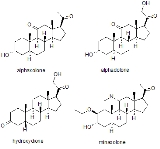
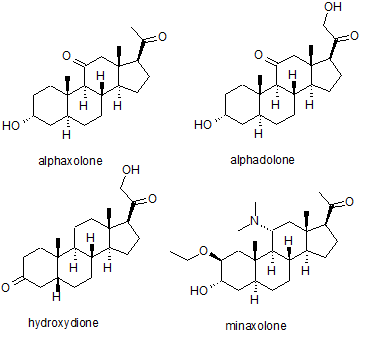
s for the purpose of general anaesthesia
for carrying out surgical procedures. The best known of these are alphaxolone, alphadolone
, hydroxydione
and minaxolone
. The first of these to be introduced was hydroxydione, which is the esterified 21-hydroxy derivative of 5β-pregnanedione. Hydroxydione proved to be a useful anaesthetic drug with a good safety profile, but was painful and irritating when injected probably due to poor water solubility. This led to the development of newer neuroactive steroids. The next drug from this family to be marketed was a mixture of alphaxolone and alphadolone, known as Althesin
. This was withdrawn from human use due to rare but serious toxic reactions, but is still used in veterinary medicine
. The next neurosteroid anaesthetic introduced into human medicine was the newer drug minaxolone, which is around three times more potent than althesin and retains the favourable safety profile, without the toxicity problems seen with althesin. However this drug was also ultimately withdrawn, not because of problems in clinical use, but because animal studies suggested potential carcinogenicity and since alternative agents were available it was felt that the possible risk outweighed the benefit of keeping the drug on the market.
The neurosteroid ganaxolone
, an analog of the progesterone metabolite allopregnanolone, has been extensively investigated in animal models and is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of epilepsy
. Neurosteroids, including ganaxolone have a broad spectrum of activity in animal models. They may have advantages over other GABAA receptor modulators, notably benzodiazepines, in that tolerance does not appear to occur with extended use.
In clinical trials, ganaxolone was effective in the treatment of partial seizures in adults and was tolerated.
drugs such as fluoxetine
and fluvoxamine
which are generally thought to act primarily as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
s have also been found to increase the levels of certain neurosteroids. Based on these studies, it has been proposed that increased levels of neurosteroids induced by fluoxetine or fluvoxamine may significantly contribute to or even be the predominant mechanism of action of these antidepressant drugs.
Steroid
A steroid is a type of organic compound that contains a characteristic arrangement of four cycloalkane rings that are joined to each other. Examples of steroids include the dietary fat cholesterol, the sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, and the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone.The core...
s (or neurosteroids) rapidly alter neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
al excitability through interaction with neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals that transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse. Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind to...
-gated ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channel
Ligand-gated ion channels are one type of ionotropic receptor or channel-linked receptor. They are a group of transmembrane ion channels that are opened or closed in response to the binding of a chemical messenger , such as a neurotransmitter.The binding site of endogenous ligands on LGICs...
s. In addition, these steroids may also exert effects on gene expression
Gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein coding genes such as ribosomal RNA , transfer RNA or small nuclear RNA genes, the product is a functional RNA...
via intracellular steroid hormone receptor
Steroid hormone receptor
Steroid hormone receptors are found on the plasma membrane, in the cytosol and also in the nucleus of target cells. They are generally intracellular receptors and initiate signal transduction for steroid hormones which lead to changes in gene expression over a time period of hours to days...
s. Neurosteroids have a wide range of potential clinical applications from sedation
Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure...
to treatment of epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
and traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic brain injury , also known as intracranial injury, occurs when an external force traumatically injures the brain. TBI can be classified based on severity, mechanism , or other features...
. Ganaxolone
Ganaxolone
Ganaxolone is a steroid drug, with the molecular formula C22H36O2, related to allopregnanolone that has sedative, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant effects. It is a potent and selective positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors. Ganaxolone protects against seizures in diverse animal models,...
, an analog of the endogenous neurosteroid allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone is a prototypic neurosteroid present in the blood and also the brain. It is a metabolite of progesterone and potent modulator of GABAA receptors...
, is under investigation for the treatment of epilepsy.
Biosynthesis
Several of these steroids accumulate in the brain after local synthesis or after metabolism of adrenal steroids or gonadal steroids, especially testosterone. Neurosteroids are synthesized in the central and peripheral nervous system, especially in myelinating glial cells, from cholesterol or steroidal precursors imported from peripheral sources. They include 3β-hydroxy-Δ5 derivatives, such as pregnenolonePregnenolone
Pregnenolone is a steroid hormone involved in the steroidogenesis of progesterone, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. As such it is a prohormone. Pregnenolone sulfate is a GABAA antagonist and increases neurogenesis in the hippocampus.-Chemistry:Like other steroids,...
(PREG) and dehydroepiandrosterone
Dehydroepiandrosterone
5-Dehydroepiandrosterone is a 19-carbon endogenous steroid hormone. It is the major secretory steroidal product of the adrenal glands and is also produced by the gonads and the brain. DHEA is the most abundant circulating steroid in humans....
(DHEA), their sulfates, and reduced metabolites such as the tetrahydroderivative of progesterone 3α-hydroxy-5α-pregnane-20-one (3α,5α-THPROG).
Mechanism
These compounds can act as allosteric modulators of neurotransmitter receptors, such as GABAA, NMDANMDA receptor
The NMDA receptor , a glutamate receptor, is the predominant molecular device for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function....
, and sigma receptor
Sigma receptor
The sigma receptors σ1 and σ2 bind to ligands such as 4-PPBP, SA 4503, ditolylguanidine, dimethyltryptamine and siramesine.- Classification :...
s. Progesterone
Progesterone
Progesterone also known as P4 is a C-21 steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy and embryogenesis of humans and other species...
(PROG) is also a neurosteroid which activates progesterone receptor
Progesterone receptor
The progesterone receptor also known as NR3C3 , is an intracellular steroid receptor that specifically binds progesterone...
s expressed in peripheral and central glial cells. The 3α-hydroxy ring A-reduced pregnane steroids allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone
Allopregnanolone is a prototypic neurosteroid present in the blood and also the brain. It is a metabolite of progesterone and potent modulator of GABAA receptors...
and tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone
Tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone
Tetrahydrodeoxycorticosterone , or more preferred allotetrahydroxycorticosterone, is an endogenous neurosteroid. It is synthesized from the adrenal hormone deoxycorticosterone by the action of two enzymes, 5α-reductase type I and 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. THDOC has sedative, anxiolytic and...
have been surmised to enhance GABA
Gabâ
Gabâ or gabaa, for the people in many parts of the Philippines), is the concept of a non-human and non-divine, imminent retribution. A sort of negative karma, it is generally seen as an evil effect on a person because of their wrongdoings or transgressions...
-mediated chloride currents, whereas pregnenolone
Pregnenolone
Pregnenolone is a steroid hormone involved in the steroidogenesis of progesterone, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. As such it is a prohormone. Pregnenolone sulfate is a GABAA antagonist and increases neurogenesis in the hippocampus.-Chemistry:Like other steroids,...
sulfate and dehydroepiandrosterone
Dehydroepiandrosterone
5-Dehydroepiandrosterone is a 19-carbon endogenous steroid hormone. It is the major secretory steroidal product of the adrenal glands and is also produced by the gonads and the brain. DHEA is the most abundant circulating steroid in humans....
(DHEA) sulfate display functional antagonistic properties at GABAA receptors.
Therapeutic application
Several synthetic neurosteroids have been used as sedativeSedative
A sedative or tranquilizer is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement....
s for the purpose of general anaesthesia
General anaesthesia
General anaesthesia is a state of unconsciousness and loss of protective reflexes resulting from the administration of one or more general anaesthetic agents...
for carrying out surgical procedures. The best known of these are alphaxolone, alphadolone
Althesin
Alfaxolone/alfadolone is a short acting intravenous anaesthetic agent, now withdrawn from the market due to severe drug reactions. It is composed of a mixture of alfaxalone and alfadolone, two neurosteroids.Cremophor EL Alfaxolone/alfadolone (Althesin) is a short acting intravenous anaesthetic...
, hydroxydione
Hydroxydione
Hydroxydione is a neuroactive steroid used as a general anesthetic....
and minaxolone
Minaxolone
Minaxolone is a general anaesthetic and neuroactive steroid....
. The first of these to be introduced was hydroxydione, which is the esterified 21-hydroxy derivative of 5β-pregnanedione. Hydroxydione proved to be a useful anaesthetic drug with a good safety profile, but was painful and irritating when injected probably due to poor water solubility. This led to the development of newer neuroactive steroids. The next drug from this family to be marketed was a mixture of alphaxolone and alphadolone, known as Althesin
Althesin
Alfaxolone/alfadolone is a short acting intravenous anaesthetic agent, now withdrawn from the market due to severe drug reactions. It is composed of a mixture of alfaxalone and alfadolone, two neurosteroids.Cremophor EL Alfaxolone/alfadolone (Althesin) is a short acting intravenous anaesthetic...
. This was withdrawn from human use due to rare but serious toxic reactions, but is still used in veterinary medicine
Veterinary medicine
Veterinary Medicine is the branch of science that deals with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of disease, disorder and injury in non-human animals...
. The next neurosteroid anaesthetic introduced into human medicine was the newer drug minaxolone, which is around three times more potent than althesin and retains the favourable safety profile, without the toxicity problems seen with althesin. However this drug was also ultimately withdrawn, not because of problems in clinical use, but because animal studies suggested potential carcinogenicity and since alternative agents were available it was felt that the possible risk outweighed the benefit of keeping the drug on the market.

The neurosteroid ganaxolone
Ganaxolone
Ganaxolone is a steroid drug, with the molecular formula C22H36O2, related to allopregnanolone that has sedative, anxiolytic, and anticonvulsant effects. It is a potent and selective positive allosteric modulator of GABAA receptors. Ganaxolone protects against seizures in diverse animal models,...
, an analog of the progesterone metabolite allopregnanolone, has been extensively investigated in animal models and is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of epilepsy
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
. Neurosteroids, including ganaxolone have a broad spectrum of activity in animal models. They may have advantages over other GABAA receptor modulators, notably benzodiazepines, in that tolerance does not appear to occur with extended use.
In clinical trials, ganaxolone was effective in the treatment of partial seizures in adults and was tolerated.
Role in antidepressant action
Certain antidepressantAntidepressant
An antidepressant is a psychiatric medication used to alleviate mood disorders, such as major depression and dysthymia and anxiety disorders such as social anxiety disorder. According to Gelder, Mayou &*Geddes people with a depressive illness will experience a therapeutic effect to their mood;...
drugs such as fluoxetine
Fluoxetine
Fluoxetine is an antidepressant of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor class. It is manufactured and marketed by Eli Lilly and Company...
and fluvoxamine
Fluvoxamine
Fluvoxamine is an antidepressant which functions as a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor . Fluvoxamine was first approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 1993 for the treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder . Fluvoxamine CR is approved to treat social anxiety disorder...
which are generally thought to act primarily as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors or serotonin-specific reuptake inhibitor are a class of compounds typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of depression, anxiety disorders, and some personality disorders. The efficacy of SSRIs is disputed...
s have also been found to increase the levels of certain neurosteroids. Based on these studies, it has been proposed that increased levels of neurosteroids induced by fluoxetine or fluvoxamine may significantly contribute to or even be the predominant mechanism of action of these antidepressant drugs.
Benzodiazepine effects on neurosteroids
Benzodiazepines may influence neurosteroid metabolism by virtue of their actions on translocator protein (TSPO; "peripheral benzodiazepine receptor"). The pharmacological actions of benzodiazepines at the GABAA receptor are similar to those of neurosteroids. Factors which affect the ability of individual benzodiazepines to alter neurosteroid levels may depend upon whether the individual benzodiazepine drug interacts with TSPO. Some benzodiazepines may also inhibit neurosteroidogenic enzymes reducing neurosteroid synthesis.Antagonists
- 17-Phenylandrostenol17-Phenylandrostenol17-Phenylandrostenol is a steroid drug which binds to GABAA receptors. It acts as an antagonist against the sedative effects of neuroactive steroids, but has little effect when administered by itself, and does not block the effects of benzodiazepines or barbiturates....
- blocks the effects of neuroactive steroids without affecting responses produced by benzodiazepines or barbiturates

