Navigation function
Encyclopedia
Navigation function usually refers to a function of position, velocity, acceleration and time which is used to plan robot trajectories through the environment. Generally, the goal of a navigation function is to create feasible, safe paths that avoid obstacles while allowing a robot to move from its starting configuration to its goal configuration.
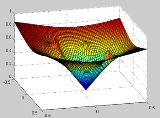
 Potential functions assume that the environment or work space is known. Obstacles are assigned a high potential value, and the goal position is assigned a low potential. To reach the goal position, a robot only needs to follow the negative gradient
Potential functions assume that the environment or work space is known. Obstacles are assigned a high potential value, and the goal position is assigned a low potential. To reach the goal position, a robot only needs to follow the negative gradient
of the surface.
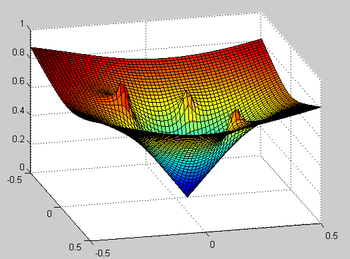
Potential functions as navigation functions

Gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar field is a vector field that points in the direction of the greatest rate of increase of the scalar field, and whose magnitude is the greatest rate of change....
of the surface.

