Naegeli-Franceschetti-Jadassohn syndrome
Encyclopedia
Naegeli–Franceschetti–Jadassohn syndrome (NFJS), also known as chromatophore nevus of Naegeli and Naegeli syndrome, is a rare autosomal
dominant form of ectodermal dysplasia
, characterized by reticular skin pigmentation, diminished function of the sweat glands, the absence of teeth and hyperkeratosis
of the palms and soles. One of the most striking features is the absence of fingerprint
lines on the fingers.
Naegeli syndrome is similar to Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis
, both of which are caused by a specific defect in the keratin 14 protein.
 NFJS is caused by mutations in the keratin 14
NFJS is caused by mutations in the keratin 14
(KRT14) gene, located on chromosome
17q12-21
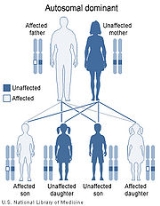
. The disorder is inerited in an autosomal dominant manner, which means that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome
(chromosome 17 is an autosome), and only one copy of the defective gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
dominant form of ectodermal dysplasia
Ectodermal dysplasia
Ectodermal dysplasia is not a single disorder, but a group of syndromes all deriving from abnormalities of the ectodermal structures. More than 150 different syndromes have been identified. Despite some of the syndromes having different genetic causes the symptoms are sometimes very similar...
, characterized by reticular skin pigmentation, diminished function of the sweat glands, the absence of teeth and hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum, often associated with a qualitative abnormality of the keratin, and also usually accompanied by an increase also in the granular layer...
of the palms and soles. One of the most striking features is the absence of fingerprint
Fingerprint
A fingerprint in its narrow sense is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. In a wider use of the term, fingerprints are the traces of an impression from the friction ridges of any part of a human hand. A print from the foot can also leave an impression of friction ridges...
lines on the fingers.
Naegeli syndrome is similar to Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis
Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis
Dermatopathia pigmentosa reticularis is a rare, autosomal dominant congenital disorder that is a form of ectodermal dysplasia...
, both of which are caused by a specific defect in the keratin 14 protein.
Cause and Genetics

Keratin 14
Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 14 also known as cytokeratin-14 or keratin-14 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KRT14 gene....
(KRT14) gene, located on chromosome
Chromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
17q12-21
Chromosome 17 (human)
125px|rightChromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 81 million base pairs and represents between 2.5 and 3 % of the total DNA in cells.Identifying genes on each chromosome is an active area of...
. The disorder is inerited in an autosomal dominant manner, which means that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
(chromosome 17 is an autosome), and only one copy of the defective gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.

