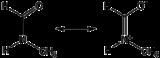
N-Methylformamide
Encyclopedia
N-Methylformamide is a colorless, nearly odorless, organic compound
with molecular formula CH3NHCHO, which is a liquid at room temperature. It is infinitely soluble in water. NMF is mainly used as a reagent in various organic syntheses with limited applications as a highly polar solvent.
NMF is closely related to other formamides, notably formamide
and dimethylformamide
(DMF). However, industrial use and production of NMF are far less than for either of these other formamides. DMF is favored over NMF as a solvent
due to its greater stability. Annual production of NMF can be assumed to be significantly less than the production of either formamide (100,000 tons) or DMF (500,000 tons).
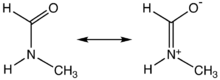
This description highlights the partial double bond
that exists between the carbonyl carbon and nitrogen, which gives rise to a high rotational barrier. Thus, the molecule is not able to freely rotate around its main axis and the E-configuration is preferred due to steric repulsion of the larger substituents.
to react with methyl formate
:
A less common alternative to this process is transamidation involving formamide
:
These reactions typically proceed in high yields.
NMF is the precursor to methyl isocyanide
, a ligand in coordination chemistry and an intermediate in the production of some pharmaceutical compounds.
Organic compound
An organic compound is any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon. For historical reasons discussed below, a few types of carbon-containing compounds such as carbides, carbonates, simple oxides of carbon, and cyanides, as well as the...
with molecular formula CH3NHCHO, which is a liquid at room temperature. It is infinitely soluble in water. NMF is mainly used as a reagent in various organic syntheses with limited applications as a highly polar solvent.
NMF is closely related to other formamides, notably formamide
Formamide
Formamide, also known as methanamide, is an amide derived from formic acid. It is a clear liquid which is miscible with water and has an ammonia-like odor. It is used primarily for manufacturing sulfa drugs and synthesizing vitamins and as a softener for paper and fiber...
and dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide
Dimethylformamide is an organic compound with the formula 2NCH. Commonly abbreviated as DMF , this colourless liquid is miscible with water and the majority of organic liquids. DMF is a common solvent for chemical reactions...
(DMF). However, industrial use and production of NMF are far less than for either of these other formamides. DMF is favored over NMF as a solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
due to its greater stability. Annual production of NMF can be assumed to be significantly less than the production of either formamide (100,000 tons) or DMF (500,000 tons).
Structure and properties
Like DMF and formamide, each of the two rotamers of NMF are described by two principal resonance structures:This description highlights the partial double bond
Double bond
A double bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two chemical elements involving four bonding electrons instead of the usual two. The most common double bond, that between two carbon atoms, can be found in alkenes. Many types of double bonds between two different elements exist, for example in...
that exists between the carbonyl carbon and nitrogen, which gives rise to a high rotational barrier. Thus, the molecule is not able to freely rotate around its main axis and the E-configuration is preferred due to steric repulsion of the larger substituents.
Preparation
NMF is typically prepared by allowing methylamineMethylamine
Methylamine is the organic compound with a formula of CH3NH2. This colourless gas is a derivative of ammonia, but with one H atom replaced by a methyl group. It is the simplest primary amine. It is sold as a solution in methanol, ethanol, THF, and water, or as the anhydrous gas in pressurized...
to react with methyl formate
Methyl formate
Methyl formate, also called methyl methanoate, is the methyl ester of formic acid. The simplest example of an ester, it is a clear liquid with an ethereal odor, high vapor pressure, and low surface tension.-Production:...
:
- CH3NH2 + HCOOCH3 → CH3NHCHO + CH3OH
A less common alternative to this process is transamidation involving formamide
Formamide
Formamide, also known as methanamide, is an amide derived from formic acid. It is a clear liquid which is miscible with water and has an ammonia-like odor. It is used primarily for manufacturing sulfa drugs and synthesizing vitamins and as a softener for paper and fiber...
:
- HCONH2 + CH3NH2 → CH3NHCHO + NH3
Uses
NMF is used in specialized amidation reactions where formamide would not be suitable. These reactions can generally be categorized by the following equation:- R-Lg + CH3NHCHO → R-NCH3CHO + H-Lg (where Lg is a leaving groupLeaving groupIn chemistry, a leaving group is a molecular fragment that departs with a pair of electrons in heterolytic bond cleavage. Leaving groups can be anions or neutral molecules. Common anionic leaving groups are halides such as Cl−, Br−, and I−, and sulfonate esters, such as para-toluenesulfonate...
)
These reactions typically proceed in high yields.
NMF is the precursor to methyl isocyanide
Methyl isocyanide
Methyl isocyanide or Isocyanomethane is an organic compound and a member of the isocyanide family. This colorless liquid is structurally similar to the isomeric methyl cyanide , but its reactivity is very different...
, a ligand in coordination chemistry and an intermediate in the production of some pharmaceutical compounds.