Muenke syndrome
Encyclopedia
Muenke Syndrome, also known as FGFR3-related craniosynostosis, is a human specific condition characterized by the premature closure of certain bone
s of the skull
during development
, which affects the shape of the head
and face
. Muenke syndrome occurs in about 1 in 30,000 newborns. This condition accounts for an estimated 8 percent of all cases of craniosynostosis
.
. Other parts of the skull
may be malformed as well. This will usually cause an abnormally shaped head, wide-set eyes, and flattened cheekbones in these patients. About 5 percent of affected individuals have an enlarged head (macrocephaly
).There may also be associated hearing loss in 10 - 30% of cases and it is important for affected individuals to have hearing tests to check on the possibility of a problem.
Most people with this condition have normal intellect, but developmental delay and learning disabilities are possible. The signs and symptoms of Muenke syndrome vary among affected people, and some findings overlap with those seen in other craniosynostosis syndromes. Between 6 percent and 7 percent of people with the gene mutation associated with Muenke syndrome do not have any of the characteristic features of the disorder.
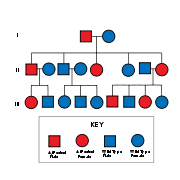 Muenke Syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. In some cases, an affected person inherits the mutation from one affected parent. Other cases may result from new mutations in the gene. These cases occur in people with no history of the disorder in their family.
Muenke Syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. In some cases, an affected person inherits the mutation from one affected parent. Other cases may result from new mutations in the gene. These cases occur in people with no history of the disorder in their family.
A single mutation in the FGFR3
gene cause this syndrome. The FGFR3
gene provides instructions for making a protein that is involved in the development and maintenance of bone and brain tissue. This mutation causes the FGFR3
protein to be overly active, which interferes with normal bone growth and allows the bones of the skull to fuse before they should.
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
s of the skull
Human skull
The human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
during development
Child development
Child development stages describe theoretical milestones of child development. Many stage models of development have been proposed, used as working concepts and in some cases asserted as nativist theories....
, which affects the shape of the head
Head
In anatomy, the head of an animal is the rostral part that usually comprises the brain, eyes, ears, nose and mouth . Some very simple animals may not have a head, but many bilaterally symmetric forms do....
and face
Face
The face is a central sense organ complex, for those animals that have one, normally on the ventral surface of the head, and can, depending on the definition in the human case, include the hair, forehead, eyebrow, eyelashes, eyes, nose, ears, cheeks, mouth, lips, philtrum, temple, teeth, skin, and...
. Muenke syndrome occurs in about 1 in 30,000 newborns. This condition accounts for an estimated 8 percent of all cases of craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in an infant skull prematurely fuses by ossification, thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull...
.
Symptoms
Many people with this disorder have a premature fusion of skull bones along the coronal sutureCoronal suture
The coronal suture is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint that separates the frontal and parietal bones of the skull. At birth, the bones of the skull do not meet.-Pathology:...
. Other parts of the skull
Human skull
The human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
may be malformed as well. This will usually cause an abnormally shaped head, wide-set eyes, and flattened cheekbones in these patients. About 5 percent of affected individuals have an enlarged head (macrocephaly
Macrocephaly
Macrocephaly , occurs when the head is abnormally large; this includes the scalp, the cranial bone, and the contents of the cranium.-Causes:...
).There may also be associated hearing loss in 10 - 30% of cases and it is important for affected individuals to have hearing tests to check on the possibility of a problem.
Most people with this condition have normal intellect, but developmental delay and learning disabilities are possible. The signs and symptoms of Muenke syndrome vary among affected people, and some findings overlap with those seen in other craniosynostosis syndromes. Between 6 percent and 7 percent of people with the gene mutation associated with Muenke syndrome do not have any of the characteristic features of the disorder.
Genetics

A single mutation in the FGFR3
FGFR3
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGFR3 gene. FGFR3 has also been designated as CD333 .-Structure and function:-Disease linkage:...
gene cause this syndrome. The FGFR3
FGFR3
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGFR3 gene. FGFR3 has also been designated as CD333 .-Structure and function:-Disease linkage:...
gene provides instructions for making a protein that is involved in the development and maintenance of bone and brain tissue. This mutation causes the FGFR3
FGFR3
Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGFR3 gene. FGFR3 has also been designated as CD333 .-Structure and function:-Disease linkage:...
protein to be overly active, which interferes with normal bone growth and allows the bones of the skull to fuse before they should.

