
Mu Boötis
Encyclopedia
Mu Boötis is a triple star system in the constellation
Boötes
. It has the traditional name Alkalurops (also Inkalunis, Clava, and Venabulum), and the Flamsteed designation
51 Boötis. Mu Boötis is approximately 121 light-years from Earth.
The name Alkalurops is from Greek καλαύροψ kalaurops "shepherd's staff", through the Arabic.
It is known as 七公六 (the Sixth Star of the Seven Excellencies) in Chinese.
The primary component, μ¹ Boötis, is a yellow-white F-type
subgiant with an apparent magnitude
of +4.31.
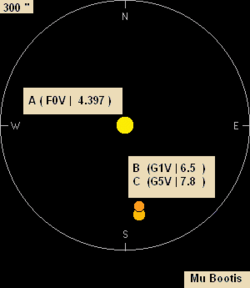 Separated from the primary by 108 arcseconds in the sky is the binary star
Separated from the primary by 108 arcseconds in the sky is the binary star
μ² Boötis, which has a combined spectral type of G1V and a combined brightness of +6.51 magnitudes
. The components of μ² Boötis have apparent magnitudes of +7.2 and +7.8 and are separated by 2.2 arcseconds. They complete one orbit about their common centre of mass every 260 years.
Constellation
In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky....
Boötes
Boötes
Boötes is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman...
. It has the traditional name Alkalurops (also Inkalunis, Clava, and Venabulum), and the Flamsteed designation
Flamsteed designation
Flamsteed designations for stars are similar to Bayer designations, except that they use numbers instead of Greek letters. Each star is assigned a number and the Latin genitive of the constellation it lies in...
51 Boötis. Mu Boötis is approximately 121 light-years from Earth.
The name Alkalurops is from Greek καλαύροψ kalaurops "shepherd's staff", through the Arabic.
It is known as 七公六 (the Sixth Star of the Seven Excellencies) in Chinese.
The primary component, μ¹ Boötis, is a yellow-white F-type
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is a classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. The spectral class of a star is a designated class of a star describing the ionization of its chromosphere, what atomic excitations are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure...
subgiant with an apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
of +4.31.
Position

Binary star
A binary star is a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass. The brighter star is called the primary and the other is its companion star, comes, or secondary...
μ² Boötis, which has a combined spectral type of G1V and a combined brightness of +6.51 magnitudes
Apparent magnitude
The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere...
. The components of μ² Boötis have apparent magnitudes of +7.2 and +7.8 and are separated by 2.2 arcseconds. They complete one orbit about their common centre of mass every 260 years.
See also
- Mu Boötis in fiction
Components
| NAME | Right ascension Right ascension Right ascension is the astronomical term for one of the two coordinates of a point on the celestial sphere when using the equatorial coordinate system. The other coordinate is the declination.-Explanation:... |
Declination Declination In astronomy, declination is one of the two coordinates of the equatorial coordinate system, the other being either right ascension or hour angle. Declination in astronomy is comparable to geographic latitude, but projected onto the celestial sphere. Declination is measured in degrees north and... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... (V) |
Spectral type | Database references |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADS 9626 B (ADS 9626 Aa) | 15h 24m 36s | Simbad | |||
| ADS 9626 C (CCDM J15245+3722BC) | 15h 24m 30.8663s | +37° 20' 50.28 | 6.5 | G1V | Simbad |

