
Monoamniotic twins
Encyclopedia
Amniotic sac
The amniotic sac is the sac in which the fetus develops in amniotes. It is a tough but thin transparent pair of membranes, which hold a developing embryo until shortly before birth. The inner membrane, the amnion, contains the amniotic fluid and the fetus. The outer membrane, the Chorion,...
within their mother’s uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
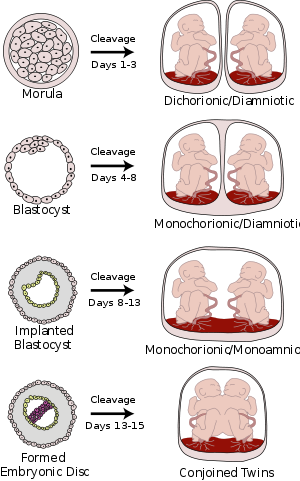
. Monoamniotic twins are always identical, and always monochorionic as well (sharing the same placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
), and are sometimes termed Monoamniotic-Monochorionic ("MoMo") twins. They also share the placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
, but have two separate umbilical cords. Monozygotic twins develop when an embryo does not split until after formation of the amniotic sac, at about 9 days after fertilization. Monoamniotic triplets or other monoamniotic multiples are possible, but extremely rare. Other obscure possibilities include multiples sets where monoamniotic twins are part of a larger gestation such as triplets, quadruplets, or more.
Occurrence
Monoamniotic twins are rare, with an occurrence of 1 in 35,000 to 1 in 60,000 pregnancies, corresponding to about 1% of twin pregnancies.Complications
The survival rate for monoamniotic twins has been shown to be as high as 81% to 95% in 2009 with aggressive fetal monitoring, although previously reported as being between 50% to 60%.. Causes of mortality and morbidity include:- Cord entanglement: The close proximity and absence of amniotic membrane separating the two umbilical cords makes it particularly easy for the twins to become entangled in each other’s cords, hindering fetal movement and development. Additionally, entanglement may cause one twin to become stuck in the birth canal during laborChildbirthChildbirth is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus...
and expulsion. Cord entanglement happens to some degree in almost every monoamniotic pregnancy. - Cord compression: One twin may compress the other’s umbilical cord, potentially stopping the flow of nutrients and blood and resulting in fetal death.
- Twin-to-twin transfusion syndromeTwin-to-twin transfusion syndromeTwin-to-twin transfusion syndrome is a complication of disproportionate blood supply, resulting in high morbidity and mortality. It can affect monochorionic multiples, that is multiple pregnancies where two or more fetuses share a chorion and hence a single placenta...
(TTTS): One twin receives the majority of the nourishment, causing the other twin to become undernourished. TTTS is much more difficult to diagnose in monoamniotic twins than diamniotic ones, since the standard method otherwise is to compare the fluid in the sacs. Rather, TTTS diagnosis in monoamniotic twins relies on comparing the physical development of the twins.
Diagnosis
Ultrasound is the only way to detect MoMo twins before birth. It can show the lack of a membrane between the twins after a couple of weeks' gestation, when the membrane would be visible if present.Further ultrasounds with high resolution doppler imaging
Doppler imaging
Inhomogeneous structures on stellar surfaces, i.e. temperature differences, chemical composition or magnetic fields, create characteristic distortions in the spectral lines due to the Doppler effect. These distortions will move across spectral line profiles due to the stellar rotation...
and non-stress tests help to assess the situation and identify potential cord problems.
There is a correlation between having a single yolk sac
Yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, providing early nourishment in the form of yolk in bony fishes, sharks, reptiles, birds, and primitive mammals...
and having a single amniotic sac. However, it is difficult to detect the number of yolk sacs, because the yolk sac disappears during embryogenesis
Embryogenesis
Embryogenesis is the process by which the embryo is formed and develops, until it develops into a fetus.Embryogenesis starts with the fertilization of the ovum by sperm. The fertilized ovum is referred to as a zygote...
.
Cord entanglement and compression generally progress slowly, allowing parents and medical caregivers to make decisions carefully.
Treatment
Only a few treatments can give any improvements.Sulindac
Sulindac
Sulindac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug of the arylalkanoic acid class that is marketed in the UK & U.S. by Merck as Clinoril.-Uses:...
has been used experimentally in some monoamniotic twins, lowering the amount of amniotic fluid and thereby inhibiting fetal movement. This is believed to lower the risk of cord entanglement and compression. However, the potential side effects of the drug have been insufficiently investigated.
Regular and aggressive fetal monitoring is recommended for cases of monoamniotic twins to look for cord entanglement beginning after viability. Many women enter inpatient care, with continuous monitoring, preferably in the care of a perinatologist, an obstetrician that specialises in high risk pregnancies.
All monoamniotic twins are delivered prematurely by cesarean section, since the risk of cord entanglement and/or cord compression becomes too great in the third trimester. The cesarean is usually performed at 32, 34 or 36 weeks. Many monoamniotic twins experience life-threatening complications as early as 26 weeks, motivating immediate delivery. However, delivery around 26 weeks is associated with life-threatening complications of preterm birth. Steroids may be administered to stimulate the babies' lung development and decrease the risk of infant respiratory distress syndrome
Infant respiratory distress syndrome
Infant respiratory distress syndrome , also called neonatal respiratory distress syndrome or respiratory distress syndrome of newborn, previously called hyaline membrane disease, is a syndrome in premature infants caused by developmental insufficiency of surfactant production and structural...
. Natural birth rather than cesarean section causes cord prolapse
Cord prolapse
Umbilical cord prolapse happens when the umbilical cord precedes the fetus' exit from the uterus. It is an obstetric emergency during pregnancy or labor that imminently endangers the life of the fetus. Cord prolapse is rare...
, with the first baby delivered pulling the placenta shared with the baby being left inside.

