Methylmalonic acidemia
Encyclopedia
Methylmalonic acidemia (MMA), also called methylmalonic aciduria, is an autosomal recessive
metabolic disorder. It is a classical type of organic acidemia
.
Methylmalonic acidemia stems from several genotype
s, all forms of the disorder usually diagnosed in the early neonatal period, presenting progressive encephalopathy
, and secondary hyperammonemia
. The disorder can result in death if undiagnosed or left untreated.

The inherited forms of methylmalonic acidemia cause defects in the metabolic pathway where methylmalonyl-coenzyme A (CoA) is converted into succinyl-CoA
by the enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
.
Vitamin B12
is also needed for the conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to Succinyl-CoA. Mutations leading to defects in vitamin B12 metabolism or in its transport frequently result in the development of methylmalonic acidemia.
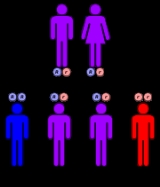
This disorder has an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - must be inherited to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers of one copy of the defective gene, but are usually not affected by the disorder.
.
Recessive
In genetics, the term "recessive gene" refers to an allele that causes a phenotype that is only seen in a homozygous genotype and never in a heterozygous genotype. Every person has two copies of every gene on autosomal chromosomes, one from mother and one from father...
metabolic disorder. It is a classical type of organic acidemia
Organic acidemia
Organic acidemia, also called organic aciduria, is a term used to classify a group of metabolic disorders which disrupt normal amino acid metabolism, particularly branched-chain amino acids, causing a buildup of acids which are usually not present....
.
Methylmalonic acidemia stems from several genotype
Genotype
The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usually with reference to a specific character under consideration...
s, all forms of the disorder usually diagnosed in the early neonatal period, presenting progressive encephalopathy
Encephalopathy
Encephalopathy means disorder or disease of the brain. In modern usage, encephalopathy does not refer to a single disease, but rather to a syndrome of global brain dysfunction; this syndrome can be caused by many different illnesses.-Terminology:...
, and secondary hyperammonemia
Hyperammonemia
Hyperammonemia is a metabolic disturbance characterised by an excess of ammonia in the blood. It is a dangerous condition that may lead to encephalopathy and death. It may be primary or secondary....
. The disorder can result in death if undiagnosed or left untreated.
Genetic

The inherited forms of methylmalonic acidemia cause defects in the metabolic pathway where methylmalonyl-coenzyme A (CoA) is converted into succinyl-CoA
Succinyl-CoA
Succinyl-Coenzyme A, abbreviated as Succinyl-CoA or SucCoA, is a combination of succinic acid and coenzyme A.-Source:It is an important intermediate in the citric acid cycle, where it is synthesized from α-Ketoglutarate by α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase through decarboxylation...
by the enzyme methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase, also known as MCM is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA and it is involved in key metabolic pathways...
.
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12, vitamin B12 or vitamin B-12, also called cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin with a key role in the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system, and for the formation of blood. It is one of the eight B vitamins...
is also needed for the conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to Succinyl-CoA. Mutations leading to defects in vitamin B12 metabolism or in its transport frequently result in the development of methylmalonic acidemia.
This disorder has an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - must be inherited to be affected by the disorder. The parents of a child with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers of one copy of the defective gene, but are usually not affected by the disorder.
Nutritional
A severe nutritional deficiency of vitamin B12 can also result in methylmalonic acidemia. Methylmalonyl CoA requires vitamin B12 to form succinyl-CoA. When the amount of B12 is insufficient for the conversion of cofactor methylmalonyl-CoA into succinyl-CoA, the buildup of unused methylmalonyl-CoA eventually leads to methylmalonic acidemia. This diagnosis is often used as an indicator of vitamin B12 deficiency in serumBlood test
A blood test is a laboratory analysis performed on a blood sample that is usually extracted from a vein in the arm using a needle, or via fingerprick....
.
Pathogenesis
Methylmalonic acidemia has varying diagnoses, treatment requirements and prognoses, which are determined by the specific genetic mutation causing the inherited form of the disorder. The following are the known genotypes responsible for methylmalonic acidemia:| OMIM | Name | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| cblA type | MMAA MMAA Methylmalonic aciduria type A protein, mitochondrial also known as MMAA is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MMAA gene.-Function:... |
|
| cblB type | MMAB MMAB Cobyrinic acid a,c-diamide adenosyltransferase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MMAB gene.-External links:* -Further reading:... |
|
| cblC type | MMACHC MMACHC Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type C protein also known as MMACHC is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MMACHC gene.- Function :... |
|
| cblD type | MMADHC MMADHC Methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria type D protein, mitochondrial also known as MMADHC is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MMADHC gene.- Function :... |
|
| cblF type | LMBRD1 LMBRD1 Probable lysosomal cobalamin transporter is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMBRD1 gene.-External links:*... |
|
| mut type | MUT Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase Methylmalonyl Coenzyme A mutase, also known as MCM is an enzyme that catalyzes the isomerization of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA and it is involved in key metabolic pathways... |
External links
- Organic Acidemia Association
- Washington Health Center
- GeneReviews article on Methylmalonic Acidemia
- GeneReviews article on Disorders of Intracellular Cobalamin Metabolism
- http://www.newbornscreening.info/Parents/organicaciddisorders/images/MMA.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.newbornscreening.info/Parents/organic

