
Meteosat
Encyclopedia
The Meteosat series of satellite
s are geostationary meteorological satellites operated by EUMETSAT under the Meteosat Transition Programme (MTP) and the Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) program.
The MTP program was established to ensure the operational continuity between the end of the successful Meteosat Operational Programme in 1995 and Meteosat Second Generation (MSG), which came into operation at the start of 2004 using improved satellites. The MTP provides an overlap with MSG by continuing the current Meteosat system until at least the end of the year 2005. The MSG program will provide service until the MTG (Meteosat Third Generation) program takes over.
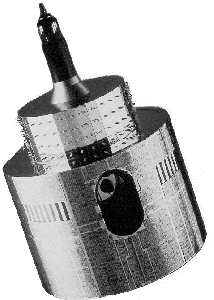 The first generation of Meteosat satellites, Meteosat-1 to Meteosat-7, provide continuous and reliable meteorological observations from space to a large user community. In addition to the provision of images of the Earth and its atmosphere every half-hour in three spectral channels (Visible, Infrared) and Water Vapour
The first generation of Meteosat satellites, Meteosat-1 to Meteosat-7, provide continuous and reliable meteorological observations from space to a large user community. In addition to the provision of images of the Earth and its atmosphere every half-hour in three spectral channels (Visible, Infrared) and Water Vapour
, via the Meteosat Visible and Infrared Imager
(MVIRI) instrument
, a range of processed meteorological products is produced. Meteosat also supports the retransmission of data from data collection platforms in remote locations, at sea and on board aircraft, as well as the dissemination of meteorological information in graphical and text formats.
The satellites were manufactured by a consortium COSMOS, with Aérospatiale
in its Cannes Mandelieu Space Center
, as Prime, and included Matra
, MBB
, Selenia Spazio
, Marconi Company
.
They are 2.1 metres in diameter and 3.195 metres long. Its initial mass in orbit is 282 kg, and in orbit, the satellite spins at 100 rpm around its main axis
in its Cannes Mandelieu Space Center
(now Thales Alenia Space
), with main subcontractors as Matra
, Messerschmitt
, Alenia.
Meteosat Second Generation was designed in response to user requirements to serve the needs of Nowcasting applications and numerical weather prediction
. In addition the GERB
instrument provides important data for climate monitoring and research.
The new satellites are spin-stabilised like the previous generation, but with many design improvements. The more frequent and comprehensive data collected by MSG also aids the weather forecaster in the swift recognition and prediction of dangerous weather phenomena such as thunderstorms, fog and explosive development of small but intense depressions which can lead to devastating wind storms.
The MSG satellites are 3.2 m in diameter and 2.4 m high and spins anti-clockwise at 100 RPM at an altitude of 36,000 km.
On January 29, 2004 the first Meteosat Second Generation satellite MSG-1, renamed to Meteosat-8
, commenced routine operations. In addition to the main optical payload SEVIRI (Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager), Meteosat-8 also carries the secondary payload GERB (Geostationary Earth Radiation Budget) instrument.
The launch of MSG-2 (renamed to Meteosat-9) took place on December 21, 2005.
 In 2011 Meteosat-7, -8 and -9 are all operational. Meteosat-7 is stationed over the Indian Ocean
In 2011 Meteosat-7, -8 and -9 are all operational. Meteosat-7 is stationed over the Indian Ocean
. Meteosat-8, and -9 are both located over Africa with various differences in operational configuration. Meteosat-7 provides the primary imagery coverage over the Indian Ocean (with images every 30-minutes) and provides a service relaying data from Data Collection Platforms (DCP), such as buoys, in support of the Tsunami Warning System for the Indian Ocean. Meteosat-8 is a backup to Meteosat-9 (and Meteosat-8 also provides an operational European 'rapid scan' mode service, which commenced in the second quarter of 2008 (with images of Europe every 5 minutes)). Meteosat-9 provides the main full earth imagery service over Europe and Africa (with images every 15-minutes).
The launch of MSG-3 is tentatively planned for 2012 and MSG-4 tentatively planned for 2014. Like MSG-1 and MSG-2, MSG-3 and MSG-4 are planned for launch by Arianespace
.
) that detects 406 MHz distress signals from distress radiobeacons. See more under Cospas-Sarsat
.
MTG preparatory activities started end of 2000 in cooperation with the European Space Agency (ESA), following the decision of the EUMETSAT Council to proceed with a Post-MSG User Consultation Process. The process is aimed at capturing the foreseeable needs of users of EUMETSAT's satellite data in the 2015-2025 timeframe.
On March 19, 2010, ESA choose Thales Alenia Space
for a final negotiation leading to a contract to be signed during June.
On June 22, 2010, Eumetsat confirm the choice of Thales Alenia Space.
Satellite
In the context of spaceflight, a satellite is an object which has been placed into orbit by human endeavour. Such objects are sometimes called artificial satellites to distinguish them from natural satellites such as the Moon....
s are geostationary meteorological satellites operated by EUMETSAT under the Meteosat Transition Programme (MTP) and the Meteosat Second Generation (MSG) program.
The MTP program was established to ensure the operational continuity between the end of the successful Meteosat Operational Programme in 1995 and Meteosat Second Generation (MSG), which came into operation at the start of 2004 using improved satellites. The MTP provides an overlap with MSG by continuing the current Meteosat system until at least the end of the year 2005. The MSG program will provide service until the MTG (Meteosat Third Generation) program takes over.
First generation

Water vapor
Water vapor or water vapour , also aqueous vapor, is the gas phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously...
, via the Meteosat Visible and Infrared Imager
Meteosat Visible and Infrared Imager
The Meteosat visible and infrared imager is the scientific instrument package on board the seven Meteosat first-generation geostationary meteorological satellites...
(MVIRI) instrument
Measuring instrument
In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Established standard objects and events are used as units, and the process of measurement gives a number relating the item...
, a range of processed meteorological products is produced. Meteosat also supports the retransmission of data from data collection platforms in remote locations, at sea and on board aircraft, as well as the dissemination of meteorological information in graphical and text formats.
The satellites were manufactured by a consortium COSMOS, with Aérospatiale
Aérospatiale
Aérospatiale was a French aerospace manufacturer that built both civilian and military aircraft, rockets and satellites. It was originally known as Société Nationale Industrielle Aérospatiale...
in its Cannes Mandelieu Space Center
Cannes Mandelieu Space Center
The Cannes Mandelieu Space Center is an industrial plant dedicated to spacecraft manufacturing, located in both the towns of Cannes and Mandelieu in France...
, as Prime, and included Matra
Matra
Mécanique Aviation Traction or Matra was a French company covering a wide range of activities mainly related to automobile, bicycles, aeronautics and weaponry. In 1994, it became a subsidiary of the Lagardère Group and now operates under that name.Matra was owned by the Floirat family...
, MBB
MBB
MBB may refer to:* Magandang Balita Biblia, a Tagalog translation of the Holy Bible* Make-before-break, a type of contact arrangement of an electrical switch, which ensures that when a switch transition happens, the new contact is always made before the old one is broken* Malayan Banking Berhad, a...
, Selenia Spazio
Alenia Aeronautica
Alenia Aeronautica, a Finmeccanica subsidiary, is a European aerospace company from Italy. Its subsidiaries include Alenia Aermacchi and Alenia Aeronavali...
, Marconi Company
Marconi Company
The Marconi Company Ltd. was founded by Guglielmo Marconi in 1897 as The Wireless Telegraph & Signal Company...
.
They are 2.1 metres in diameter and 3.195 metres long. Its initial mass in orbit is 282 kg, and in orbit, the satellite spins at 100 rpm around its main axis
Second Generation
The contract for the second generation was awarded to AérospatialeAérospatiale
Aérospatiale was a French aerospace manufacturer that built both civilian and military aircraft, rockets and satellites. It was originally known as Société Nationale Industrielle Aérospatiale...
in its Cannes Mandelieu Space Center
Cannes Mandelieu Space Center
The Cannes Mandelieu Space Center is an industrial plant dedicated to spacecraft manufacturing, located in both the towns of Cannes and Mandelieu in France...
(now Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space is an aerospace company born after the Thales Group bought the participation of Alcatel in the two joint-ventures between Alcatel and Finmeccanica, Alcatel Alenia Space and Telespazio.-History:...
), with main subcontractors as Matra
Matra
Mécanique Aviation Traction or Matra was a French company covering a wide range of activities mainly related to automobile, bicycles, aeronautics and weaponry. In 1994, it became a subsidiary of the Lagardère Group and now operates under that name.Matra was owned by the Floirat family...
, Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt
Messerschmitt AG was a famous German aircraft manufacturing corporation named for its chief designer, Willy Messerschmitt, and known primarily for its World War II fighter aircraft, notably the Bf 109 and Me 262...
, Alenia.
Meteosat Second Generation was designed in response to user requirements to serve the needs of Nowcasting applications and numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction
Numerical weather prediction uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic...
. In addition the GERB
Geostationary Earth Radiation Budget
The Geostationary Earth Radiation Budget is an instrument aboard EUMETSAT's Meteosat Second Generation geostationary satellites designed to make accurate measurements of the Earth Radiation Budget....
instrument provides important data for climate monitoring and research.
The new satellites are spin-stabilised like the previous generation, but with many design improvements. The more frequent and comprehensive data collected by MSG also aids the weather forecaster in the swift recognition and prediction of dangerous weather phenomena such as thunderstorms, fog and explosive development of small but intense depressions which can lead to devastating wind storms.
The MSG satellites are 3.2 m in diameter and 2.4 m high and spins anti-clockwise at 100 RPM at an altitude of 36,000 km.
On January 29, 2004 the first Meteosat Second Generation satellite MSG-1, renamed to Meteosat-8
Meteosat 8
Meteosat 8 is a weather satellite, also known as MSG 1. The Meteosat series are operated by EUMETSAT under the Meteosat Transition Programme and the Meteosat Second Generation program. Notable for imaging the first meteor to be predicted to strike the earth, 2008 TC3...
, commenced routine operations. In addition to the main optical payload SEVIRI (Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager), Meteosat-8 also carries the secondary payload GERB (Geostationary Earth Radiation Budget) instrument.
The launch of MSG-2 (renamed to Meteosat-9) took place on December 21, 2005.

Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
. Meteosat-8, and -9 are both located over Africa with various differences in operational configuration. Meteosat-7 provides the primary imagery coverage over the Indian Ocean (with images every 30-minutes) and provides a service relaying data from Data Collection Platforms (DCP), such as buoys, in support of the Tsunami Warning System for the Indian Ocean. Meteosat-8 is a backup to Meteosat-9 (and Meteosat-8 also provides an operational European 'rapid scan' mode service, which commenced in the second quarter of 2008 (with images of Europe every 5 minutes)). Meteosat-9 provides the main full earth imagery service over Europe and Africa (with images every 15-minutes).
The launch of MSG-3 is tentatively planned for 2012 and MSG-4 tentatively planned for 2014. Like MSG-1 and MSG-2, MSG-3 and MSG-4 are planned for launch by Arianespace
Arianespace
Arianespace SA is a French company founded in 1980 as the world's first commercial space transportation company. It undertakes the production, operation, and marketing of the Ariane 5 rocket launcher as part of the Ariane programme....
.
Secondary Payloads
Both MSG-1 and MSG-2 carry a DCP service and a Search and Rescue signal Processor (SARPSARP
Standards And Recommended Practices are technical specifications adopted by the Council of ICAO in accordance with Article 37 of the Convention on International Civil Aviation in order to achieve "the highest practicable degree of uniformity in regulations, standards, procedures and organization...
) that detects 406 MHz distress signals from distress radiobeacons. See more under Cospas-Sarsat
Cospas-Sarsat
Cospas-Sarsat is an international satellite-based search and rescue distress alert detection and information distribution system, established by Canada, France, the United States, and the former Soviet Union in 1979. It is best known as the system that detects and locates emergency beacons...
.
Third Generation
Considering the long development cycle for a new observational space system, EUMETSAT has been working on the definition and the planning for a Meteosat Third Generation (MTG) system since the year 2000. MTG components providing continuity of MSG services need to be available around 2015, before the end of the nominal lifetime of MSG.MTG preparatory activities started end of 2000 in cooperation with the European Space Agency (ESA), following the decision of the EUMETSAT Council to proceed with a Post-MSG User Consultation Process. The process is aimed at capturing the foreseeable needs of users of EUMETSAT's satellite data in the 2015-2025 timeframe.
On March 19, 2010, ESA choose Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space
Thales Alenia Space is an aerospace company born after the Thales Group bought the participation of Alcatel in the two joint-ventures between Alcatel and Finmeccanica, Alcatel Alenia Space and Telespazio.-History:...
for a final negotiation leading to a contract to be signed during June.
On June 22, 2010, Eumetsat confirm the choice of Thales Alenia Space.
External links
- Compare Meteosat images with other meteorological satellites
- Meteosat weather satellite viewer Online Meteosat-7 and Meteosat-9 weather satellite viewer with 2 months of archived data.

