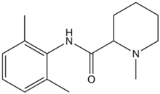
Mepivacaine
Encyclopedia
Mepivacaine is a local anesthetic
of the amide type. Mepivacaine has a reasonably rapid onset (more rapid than that of procaine
) and medium duration of action (shorter than that of procaine) and is marketed under various trade name
s including Carbocaine and Polocaine.
Mepivacaine became available in the United States
in the 1960s.
Mepivacaine is used in any infiltration and regional anesthesia.
It is supplied as the hydrochloride salt of the racemate.
According to the second method, reacting 2,6-dimethylaniline with the acid chloride of pyridine-
carboxylic acid first gives the 2,6-xylidide of α-picolinic acid
. Then the aromatic
pyridine ring is reduced to piperidine by hydrogen in the presence of a platinum on
carbon catalyst. The resulting 2,6-xylidide α-pipecolic acid
is methylated to mepivacaine using formaldehyde with simultaneous reduction by hydrogen in the presence of platinum on
carbon catalyst.
Local anesthetic
A local anesthetic is a drug that causes reversible local anesthesia, generally for the aim of having local analgesic effect, that is, inducing absence of pain sensation, although other local senses are often affected as well...
of the amide type. Mepivacaine has a reasonably rapid onset (more rapid than that of procaine
Procaine
Procaine is a local anesthetic drug of the amino ester group. It is used primarily to reduce the pain of intramuscular injection of penicillin, and it was also used in dentistry. Owing to the ubiquity of the trade name Novocain, in some regions procaine is referred to generically as novocaine...
) and medium duration of action (shorter than that of procaine) and is marketed under various trade name
Trade name
A trade name, also known as a trading name or a business name, is the name which a business trades under for commercial purposes, although its registered, legal name, used for contracts and other formal situations, may be another....
s including Carbocaine and Polocaine.
Mepivacaine became available in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
in the 1960s.
Mepivacaine is used in any infiltration and regional anesthesia.
It is supplied as the hydrochloride salt of the racemate.
Chemistry
Two primary methods of synthesis have been suggested. According to the first, mepivacaine is synthesized by reacting the ethyl ester of 1-methylpiperindine-2-carboxylic acid with 2,6-dimethylanilinomagnesium bromide, which is synthesized from 2,6-dimethylaniline and ethylmagnesium bromide.- E. Thuresson, H. Egner, (1957).
- B.T. Ekenstam, B. von Egner, G. Petterson, Acta Chem. Scand., 11, 1183 (1957).
According to the second method, reacting 2,6-dimethylaniline with the acid chloride of pyridine-
carboxylic acid first gives the 2,6-xylidide of α-picolinic acid
Picolinic acid
Picolinic acid is a pyridine compound with a carboxyl side chain at the 2-position. It is an isomer of nicotinic acid, which has the carboxyl side chain at the 3-position. It is a catabolite of the amino acid tryptophan.- Chelating properties :...
. Then the aromatic
pyridine ring is reduced to piperidine by hydrogen in the presence of a platinum on
carbon catalyst. The resulting 2,6-xylidide α-pipecolic acid
Pipecolic acid
Pipecolic acid is a small organic molecule which accumulates in pipecolic acidemia. It is the carboxylic acid of piperidine.It can be associated with some forms of epilepsy....
is methylated to mepivacaine using formaldehyde with simultaneous reduction by hydrogen in the presence of platinum on
carbon catalyst.
- B.G. Petterson, (1977).

