Mental Practice of Action
Encyclopedia
Mental practice, or motor imagery
, refers to use of visuo-motor imagery, or mental imagery with the purpose of improving motor behavior. Visuo-motor imagery requires the use of one’s imagination
to simulate an action. It has come to the fore due to the relevance of imagery in enhancing sports performance. Although imagery has been described as a pillar of sport psychology
practice, its foundations lie in research from other academic domains, including cognitive science
, neurophysiology
and even clinical neuropsychology
.
 The basis for the use of mental practice comes from an array of empirical research that includes chronometric explorations of actual and imagined actions. The mental chronometric paradigm documented striking similarities between the duration times of actual and imagined movements. Such similarities are considered to reflect the motor processes involved in action preparation and programming. Research also demonstrates that there are cases when imagined movement durations are dissimilar when the task is particularly novel such as spring board dives.
The basis for the use of mental practice comes from an array of empirical research that includes chronometric explorations of actual and imagined actions. The mental chronometric paradigm documented striking similarities between the duration times of actual and imagined movements. Such similarities are considered to reflect the motor processes involved in action preparation and programming. Research also demonstrates that there are cases when imagined movement durations are dissimilar when the task is particularly novel such as spring board dives.
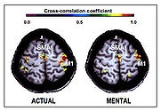
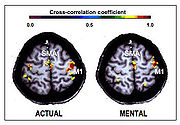
There is also an impressive number of studies using functional neuroimaging
techniques, such as positron emission tomography
and functional magnetic resonance imaging
, that demonstrate that cortical and subcortical regions involved in motor control are activated when an individual mentally simulates an action.
, and balance in elderly women (Fansler, Poff, & Shepard, 1985). For instance, mental practice has been used with success in combination with actual practice to rehabilitate motor deficits in a patient with sub-acute stroke. Several studies have also shown improvement in strength, function, and use of both upper and lower extremities in chronic stroke. For a complete listing of the current literature on mental practice, see http://www.rehabafterstroke.com/health-professionals/evidence/
, which is concerned with understanding the computational mechanisms and their neural underpinnings associated with action and its functional role in social cognition
, includes imagery within its remit and offers the potential for research at the interface of these two domains. One approach that has emerged is the use of elite participants in the sport context as experts in human movement. This is essentially a paradigmatic shift away from the traditional neuroscience model of studying those with neurological deficits, and augmenting it by studying experts (e.g., athletes). It has been suggested that this paradigm offers great potential for understanding imagery and action. While the field of motor cognition is embryonic, the parallel field of social cognition
has a more developed empirical and theoretical base.
Motor imagery
Motor imagery is a mental process by which an individual rehearses or simulates a given action. It is widely used in sport training , neurological rehabilitation, and has also been employed as a research paradigm in cognitive neuroscience and cognitive psychology to investigate the content and the...
, refers to use of visuo-motor imagery, or mental imagery with the purpose of improving motor behavior. Visuo-motor imagery requires the use of one’s imagination
Imagination
Imagination, also called the faculty of imagining, is the ability of forming mental images, sensations and concepts, in a moment when they are not perceived through sight, hearing or other senses...
to simulate an action. It has come to the fore due to the relevance of imagery in enhancing sports performance. Although imagery has been described as a pillar of sport psychology
Sport psychology
Sport psychology is an interdisciplinary science that draws on knowledge from the fields of kinesiology and psychology. It involves the study of how psychological factors affect performance and how participation in sport and exercise affect psychological and physical factors...
practice, its foundations lie in research from other academic domains, including cognitive science
Cognitive science
Cognitive science is the interdisciplinary scientific study of mind and its processes. It examines what cognition is, what it does and how it works. It includes research on how information is processed , represented, and transformed in behaviour, nervous system or machine...
, neurophysiology
Neurophysiology
Neurophysiology is a part of physiology. Neurophysiology is the study of nervous system function...
and even clinical neuropsychology
Neuropsychology
Neuropsychology studies the structure and function of the brain related to specific psychological processes and behaviors. The term neuropsychology has been applied to lesion studies in humans and animals. It has also been applied to efforts to record electrical activity from individual cells in...
.
Neurological mechanisms

There is also an impressive number of studies using functional neuroimaging
Functional neuroimaging
Functional neuroimaging is the use of neuroimaging technology to measure an aspect of brain function, often with a view to understanding the relationship between activity in certain brain areas and specific mental functions...
techniques, such as positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography is nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide , which is introduced into the body on a...
and functional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging
Functional magnetic resonance imaging or functional MRI is a type of specialized MRI scan used to measure the hemodynamic response related to neural activity in the brain or spinal cord of humans or other animals. It is one of the most recently developed forms of neuroimaging...
, that demonstrate that cortical and subcortical regions involved in motor control are activated when an individual mentally simulates an action.
Use of mental practice in rehabilitation
Mental practice has been used to rehabilitate motor deficits in a variety of neurological disorders. Mental practice of action seems to improve balance in individuals with multiple sclerosisMultiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms...
, and balance in elderly women (Fansler, Poff, & Shepard, 1985). For instance, mental practice has been used with success in combination with actual practice to rehabilitate motor deficits in a patient with sub-acute stroke. Several studies have also shown improvement in strength, function, and use of both upper and lower extremities in chronic stroke. For a complete listing of the current literature on mental practice, see http://www.rehabafterstroke.com/health-professionals/evidence/
Future directions
While the literature has evolved within sport psychology and cognitive neuroscience on mental imagery, cross-fertilization of research is still rare. However, a new emerging field called motor cognitionMotor cognition
The concept of motor cognition grasps the notion that cognition is embodied in action, and that the motor system participates in what is usually considered as mental processing, including those involved in social interaction...
, which is concerned with understanding the computational mechanisms and their neural underpinnings associated with action and its functional role in social cognition
Social cognition
Social cognition is the encoding, storage, retrieval, and processing, in the brain, of information relating to conspecifics, or members of the same species. At one time social cognition referred specifically to an approach to social psychology in which these processes were studied according to the...
, includes imagery within its remit and offers the potential for research at the interface of these two domains. One approach that has emerged is the use of elite participants in the sport context as experts in human movement. This is essentially a paradigmatic shift away from the traditional neuroscience model of studying those with neurological deficits, and augmenting it by studying experts (e.g., athletes). It has been suggested that this paradigm offers great potential for understanding imagery and action. While the field of motor cognition is embryonic, the parallel field of social cognition
Social cognition
Social cognition is the encoding, storage, retrieval, and processing, in the brain, of information relating to conspecifics, or members of the same species. At one time social cognition referred specifically to an approach to social psychology in which these processes were studied according to the...
has a more developed empirical and theoretical base.
See also
- Cognitive neuropsychologyCognitive neuropsychologyCognitive neuropsychology is a branch of cognitive psychology that aims to understand how the structure and function of the brain relates to specific psychological processes. It places a particular emphasis on studying the cognitive effects of brain injury or neurological illness with a view to...
- Common coding theoryCommon coding theoryCommon coding theory is a cognitive psychology theory describing how perceptual representations and motor representations are linked. The theory claims that there is a shared representation for both perception and action...
- Sense of agencySense of agencyThe "sense of agency" refers to the subjective awareness that one is initiating, executing, and controlling one's own volitional actions in the world. It is the pre-reflective awareness or implicit sense that it is me who is presently executing bodily movement or thinking thoughts...
- Social cognitionSocial cognitionSocial cognition is the encoding, storage, retrieval, and processing, in the brain, of information relating to conspecifics, or members of the same species. At one time social cognition referred specifically to an approach to social psychology in which these processes were studied according to the...
- Motor cognitionMotor cognitionThe concept of motor cognition grasps the notion that cognition is embodied in action, and that the motor system participates in what is usually considered as mental processing, including those involved in social interaction...
- Motor imageryMotor imageryMotor imagery is a mental process by which an individual rehearses or simulates a given action. It is widely used in sport training , neurological rehabilitation, and has also been employed as a research paradigm in cognitive neuroscience and cognitive psychology to investigate the content and the...
- Motor cortexMotor cortexMotor cortex is a term that describes regions of the cerebral cortex involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary motor functions.-Anatomy of the motor cortex :The motor cortex can be divided into four main parts:...
- Social neuroscienceSocial neuroscienceSocial neuroscience is an interdisciplinary field devoted to understanding how biological systems implement social processes and behavior, and to using biological concepts and methods to inform and refine theories of social processes and behavior. Humans are fundamentally a social species, rather...
Selected works
- Caeyenberghs, K., van Roon, D., Swinnen, S.P., & Smits-Engelsman, B.C. (2008). Deficits in executed and imagined aiming performance in brain-injured children. Brain and Cognition, Epub ahead of time.
- Holmes, P., & Calmels, C. (2008). A neuroscientific review of imagery and observation use in sport. Journal of Motor Behavior, 40, 433-445.
- Malouin, F., Richards, C.L., Jackson, P.L., Dumas, F., Doyon, J. (2003). Brain activations during motor imagery of locomotor-related tasks: a PET study. Human Brain Mapping, 19, 47-62.
- Thobois, S., Dominey, P.F., Decety, J., Pollak, P.P., Gregoire, M.C., Le Bars, P.D., & Broussolle, E. (2000). Motor imagery in normal subjects and in asymmetrical Parkinson's disease: a PET study. Neurology, 55, 996-1002.
- Verbunt, J.A., Seelen, H.A., Ramos, F.P., Michielsen, B.H,, Wetzelaer, W.L., & Moennekens, M. (2008). Mental practice-based rehabilitation training to improve arm function and daily activity performance in stroke patients: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Neurology, April 11, 8:7.

