
Mean arterial pressure
Encyclopedia
The mean arterial pressure (MAP) is a term used in medicine to describe an average blood pressure
in an individual. It is defined as the average arterial pressure during a single cardiac cycle
.
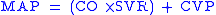
where:
 can be approximated using the more easily measured systolic
can be approximated using the more easily measured systolic
and diastolic pressures, and
and  :
:
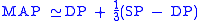
or equivalently
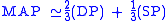
or equivalently
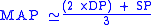
or equivalently

where is the pulse pressure
is the pulse pressure
,
At high heart rates is more closely approximated by the arithmetic mean
is more closely approximated by the arithmetic mean
of systolic and diastolic pressures because of the change in shape of the arterial pressure pulse.
 is considered to be the perfusion pressure seen by organs
is considered to be the perfusion pressure seen by organs
in the body.
It is believed that a that is greater than 60 mmHg is enough to sustain the organs of the average person.
that is greater than 60 mmHg is enough to sustain the organs of the average person.  is normally between 70 to 110 mmHg
is normally between 70 to 110 mmHg
If the falls significantly below this number for an appreciable time, the end organ will not get enough blood flow, and will become ischemic
falls significantly below this number for an appreciable time, the end organ will not get enough blood flow, and will become ischemic
.
Blood pressure
Blood pressure is the pressure exerted by circulating blood upon the walls of blood vessels, and is one of the principal vital signs. When used without further specification, "blood pressure" usually refers to the arterial pressure of the systemic circulation. During each heartbeat, BP varies...
in an individual. It is defined as the average arterial pressure during a single cardiac cycle
Cardiac cycle
The cardiac cycle is a term referring to all or any of the events related to the flow or blood pressure that occurs from the beginning of one heartbeat to the beginning of the next. The frequency of the cardiac cycle is described by the heart rate. Each beat of the heart involves five major stages...
.
Calculation
Mean arterial pressure can be determined from: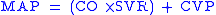
where:
 is cardiac outputCardiac outputCardiac output is the volume of blood being pumped by the heart, in particular by a left or right ventricle in the time interval of one minute. CO may be measured in many ways, for example dm3/min...
is cardiac outputCardiac outputCardiac output is the volume of blood being pumped by the heart, in particular by a left or right ventricle in the time interval of one minute. CO may be measured in many ways, for example dm3/min... is systemic vascular resistance
is systemic vascular resistance is central venous pressureCentral venous pressureCentral venous pressure describes the pressure of blood in the thoracic vena cava, near the right atrium of the heart...
is central venous pressureCentral venous pressureCentral venous pressure describes the pressure of blood in the thoracic vena cava, near the right atrium of the heart...
and usually small enough to be neglected in this formula.
Estimation
At normal resting heart rates can be approximated using the more easily measured systolic
can be approximated using the more easily measured systolicSystole (medicine)
Systole is the contraction of the heart. Used alone, it usually means the contraction of the left ventricle.In all mammals, the heart has 4 chambers. The left and right ventricles pump together. The atria and ventricles pump in sequence...
and diastolic pressures,
 and
and  :
: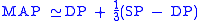
or equivalently
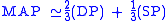
or equivalently
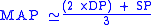
or equivalently

where
 is the pulse pressure
is the pulse pressurePulse pressure
Pulse Pressure is most easily defined as being the amount of pressure required to create the feeling of a pulse. Measured in millimeters of mercury , the pressure difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures give you the amount of pressure change to create the pulse, which is the pulse...
,

At high heart rates
 is more closely approximated by the arithmetic mean
is more closely approximated by the arithmetic meanArithmetic mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, often referred to as simply the mean or average when the context is clear, is a method to derive the central tendency of a sample space...
of systolic and diastolic pressures because of the change in shape of the arterial pressure pulse.
Clinical significance
 is considered to be the perfusion pressure seen by organs
is considered to be the perfusion pressure seen by organsOrgan (anatomy)
In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in structural unit to serve a common function. Usually there is a main tissue and sporadic tissues . The main tissue is the one that is unique for the specific organ. For example, main tissue in the heart is the myocardium, while sporadic are...
in the body.
It is believed that a
 that is greater than 60 mmHg is enough to sustain the organs of the average person.
that is greater than 60 mmHg is enough to sustain the organs of the average person.  is normally between 70 to 110 mmHg
is normally between 70 to 110 mmHgIf the
 falls significantly below this number for an appreciable time, the end organ will not get enough blood flow, and will become ischemic
falls significantly below this number for an appreciable time, the end organ will not get enough blood flow, and will become ischemicIschemia
In medicine, ischemia is a restriction in blood supply, generally due to factors in the blood vessels, with resultant damage or dysfunction of tissue. It may also be spelled ischaemia or ischæmia...
.

