
Markov switching multifractal
Encyclopedia
In financial econometrics
, the Markov-switching multifractal (MSM) is a model of asset returns that incorporates stochastic volatility
components of heterogeneous durations
. MSM captures the outliers, log-memory-like volatility
persistence and power variation of financial returns. In currency and equity series, MSM compares favorably with standard volatility models
such as GARCH(1,1) and FIGARCH both in- and out-of-sample. MSM is used by practitioners in the financial industry to forecast volatility
, compute value-at-risk
, and price derivatives
.
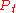 denote the price of a financial asset, and let
denote the price of a financial asset, and let 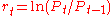 denote the return over two consecutive periods. In MSM, returns are specified as
denote the return over two consecutive periods. In MSM, returns are specified as
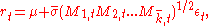
where and
and  are constants and {
are constants and {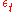 } are independent standard Gaussians. Volatility is driven by the first-order latent Markov state vector:
} are independent standard Gaussians. Volatility is driven by the first-order latent Markov state vector:
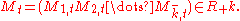
Given the volatility state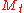 , the next-period multiplier
, the next-period multiplier 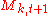 is drawn from a fixed distribution
is drawn from a fixed distribution  with probability
with probability 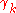 , and is otherwise left unchanged.
, and is otherwise left unchanged.
The transition probabilities are specified by
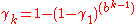 .
.
The sequence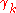 is approximately geometric
is approximately geometric 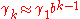 at low frequency. The marginal distribution
at low frequency. The marginal distribution  has a unit mean, has a positive support, and is independent of
has a unit mean, has a positive support, and is independent of 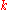 .
.
 is often a discrete distribution that can take the values
is often a discrete distribution that can take the values 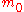 or
or 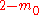 with equal probability. The return process
with equal probability. The return process 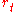 is then specified by the parameters
is then specified by the parameters 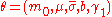 . Note that the number of parameters is the same for all
. Note that the number of parameters is the same for all 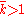 .
.

where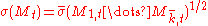 ,
,  is a standard Brownian motion, and
is a standard Brownian motion, and 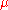 and
and 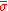 are constants. Each component follows the dynamics:
are constants. Each component follows the dynamics:
The intensities vary geometrically with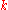 :
:
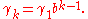
When the number of components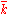 goes to infinity, continuous-time MSM converges to a multifractal diffusion, whose sample paths take a continuum of local Hölder exponents on any finite time interval.
goes to infinity, continuous-time MSM converges to a multifractal diffusion, whose sample paths take a continuum of local Hölder exponents on any finite time interval.
 has a discrete distribution, the Markov state vector
has a discrete distribution, the Markov state vector 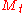 takes finitely many values
takes finitely many values 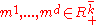 . For instance, there are
. For instance, there are 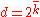 possible states in binomial MSM. The Markov dynamics are characterized by the transition matrix
possible states in binomial MSM. The Markov dynamics are characterized by the transition matrix 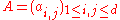 with components
with components 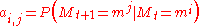 .
.
Conditional on the volatility state, the return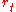 has Gaussian density
has Gaussian density
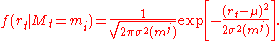
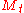 . Given past returns, we can define the conditional probabilities:
. Given past returns, we can define the conditional probabilities:
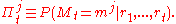
The vector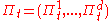 is computed recursively:
is computed recursively:
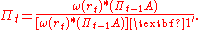
where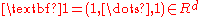 ,
, 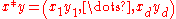 for any
for any 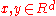 , and
, and
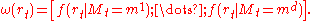
The initial vector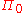 is set equal to the ergodic distribution of
is set equal to the ergodic distribution of 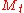 . For binomial MSM,
. For binomial MSM, 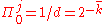 for all
for all 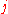 .
.
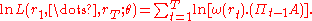
Maximum likelihood provides reasonably precise estimates in finite samples.
 has a continuous distribution, estimation can proceed by simulated method of moments, or simulated likelihood via a particle filter.
has a continuous distribution, estimation can proceed by simulated method of moments, or simulated likelihood via a particle filter.
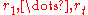 , the conditional distribution of the latent state vector at date
, the conditional distribution of the latent state vector at date 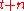 is given by:
is given by:
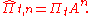
MSM often provides better volatility forecasts than some of the best traditional models both in and out of sample. Calvet and Fisher report considerable gains in exchange rate volatility forecasts at horizons of 10 to 50 days as compared with GARCH(1,1), Markov-Switching GARCH, and Fractionally Integrated GARCH. Lux obtains similar results using linear predictions.
.
MSM is closely related to the Multifractal Model of Asset Returns. MSM improves on the MMAR’s combinatorial construction by randomizing arrival times, guaranteeing a strictly stationary process.
MSM provides a pure regime-switching formulation of multifractal measures, which were pioneered by Benoit Mandelbrot
.
Econometrics
Econometrics has been defined as "the application of mathematics and statistical methods to economic data" and described as the branch of economics "that aims to give empirical content to economic relations." More precisely, it is "the quantitative analysis of actual economic phenomena based on...
, the Markov-switching multifractal (MSM) is a model of asset returns that incorporates stochastic volatility
Stochastic volatility
Stochastic volatility models are used in the field of mathematical finance to evaluate derivative securities, such as options. The name derives from the models' treatment of the underlying security's volatility as a random process, governed by state variables such as the price level of the...
components of heterogeneous durations
Homogeneity (statistics)
In statistics, homogeneity and its opposite, heterogeneity, arise in describing the properties of a dataset, or several datasets. They relate to the validity of the often convenient assumption that the statistical properties of any one part of an overall dataset are the same as any other part...
. MSM captures the outliers, log-memory-like volatility
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
persistence and power variation of financial returns. In currency and equity series, MSM compares favorably with standard volatility models
Stochastic volatility
Stochastic volatility models are used in the field of mathematical finance to evaluate derivative securities, such as options. The name derives from the models' treatment of the underlying security's volatility as a random process, governed by state variables such as the price level of the...
such as GARCH(1,1) and FIGARCH both in- and out-of-sample. MSM is used by practitioners in the financial industry to forecast volatility
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
, compute value-at-risk
Var
Var, VAR, VAr, VaR or var can mean:VAR* Varna Airport IATA airport code* Vacuum arc remelting, a process for production of steel and special alloys...
, and price derivatives
Derivative (finance)
A derivative instrument is a contract between two parties that specifies conditions—in particular, dates and the resulting values of the underlying variables—under which payments, or payoffs, are to be made between the parties.Under U.S...
.
Discrete time
Let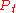 denote the price of a financial asset, and let
denote the price of a financial asset, and let 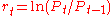 denote the return over two consecutive periods. In MSM, returns are specified as
denote the return over two consecutive periods. In MSM, returns are specified as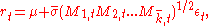
where
 and
and  are constants and {
are constants and {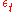 } are independent standard Gaussians. Volatility is driven by the first-order latent Markov state vector:
} are independent standard Gaussians. Volatility is driven by the first-order latent Markov state vector: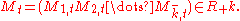
Given the volatility state
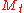 , the next-period multiplier
, the next-period multiplier 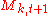 is drawn from a fixed distribution
is drawn from a fixed distribution  with probability
with probability 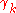 , and is otherwise left unchanged.
, and is otherwise left unchanged.  drawn from distribution drawn from distribution  |
with probability 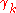 |
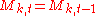 |
with probability 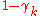 |
The transition probabilities are specified by
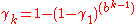 .
.The sequence
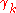 is approximately geometric
is approximately geometric 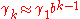 at low frequency. The marginal distribution
at low frequency. The marginal distribution  has a unit mean, has a positive support, and is independent of
has a unit mean, has a positive support, and is independent of 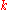 .
.Binomial MSM
In empirical applications, the distribution is often a discrete distribution that can take the values
is often a discrete distribution that can take the values 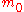 or
or 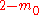 with equal probability. The return process
with equal probability. The return process 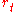 is then specified by the parameters
is then specified by the parameters 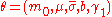 . Note that the number of parameters is the same for all
. Note that the number of parameters is the same for all  .
.Continuous time
MSM is similarly defined in continuous time. The price process follows the diffusion:
where
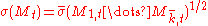 ,
,  is a standard Brownian motion, and
is a standard Brownian motion, and  and
and  are constants. Each component follows the dynamics:
are constants. Each component follows the dynamics: 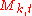 drawn from distribution drawn from distribution  |
with probability 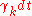 |
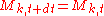 |
with probability 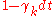 |
The intensities vary geometrically with
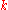 :
: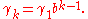
When the number of components
 goes to infinity, continuous-time MSM converges to a multifractal diffusion, whose sample paths take a continuum of local Hölder exponents on any finite time interval.
goes to infinity, continuous-time MSM converges to a multifractal diffusion, whose sample paths take a continuum of local Hölder exponents on any finite time interval.Inference and closed-form likelihood
When has a discrete distribution, the Markov state vector
has a discrete distribution, the Markov state vector 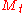 takes finitely many values
takes finitely many values 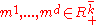 . For instance, there are
. For instance, there are 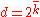 possible states in binomial MSM. The Markov dynamics are characterized by the transition matrix
possible states in binomial MSM. The Markov dynamics are characterized by the transition matrix 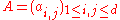 with components
with components 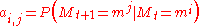 .
.Conditional on the volatility state, the return
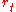 has Gaussian density
has Gaussian density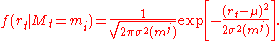
Conditional distribution
We do not directly observe the latent state vector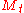 . Given past returns, we can define the conditional probabilities:
. Given past returns, we can define the conditional probabilities: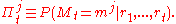
The vector
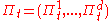 is computed recursively:
is computed recursively: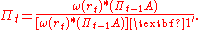
where
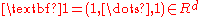 ,
, 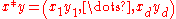 for any
for any 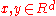 , and
, and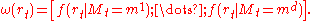
The initial vector
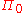 is set equal to the ergodic distribution of
is set equal to the ergodic distribution of 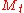 . For binomial MSM,
. For binomial MSM, 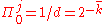 for all
for all 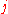 .
.Closed-form Likelihood
The log likelihood function has the following analytical expression: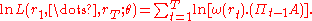
Maximum likelihood provides reasonably precise estimates in finite samples.
Other estimation methods
When has a continuous distribution, estimation can proceed by simulated method of moments, or simulated likelihood via a particle filter.
has a continuous distribution, estimation can proceed by simulated method of moments, or simulated likelihood via a particle filter.Forecasting
Given , the conditional distribution of the latent state vector at date
, the conditional distribution of the latent state vector at date  is given by:
is given by: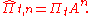
MSM often provides better volatility forecasts than some of the best traditional models both in and out of sample. Calvet and Fisher report considerable gains in exchange rate volatility forecasts at horizons of 10 to 50 days as compared with GARCH(1,1), Markov-Switching GARCH, and Fractionally Integrated GARCH. Lux obtains similar results using linear predictions.
Multiple assets and value-at-risk
Extensions of MSM to multiple assets provide reliable estimates of the value-at-risk in a portfolio of securities.Asset pricing
In financial economics, MSM has been used to analyze the pricing implications of multifrequency risk. The models have had some success in explaining the excess volatility of stock returns compared to fundamentals and the negative skewness of equity returns. They have also been used to generate multifractal jump-diffusions.Related approaches
MSM is a stochastic volatility model with arbitrarily many frequencies. MSM builds on the convenience of regime-switching models, which were advanced in economics and finance by James D. HamiltonJames D. Hamilton
James Douglas "Jim" Hamilton is an US econometrician currently teaching at University of California, San Diego. His work is especially influential in time series and energy economics...
.
MSM is closely related to the Multifractal Model of Asset Returns. MSM improves on the MMAR’s combinatorial construction by randomizing arrival times, guaranteeing a strictly stationary process.
MSM provides a pure regime-switching formulation of multifractal measures, which were pioneered by Benoit Mandelbrot
Benoît Mandelbrot
Benoît B. Mandelbrot was a French American mathematician. Born in Poland, he moved to France with his family when he was a child...
.
See also
- Brownian motionBrownian motionBrownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
- Markov chainMarkov chainA Markov chain, named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another, between a finite or countable number of possible states. It is a random process characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the...
- Multifractal model of asset returns
- Multifractal
- Stochastic volatilityStochastic volatilityStochastic volatility models are used in the field of mathematical finance to evaluate derivative securities, such as options. The name derives from the models' treatment of the underlying security's volatility as a random process, governed by state variables such as the price level of the...

