.gif)
Magnetic survey (archaeology)
Encyclopedia

Archaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
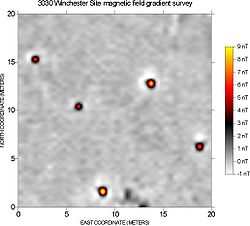
, magnetic surveys are used to detect and map archaeological artifacts
Artifact (archaeology)
An artifact or artefact is "something made or given shape by man, such as a tool or a work of art, esp an object of archaeological interest"...
and features
Feature (archaeology)
Feature in archaeology and especially excavation has several different but allied meanings. A feature is a collection of one or more contexts representing some human non-portable activity that generally has a vertical characteristic to it in relation to site stratigraphy. Examples of features are...
. Magnetic surveys are used in both terrestrial and marine archaeology.
Overview
MagnetometerMagnetometer
A magnetometer is a measuring instrument used to measure the strength or direction of a magnetic field either produced in the laboratory or existing in nature...
s used in geophysical survey may use a single sensor to measure the total magnetic field strength, or may use two (sometimes more) spatially separated sensors to measure the gradient of the magnetic field (the difference between the sensors). In most archaeological applications the latter (gradiometer) configuration is preferred because it provides better resolution of small, near-surface phenomena. Magnetometers may also use a variety of different sensor types. Proton precession magnetometers have largely been superseded by faster and more sensitive fluxgate and cesium instruments.
Every kind of material has unique magnetic properties, even those that we do not think of as being "magnetic". Different materials below the ground can cause local disturbances in the Earth’s magnetic field that are detectable with sensitive magnetometers. The chief limitation of magnetometer survey is that subtle features of interest may be obscured by highly magnetic geologic or modern materials.
Terrestrial magnetic surveys
In terrestrial archaeology, magnetic surveys are typically used for detailed mapping of archaeological features on known archaeological sites. More exceptionally, magnetometers are used for low-resolution exploratory surveys.Several types of magnetometer are used in terrestrial archaeology. Early surveys, beginning in the 1950s, were conducted with proton precession magnetometers. Data collection with proton precession instruments was slow, making high sample density surveys impracticable. Data were manually recorded and plotted. The subsequent introduction of Fluxgate and cesium vapor magnetomers improved sesitivity, and greatly increased sampling speed, making high resolution surveys of large areas practical. Equally important was the development of computers to handle, process, and display large datasets.
Magnetometers react very strongly to iron and steel, brick, burned soil, and many types of rock, and archaeological features composed of these materials are very detectable. Where these highly magnetic materials do not occur, it is often possible to detect very subtle anomalies caused by disturbed soils or decayed organic materials. Many types of sites and features have been successfully mapped with magnetometers, ranging from very ephemeral prehistoric campsites to large urban centers.
Marine Magnetic Surveys
Magnetic surveys are extremely useful in the excavation and exploration of underwater archaeological sites. The apparatus used on the water slightly differs from that on land. Marine magnetometers come in two types: Surface towed and near-bottom. Both are towed a sufficient distance (about two ship lengths) away from the ship to allow them to collect data without it being polluted by the ship's magnetic properties. Surface towed magnetometers allow for a wider range of detection at the price of precision accuracy that is afforded by the near-bottom magnetometers.The most common type of magnetometer used for marine survey is the fluxgate magnetometer. Fluxgate magnetometers utilize two ferromagnetic cores each wound with a primary coil and an outer secondary coil attached to amp meter. When an alternating current (AC) is passed through the primary coils, it creates two opposing magnetic fields that vary in intensity based on the outside magnetic fields. By floating them parallel to the seafloor, they can measure the changes in magnetic fields over the seabed.
Another common type is the newer proton precession magnetometer. This utilizes a container full of hydrogen rich liquids (commonly kerosene
Kerosene
Kerosene, sometimes spelled kerosine in scientific and industrial usage, also known as paraffin or paraffin oil in the United Kingdom, Hong Kong, Ireland and South Africa, is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid. The name is derived from Greek keros...
or methanol
Methanol
Methanol, also known as methyl alcohol, wood alcohol, wood naphtha or wood spirits, is a chemical with the formula CH3OH . It is the simplest alcohol, and is a light, volatile, colorless, flammable liquid with a distinctive odor very similar to, but slightly sweeter than, ethanol...
) that, when agitated by a direct current (DC) or Radio Frequency (RF), cause the electrons to become energized and transfer that energy to the protons due to the Overhauser Effect basically turning them into dipole magnets. When the stimulus is removed, the protons precess at a rate that can be interpreted to determine the magnetic forces of the area.
In maritime archaeology, these are often used to map the geology of wreck sites and determine the composition of magnetic materials found on the seafloor. An Overhauser magnetometer (PPM) was used in 2001 to map Sebastos (the harbor of Caesarea Maritima) and helped to identify components of the Roman concrete
Roman concrete
Roman concrete was a material used in construction during the late Roman Republic through the whole history of the Roman Empire. Roman concrete was based on a hydraulic-setting cement with many material qualities similar to modern Portland cement...
.
Related methods
The magnetic properties of archaeological materials form the basis for a number of other archaeological techniques, Including:- Magnetic susceptibilityMagnetic susceptibilityIn electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility \chi_m is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of magnetization of a material in response to an applied magnetic field...
survey - Laboratory analysis of magnetic samples
- Archaeomagnetic datingArchaeomagnetic datingArchaeomagnetic dating is the study and interpretation of the signatures of the Earth's magnetic field at past times recorded in archaeological materials. These paleomagnetic signatures are fixed when ferromagnetic materials such as magnetite cool below the Curie point, freezing the magnetic moment...

