
Magnetic impurity
Encyclopedia
A magnetic impurity is an impurity
in a host metal that has a magnetic moment
. The magnetic impurity can then interact with the conduction electrons of the metal, leading to interesting physics such as the Kondo effect
, and heavy fermion
behaviour. Some examples of magnetic impurities that metals can be doped with are iron
and nickel
. Such an impurity will contribute a Curie-Weiss term to the magnetic susceptibility
,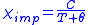 .
.
Early theoretical work concentrated on explaining the trend observed as the impurity was varied across the transition metal
group. Based on the idea of a virtual bound state, Anderson proposed a model that was successful in explaining the formation of a localized magnetic moment from a magnetic impurity.
Impurity
Impurities are substances inside a confined amount of liquid, gas, or solid, which differ from the chemical composition of the material or compound.Impurities are either naturally occurring or added during synthesis of a chemical or commercial product...
in a host metal that has a magnetic moment
Magnetic moment
The magnetic moment of a magnet is a quantity that determines the force that the magnet can exert on electric currents and the torque that a magnetic field will exert on it...
. The magnetic impurity can then interact with the conduction electrons of the metal, leading to interesting physics such as the Kondo effect
Kondo effect
In physics, the Kondo effect describes the scattering of conduction electrons in a metal due to magnetic impurities. It is a measure of how electrical resistivity changes with temperature....
, and heavy fermion
Heavy Fermion
In solid-state physics, heavy fermion materials are a specific type of intermetallic compound, containing elements with 4f or 5f electrons. Electrons, a kind of fermion, found in such materials are sometimes referred to as heavy electrons...
behaviour. Some examples of magnetic impurities that metals can be doped with are iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
and nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
. Such an impurity will contribute a Curie-Weiss term to the magnetic susceptibility
Magnetic susceptibility
In electromagnetism, the magnetic susceptibility \chi_m is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of magnetization of a material in response to an applied magnetic field...
,
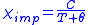 .
.Early theoretical work concentrated on explaining the trend observed as the impurity was varied across the transition metal
Transition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
group. Based on the idea of a virtual bound state, Anderson proposed a model that was successful in explaining the formation of a localized magnetic moment from a magnetic impurity.
See also
- Anderson impurity model
- Anderson orthogonality theoremAnderson orthogonality theoremThe Anderson orthogonality theorem is a theorem in physics by the physicist P. W. Anderson.It relates to the introduction of a magnetic impurity in a metal. When a magnetic impurity is introduced into a metal, the conduction electrons will tend to screen the potential V that the impurity creates...
- Magnetic semiconductors

