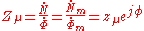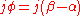Magnetic complex reluctance
Encyclopedia
Magnetic complex reluctance (SI Unit: H−1) is a measurement of a passive magnetic circuit
(or element within that circuit) dependent on sinusoidal magnetomotive force (SI Unit: At
·Wb
−1) and sinusoidal magnetic flux
(SI Unit: T
·m
2), and this is determined by deriving the ratio of their complex effective amplitudes.[Ref. 1-3]
As seen above, magnetic complex reluctance is a phasor
represented as uppercase Z mu where:
The "lossless" magnetic reluctance
, lowercase z mu, is equal to the absolute value (modulus) of the magnetic complex reluctance. The argument distinguishing the "lossy" magnetic complex reluctance from the "lossless" magnetic reluctance is equal to the natural number raised to a power equal to:
raised to a power equal to:
Where:
The "lossy" magnetic complex reluctance represents a magnetic circuit element's resistance to not only magnetic flux but also to changes in magnetic flux. When applied to harmonic regimes, this formality is similar to Ohm's Law
in ideal AC circuits. In magnetic circuits, magnetic complex reluctance equal to:
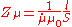
Where:
Magnetic circuit
A magnetic circuit is made up of one or more closed loop paths containing a magnetic flux. The flux is usually generated by permanent magnets or electromagnets and confined to the path by magnetic cores consisting of ferromagnetic materials like iron, although there may be air gaps or other...
(or element within that circuit) dependent on sinusoidal magnetomotive force (SI Unit: At
Ampere-turn
The ampere-turn was the MKS unit of magnetomotive force , represented by a direct current of one ampere flowing in a single-turn loop in a vacuum...
·Wb
Weber
Weber is a surname of German origin, derived from the noun meaning "weaver". In some cases, following migration to English-speaking countries, it has been anglicised to the English surname 'Webber' or even 'Weaver'.Notable people with the surname include:...
−1) and sinusoidal magnetic flux
Magnetic flux
Magnetic flux , is a measure of the amount of magnetic B field passing through a given surface . The SI unit of magnetic flux is the weber...
(SI Unit: T
Tesla (unit)
The tesla is the SI derived unit of magnetic field B . One tesla is equal to one weber per square meter, and it was defined in 1960 in honour of the inventor, physicist, and electrical engineer Nikola Tesla...
·m
Metre
The metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
2), and this is determined by deriving the ratio of their complex effective amplitudes.[Ref. 1-3]
As seen above, magnetic complex reluctance is a phasor
Phasor
Phasor is a phase vector representing a sine wave.Phasor may also be:* Phasor , a stereo music, sound and speech synthesizer for the Apple II computer* Phasor measurement unit, a device that measures phasors on an electricity grid...
represented as uppercase Z mu where:
-
 and
and 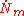 represent the magnetomotive force (complex effective amplitude)
represent the magnetomotive force (complex effective amplitude) -
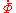 and
and 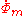 represent the magnetic flux (complex effective amplitude)
represent the magnetic flux (complex effective amplitude) -
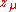 , lowercase z mu, is the real part of magnetic complex reluctance
, lowercase z mu, is the real part of magnetic complex reluctance
The "lossless" magnetic reluctance
Magnetic reluctance
Magnetic reluctance, or magnetic resistance, is a concept used in the analysis of magnetic circuits. It is analogous to resistance in an electrical circuit, but rather than dissipating magnetic energy it stores magnetic energy...
, lowercase z mu, is equal to the absolute value (modulus) of the magnetic complex reluctance. The argument distinguishing the "lossy" magnetic complex reluctance from the "lossless" magnetic reluctance is equal to the natural number
 raised to a power equal to:
raised to a power equal to:Where:
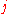 is the imaginary number
is the imaginary number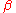 is the phase of the magnetomotive force
is the phase of the magnetomotive force is the phase of the magnetic flux
is the phase of the magnetic flux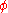 is the phase difference
is the phase difference
The "lossy" magnetic complex reluctance represents a magnetic circuit element's resistance to not only magnetic flux but also to changes in magnetic flux. When applied to harmonic regimes, this formality is similar to Ohm's Law
Ohm's law
Ohm's law states that the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the two points...
in ideal AC circuits. In magnetic circuits, magnetic complex reluctance equal to:
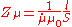
Where:
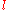 is the length of the circuit element
is the length of the circuit element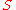 is the cross-section of the circuit element
is the cross-section of the circuit element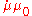 is the complex magnetic permeabilityPermeability (electromagnetism)In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...
is the complex magnetic permeabilityPermeability (electromagnetism)In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of the ability of a material to support the formation of a magnetic field within itself. In other words, it is the degree of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Magnetic permeability is typically...