
Lunar distance (astronomy)
Encyclopedia
In astronomy
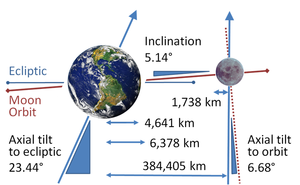
, a lunar distance (LD) is a measurement of the distance from the Earth to the Moon. The average distance from Earth to the Moon is 384,400 kilometers
(238,855 mi). The actual distance varies over the course of the orbit of the moon.
High-precision
measurements of the lunar distance are made by measuring the time taken for light to travel between LIDAR
stations on Earth and retroreflector
s placed on the Moon.
The Moon is spiraling away from Earth at an average rate of 3.8 cm per year, as detected by the Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment
. By coincidence, the diameter of corner cubes
in retroreflectors on the Moon is also 3.8 cm.
The first person to measure the distance to the Moon was the 2nd-century-BCE astronomer and geographer Hipparchus
, who used simple trigonometry
. He was approximately 26,000 km off the actual distance, an error of about 6.8%.
The NASA Near Earth Object Catalog includes the distances of asteroids and comets measured in Lunar Distances.
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, a lunar distance (LD) is a measurement of the distance from the Earth to the Moon. The average distance from Earth to the Moon is 384,400 kilometers
1 E8 m
To help compare different orders of magnitude, this page lists lengths starting at 108 metres .Distances shorter than 108 metres* 102 Mm — Diameter of HD 149026 b, an unusually dense Jovian planet...
(238,855 mi). The actual distance varies over the course of the orbit of the moon.
High-precision
Accuracy and precision
In the fields of science, engineering, industry and statistics, the accuracy of a measurement system is the degree of closeness of measurements of a quantity to that quantity's actual value. The precision of a measurement system, also called reproducibility or repeatability, is the degree to which...
measurements of the lunar distance are made by measuring the time taken for light to travel between LIDAR
LIDAR
LIDAR is an optical remote sensing technology that can measure the distance to, or other properties of a target by illuminating the target with light, often using pulses from a laser...
stations on Earth and retroreflector
Retroreflector
A retroreflector is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum scattering of light. An electromagnetic wave front is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The device or surface's angle of incidence is...
s placed on the Moon.
The Moon is spiraling away from Earth at an average rate of 3.8 cm per year, as detected by the Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment
Lunar laser ranging experiment
The ongoing Lunar Laser Ranging Experiment measures the distance between the Earth and the Moon using laser ranging. Lasers on Earth are aimed at retroreflectors planted on the moon during the Apollo program, and the time for the reflected light to return is determined...
. By coincidence, the diameter of corner cubes
Corner reflector
A corner reflector is a retroreflector consisting of three mutually perpendicular, intersecting flat surfaces, which reflects waves back directly towards the source, but shifted . Unlike a simple mirror, they work for a relatively wide-angle field of view. The three intersecting surfaces often have...
in retroreflectors on the Moon is also 3.8 cm.
The first person to measure the distance to the Moon was the 2nd-century-BCE astronomer and geographer Hipparchus
Hipparchus
Hipparchus, the common Latinization of the Greek Hipparkhos, can mean:* Hipparchus, the ancient Greek astronomer** Hipparchic cycle, an astronomical cycle he created** Hipparchus , a lunar crater named in his honour...
, who used simple trigonometry
Trigonometry
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that studies triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves...
. He was approximately 26,000 km off the actual distance, an error of about 6.8%.
The NASA Near Earth Object Catalog includes the distances of asteroids and comets measured in Lunar Distances.


