
Low back pain
Encyclopedia
Low back pain or lumbago (icon) is a common musculoskeletal disorder
affecting 80% of people at some point in their lives. In the United States it is the most common cause of job-related disability, a leading contributor to missed work, and the second most common neurological ailment — only headache
is more common. It can be either acute, subacute or chronic in duration. With conservative measures, the symptoms of low back pain
typically show significant improvement within a few weeks from onset.
or strain
, particularly in instances where pain arose suddenly during physical loading of the back, with the pain lateral to the spine. Over 99% of back pain instances fall within this category. The full differential diagnosis includes many other less common conditions.
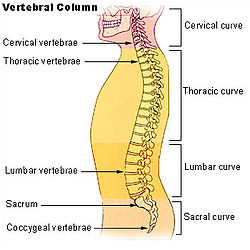 The lumbar region (or lower back region) is made up of five vertebrae (L1-L5). In between these vertebrae lie fibrocartilage discs (intervertebral discs), which act as cushions, preventing the vertebrae from rubbing together while at the same time protecting the spinal cord
The lumbar region (or lower back region) is made up of five vertebrae (L1-L5). In between these vertebrae lie fibrocartilage discs (intervertebral discs), which act as cushions, preventing the vertebrae from rubbing together while at the same time protecting the spinal cord
. Nerves stem from the spinal cord
through foramina
within the vertebrae, providing muscles with sensations and motor associated messages. Stability of the spine is provided through ligaments and muscles of the back, lower back and abdomen. Small joints which prevent, as well as direct, motion of the spine are called facet joints (zygapophysial joints).
Causes of lower back pain are varied. Most cases are believed to be due to a sprain
or strain
in the muscles and soft tissues of the back. Overactivity of the muscles of the back can lead to an injured or torn ligament in the back which in turn leads to pain. An injury can also occur to one of the intervertebral discs (disc tear, disc herniation). Due to aging, discs begin to diminish and shrink in size, resulting in vertebrae and facet joints rubbing against one another. Ligament and joint functionality also diminishes as one ages, leading to spondylolisthesis
, which causes the vertebrae to move much more than they should. Pain is also generated through lumbar spinal stenosis, sciatica
and scoliosis
. At the lowest end of the spine, some patients may have tailbone pain (also called coccyx
pain or coccydynia
). Others may have pain from their sacroiliac joint
, where the spinal column attaches to the pelvis, called sacroiliac joint dysfunction
which may be responsible for 22.6% of low back pain. Physical causes may include osteoarthritis
, rheumatoid arthritis
, degeneration of the discs
between the vertebrae or a spinal disc herniation
, a vertebral fracture (such as from osteoporosis
), or rarely, an infection or tumor.
In the vast majority of cases, no noteworthy or serious cause is ever identified. If the pain resolves after a few weeks, intensive testing is not indicated.
Cigarette smoking impacts the success and proper healing of spinal fusion surgery in patients who undergo cervical fusion; rates of nonunion are significantly greater for smokers than for nonsmokers. Smoke and nicotine accelerate spine deterioration, reduce blood flow to the lower spine, and cause discs to degenerate.
For acute cases that are not debilitating, low back pain may be best treated with conservative self-care, including: application of heat or cold, and continued activity within the limits of the pain. Firm mattresses have demonstrated less effectiveness than medium-firm mattresses.
Activity
Engaging in physical activity within the limits of pain aids recovery. Prolonged bed rest (more than 2 days) is considered counterproductive. Even with cases of severe pain, some activity is preferred to prolonged sitting or lying down - excluding movements that would further strain the back. Structured exercise in acute low back pain has demonstrated neither improvement nor harm.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy can include heat, ice, massage, ultrasound
, and electrical stimulation. Active therapies can consist of stretching, strengthening and aerobic exercises. Exercising to restore motion and strength to your lower back can be very helpful in relieving pain and preventing future episodes of low back pain.
Medications
Short term use of pain and anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs or acetaminophen may help relieve the symptoms of lower back pain. NSAIDs are slightly effective for short-term symptomatic relief in patients with acute and chronic low-back pain without sciatica. Muscle relaxant
s for acute and chronic pain have some benefit, and are more effective in relieving pain and spasms when used in combination with NSAIDs.
Spinal manipulation
As of 2011 it is not known if chiropractic
care improves clinical outcomes in those with lower back pain more or less than other possible treatments. A 2004 Cochrane review found that spinal manipulation
(SM) was no more or less effective than other commonly used therapies such as pain medication, physical therapy
, exercises, back school or the care given by a general practitioner. A 2010 systematic review found that most studies suggest SM achieves equal or superior improvement in pain and function when compared with other commonly used interventions for short, intermediate, and long-term follow-up. In 2007 the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society jointly recommended that clinicians consider spinal manipulation for patients who do not improve with self care options. Reviews published in 2008 and 2006 suggested that SM for low back pain was equally effective as other commonly used interventions. A 2007 literature synthesis found good evidence supporting SM and mobilization for low back pain. Of four systematic reviews published between 2000 and 2005, one recommended SM and three stated that there was insufficient evidence to make recommendations.
reviews the factors that predict disability from back pain. The data quantified that patients with back pain who have poor coping behaviors or who fear activity are about 2.5 times as likely to have poor outcomes at 1 year.
The following measures have been found to be effective for chronic non-specific back pain:
Epidural corticosteroid injections are said to supply the patient with temporary relief of sciatica
. However studies show that they do not decrease the rate of ensuing operations.
Therapeutic massage is proven to be effective for chronic back pain. Traditional Chinese Medical acupuncture was proven to be relatively ineffective for chronic back pain.
or spinal abscess. Spinal fusion
has been shown not to improve outcomes in those with simple chronic low back pain.
The most common types of low back surgery include microdiscectomy, discectomy, laminectomy, foraminotomy, or spinal fusion. Another less invasive surgical technique consists of an implantation of a spinal cord stimulator and typically is used for symptoms of chronic radiculopathy (sciatica
). Lumbar artificial disc replacement is a newer surgical technique for treatment of degenerative disc disease
, as are a variety of surgical procedures aimed at preserving motion in the spine. According to studies, benefits of spinal surgery are limited when dealing with degenerative discs.
A medical review in March 2009 found the following: Four randomised clinic trials showed that the benefits of spinal surgery are limited when treating degenerative discs with spinal pain (no sciatica). Between 1990 and 2001 there was a 220% increase in spinal surgery, despite the fact that during that period there were no changes, clarifications, or improvements in the indications for surgery or new evidence of improved effectiveness of spinal surgery. The review also found that higher spinal surgery rates are sometimes associated with worse outcomes and that the best surgical outcomes occurred where surgery rates were lower. It also found that use of surgical implants increased the risk of nerve injury, blood loss, overall complications, operating times and repeat surgery while it only slightly improved solid bone fusion rates. There was no added improvement in pain levels or function.
The logic behind spinal fusion is that by fusing two vertebrae together, they will act and function as a solid bone. Since lumbar pain may be caused by excessive motion of the vertebra the goal of spinal fusion surgery is to eliminate that extra motion in between the vertebrae, alleviating pain. If scoliosis or degenerative discs is the problem, the spinal fusion process may be recommended. There are several different ways of performing the spinal fusion procedure; however, none are proven to reduce pain better than the others.
:
As one gets farther along in the pregnancy, due to the additional weight of the baby, one’s center of gravity will shift forward causing one’s posture
to change. This change in posture leads to increasing lower back pain.
The increase in hormones during pregnancy is in preparation for birth. This increase of hormones softens the ligaments in the pelvic area and loosens joints. This change in ligaments and joints may alter the support in which one’s back is normally used to.
Musculoskeletal disorders
Musculoskeletal disorders can affect the body's muscles, joints, tendons, ligaments and nerves. Most work-related MSDs develop over time and are caused either by the work itself or by the employees' working environment...
affecting 80% of people at some point in their lives. In the United States it is the most common cause of job-related disability, a leading contributor to missed work, and the second most common neurological ailment — only headache
Headache
A headache or cephalalgia is pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It can be a symptom of a number of different conditions of the head and neck. The brain tissue itself is not sensitive to pain because it lacks pain receptors. Rather, the pain is caused by disturbance of the...
is more common. It can be either acute, subacute or chronic in duration. With conservative measures, the symptoms of low back pain
Pain
Pain is an unpleasant sensation often caused by intense or damaging stimuli such as stubbing a toe, burning a finger, putting iodine on a cut, and bumping the "funny bone."...
typically show significant improvement within a few weeks from onset.
Classification
Lower back pain may be classified by the duration of symptoms as acute (less than 4 weeks), sub acute (4–12 weeks), chronic (more than 12 weeks).Cause
The majority of lower back pain stems from benign musculoskeletal problems, and are referred to as non specific low back pain; this type may be due to muscle or soft tissues sprainSprain
A sprain is an injury in a joint, caused by the ligament being stretched beyond its capacity. A muscular tear caused in the same manner is referred to as a strain. In cases where either ligament or muscle tissue is torn, immobilization and surgical repair may be necessary...
or strain
Strain (injury)
A strain is an injury to a muscle or tendon in which the muscle fibres tear as a result of overstretching. A strain is also colloquially known as a pulled muscle...
, particularly in instances where pain arose suddenly during physical loading of the back, with the pain lateral to the spine. Over 99% of back pain instances fall within this category. The full differential diagnosis includes many other less common conditions.
Pathophysiology

Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
. Nerves stem from the spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
through foramina
Foramen
In anatomy, a foramen is any opening. Foramina inside the body of humans and other animals typically allow muscles, nerves, arteries, veins, or other structures to connect one part of the body with another.-Skull:...
within the vertebrae, providing muscles with sensations and motor associated messages. Stability of the spine is provided through ligaments and muscles of the back, lower back and abdomen. Small joints which prevent, as well as direct, motion of the spine are called facet joints (zygapophysial joints).
Causes of lower back pain are varied. Most cases are believed to be due to a sprain
Sprain
A sprain is an injury in a joint, caused by the ligament being stretched beyond its capacity. A muscular tear caused in the same manner is referred to as a strain. In cases where either ligament or muscle tissue is torn, immobilization and surgical repair may be necessary...
or strain
Strain (injury)
A strain is an injury to a muscle or tendon in which the muscle fibres tear as a result of overstretching. A strain is also colloquially known as a pulled muscle...
in the muscles and soft tissues of the back. Overactivity of the muscles of the back can lead to an injured or torn ligament in the back which in turn leads to pain. An injury can also occur to one of the intervertebral discs (disc tear, disc herniation). Due to aging, discs begin to diminish and shrink in size, resulting in vertebrae and facet joints rubbing against one another. Ligament and joint functionality also diminishes as one ages, leading to spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis describes the anterior or posterior displacement of a vertebra or the vertebral column in relation to the vertebrae below. It was first described in 1782 by Belgian obstetrician, Dr. Herbinaux. He reported a bony prominence anterior to the sacrum that obstructed the vagina of a...
, which causes the vertebrae to move much more than they should. Pain is also generated through lumbar spinal stenosis, sciatica
Sciatica
Sciatica is a set of symptoms including pain that may be caused by general compression or irritation of one of five spinal nerve roots that give rise to each sciatic nerve, or by compression or irritation of the left or right or both sciatic nerves. The pain is felt in the lower back, buttock, or...
and scoliosis
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a medical condition in which a person's spine is curved from side to side. Although it is a complex three-dimensional deformity, on an X-ray, viewed from the rear, the spine of an individual with scoliosis may look more like an "S" or a "C" than a straight line...
. At the lowest end of the spine, some patients may have tailbone pain (also called coccyx
Coccyx
The coccyx , commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column. Comprising three to five separate or fused vertebrae below the sacrum, it is attached to the sacrum by a fibrocartilaginous joint, the sacrococcygeal symphysis, which permits limited movement between...
pain or coccydynia
Coccydynia
Coccydynia is a medical term meaning pain in the coccyx or tailbone area, usually brought on by sitting too abruptly.-Diagnosis:A number of different conditions can cause pain in the general area of the coccyx, but not all involve the coccyx and the muscles attached to it. The first task of...
). Others may have pain from their sacroiliac joint
Sacroiliac joint
The sacroiliac joint or SI joint is the joint in the bony pelvis between the sacrum and the ilium of the pelvis, which are joined together by strong ligaments. In humans, the sacrum supports the spine and is supported in turn by an ilium on each side...
, where the spinal column attaches to the pelvis, called sacroiliac joint dysfunction
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction or SI Joint Dysfunction is a condition in which the joint is locked, partially dislocated or "subluxated" in a non-anatomically correct position due to hypermobility or hypomobility within the joint...
which may be responsible for 22.6% of low back pain. Physical causes may include osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis also known as degenerative arthritis or degenerative joint disease, is a group of mechanical abnormalities involving degradation of joints, including articular cartilage and subchondral bone. Symptoms may include joint pain, tenderness, stiffness, locking, and sometimes an effusion...
, rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. The process produces an inflammatory response of the synovium secondary to hyperplasia of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development...
, degeneration of the discs
Degenerative disc disease
Degeneration of the intervertebral disc, often called "degenerative disc disease" of the spine, is a condition that can be painful and can greatly affect the quality of one's life...
between the vertebrae or a spinal disc herniation
Spinal disc herniation
A spinal disc herniation , informally and misleadingly called a "slipped disc", is a medical condition affecting the spine due to trauma, lifting injuries, or idiopathic, in which a tear in the outer, fibrous ring of an intervertebral disc allows the soft, central portion A spinal disc herniation...
, a vertebral fracture (such as from osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
), or rarely, an infection or tumor.
In the vast majority of cases, no noteworthy or serious cause is ever identified. If the pain resolves after a few weeks, intensive testing is not indicated.
Diagnostic approach
Typically people are treated symptomatically without exact determination of the underlying cause. Only in cases with worrisome signs is diagnostic imaging needed.Imaging
X-rays, CT or MRI scans are not required in lower back pain except in the cases where "red flags" are present. If the pain is of a long duration X-rays may increase patient satisfaction. However routine imaging may be harmful to a person's health and more imaging is associated with higher rates of surgery but no resultant benefit. From 1994 to 2006, in the United States MRI scans of the lumbar region increased by more than 300%.Prevention
Exercise is effective in preventing recurrence of non-acute pain, and has shown mixed results in the treatment of acute episodes. Proper lifting techniques are prophylactic.Cigarette smoking impacts the success and proper healing of spinal fusion surgery in patients who undergo cervical fusion; rates of nonunion are significantly greater for smokers than for nonsmokers. Smoke and nicotine accelerate spine deterioration, reduce blood flow to the lower spine, and cause discs to degenerate.
Acute back pain
Self careFor acute cases that are not debilitating, low back pain may be best treated with conservative self-care, including: application of heat or cold, and continued activity within the limits of the pain. Firm mattresses have demonstrated less effectiveness than medium-firm mattresses.
Activity
Engaging in physical activity within the limits of pain aids recovery. Prolonged bed rest (more than 2 days) is considered counterproductive. Even with cases of severe pain, some activity is preferred to prolonged sitting or lying down - excluding movements that would further strain the back. Structured exercise in acute low back pain has demonstrated neither improvement nor harm.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy can include heat, ice, massage, ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
, and electrical stimulation. Active therapies can consist of stretching, strengthening and aerobic exercises. Exercising to restore motion and strength to your lower back can be very helpful in relieving pain and preventing future episodes of low back pain.
Medications
Short term use of pain and anti-inflammatory medications, such as NSAIDs or acetaminophen may help relieve the symptoms of lower back pain. NSAIDs are slightly effective for short-term symptomatic relief in patients with acute and chronic low-back pain without sciatica. Muscle relaxant
Muscle relaxant
A muscle relaxant is a drug which affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics...
s for acute and chronic pain have some benefit, and are more effective in relieving pain and spasms when used in combination with NSAIDs.
Spinal manipulation
As of 2011 it is not known if chiropractic
Chiropractic
Chiropractic is a health care profession concerned with the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of disorders of the neuromusculoskeletal system and the effects of these disorders on general health. It is generally categorized as complementary and alternative medicine...
care improves clinical outcomes in those with lower back pain more or less than other possible treatments. A 2004 Cochrane review found that spinal manipulation
Spinal manipulation
Spinal manipulation is a therapeutic intervention performed on spinal articulations which are synovial joints . These articulations in the spine that are amenable to spinal manipulative therapy include the z-joints, the atlanto-occipital, atlanto-axial, lumbosacral, sacroiliac, costotransverse...
(SM) was no more or less effective than other commonly used therapies such as pain medication, physical therapy
Physical therapy
Physical therapy , often abbreviated PT, is a health care profession. Physical therapy is concerned with identifying and maximizing quality of life and movement potential within the spheres of promotion, prevention, diagnosis, treatment/intervention,and rehabilitation...
, exercises, back school or the care given by a general practitioner. A 2010 systematic review found that most studies suggest SM achieves equal or superior improvement in pain and function when compared with other commonly used interventions for short, intermediate, and long-term follow-up. In 2007 the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society jointly recommended that clinicians consider spinal manipulation for patients who do not improve with self care options. Reviews published in 2008 and 2006 suggested that SM for low back pain was equally effective as other commonly used interventions. A 2007 literature synthesis found good evidence supporting SM and mobilization for low back pain. Of four systematic reviews published between 2000 and 2005, one recommended SM and three stated that there was insufficient evidence to make recommendations.
Chronic back pain
Low back pain is more likely to be persistent among people who previously required time off from work because of low back pain, those who expect passive treatments to help, those who believe that back pain is harmful or disabling or fear that any movement whatever will increase their pain, and people who have depression or anxiety. A systematic review (2010) published as part of the Rational Clinical Examination Series in the Journal of the American Medical AssociationJournal of the American Medical Association
The Journal of the American Medical Association is a weekly, peer-reviewed, medical journal, published by the American Medical Association. Beginning in July 2011, the editor in chief will be Howard C. Bauchner, vice chairman of pediatrics at Boston University’s School of Medicine, replacing ...
reviews the factors that predict disability from back pain. The data quantified that patients with back pain who have poor coping behaviors or who fear activity are about 2.5 times as likely to have poor outcomes at 1 year.
The following measures have been found to be effective for chronic non-specific back pain:
- Exercise therapy appears to be slightly effective at reducing pain and improving function in the treatment of chronic low back pain. Compared to usual care, exercise therapy improved post-treatment pain intensity and disability, and long-term function. Exercise programmes are effective for chronic LBP up to 6 months after treatment cessation, evidenced by pain score reduction and reoccurrence rates. There is no evidence that one particular type of exercise therapy is clearly more effective than others. The Schroth method, a specialized physical exercise therapy for scoliosisScoliosisScoliosis is a medical condition in which a person's spine is curved from side to side. Although it is a complex three-dimensional deformity, on an X-ray, viewed from the rear, the spine of an individual with scoliosis may look more like an "S" or a "C" than a straight line...
, kyphosisKyphosisKyphosis , also called roundback or Kelso's hunchback, is a condition of over-curvature of the thoracic vertebrae...
, spondylolisthesisSpondylolisthesisSpondylolisthesis describes the anterior or posterior displacement of a vertebra or the vertebral column in relation to the vertebrae below. It was first described in 1782 by Belgian obstetrician, Dr. Herbinaux. He reported a bony prominence anterior to the sacrum that obstructed the vagina of a...
, and related spinal disorders, has been shown to reduce severity and frequency of back pain in adults with scoliosis. - Tricyclic antidepressantTricyclic antidepressantTricyclic antidepressants are heterocyclic chemical compounds used primarily as antidepressants. The TCAs were first discovered in the early 1950s and were subsequently introduced later in the decade; they are named after their chemical structure, which contains three rings of atoms...
s are recommended in a 2007 guideline by the American College of Physicians and the American Pain Society. - Antibiotics can eliminate chronic pain when the cause is bacterial infection. In a Danish study, more than half the patients were either cured or much improved after 90 days of daily antibiotics.
- AcupunctureAcupunctureAcupuncture is a type of alternative medicine that treats patients by insertion and manipulation of solid, generally thin needles in the body....
may help chronic pain; however, a more recent randomized controlled trialRandomized controlled trialA randomized controlled trial is a type of scientific experiment - a form of clinical trial - most commonly used in testing the safety and efficacy or effectiveness of healthcare services or health technologies A randomized controlled trial (RCT) is a type of scientific experiment - a form of...
suggested insignificant difference between real and sham acupuncture. - Intensive multidisciplinary treatment programs may help subacute or chronic low back pain.
- Behavioral therapy
- The Alexander TechniqueAlexander TechniqueThe Alexander Technique teaches the ability to improve physical postural habits, particularly those that have become ingrained and conditioned responses...
was shown in a UK clinical trial to have long-term benefits for patients with chronic back pain. - Back schools have shown some effect in managing chronic back pain.
- Spinal manipulationSpinal manipulationSpinal manipulation is a therapeutic intervention performed on spinal articulations which are synovial joints . These articulations in the spine that are amenable to spinal manipulative therapy include the z-joints, the atlanto-occipital, atlanto-axial, lumbosacral, sacroiliac, costotransverse...
has been shown to have a clinical effect equal to that of other commonly used therapies and was considered safe. - Clinical research shows that treatment according to McKenzie methodMcKenzie methodThe McKenzie method is a comprehensive method of care primarily used in physical therapy.New Zealand physical therapist Robin McKenzie developed the method in the late 50s...
somewhat effective for acute low back pain, but the evidence suggests that it is not effective for chronic low-back pain. - Manipulation under anaesthesia, or medically-assisted manipulation, currently has insufficient evidence to make any strong recommendations.
- ProlotherapyProlotherapyProlotherapy is also known as "proliferation therapy" or "regenerative injection therapy." involves injecting an otherwise non-pharmacological and non-active irritant solution into the body, generally in the region of tendons or ligaments for the purpose of strengthening weakened connective tissue...
, facet joint injections, and intradiscal steroid injections have not been found to be effective.
Epidural corticosteroid injections are said to supply the patient with temporary relief of sciatica
Sciatica
Sciatica is a set of symptoms including pain that may be caused by general compression or irritation of one of five spinal nerve roots that give rise to each sciatic nerve, or by compression or irritation of the left or right or both sciatic nerves. The pain is felt in the lower back, buttock, or...
. However studies show that they do not decrease the rate of ensuing operations.
Therapeutic massage is proven to be effective for chronic back pain. Traditional Chinese Medical acupuncture was proven to be relatively ineffective for chronic back pain.
Surgery
Surgery may be indicated when conservative treatment is not effective in reducing pain or when the patient develops progressive and functionally limiting neurologic symptoms such as leg weakness, bladder or bowel incontinence, which can be seen with severe central lumbar disc herniation causing cauda equina syndromeCauda equina syndrome
Cauda equina syndrome ' is a serious neurologic condition in which there is acute loss of function of the lumbar plexus, neurologic elements of the spinal canal below the termination of the spinal cord.-Causes:...
or spinal abscess. Spinal fusion
Spinal fusion
Spinal fusion, also known as spondylodesis or spondylosyndesis, is a surgical technique used to join two or more vertebrae. Supplementary bone tissue, either from the patient or a donor , is used in conjunction with the body's natural bone growth processes to fuse the vertebrae.Fusing of the...
has been shown not to improve outcomes in those with simple chronic low back pain.
The most common types of low back surgery include microdiscectomy, discectomy, laminectomy, foraminotomy, or spinal fusion. Another less invasive surgical technique consists of an implantation of a spinal cord stimulator and typically is used for symptoms of chronic radiculopathy (sciatica
Sciatica
Sciatica is a set of symptoms including pain that may be caused by general compression or irritation of one of five spinal nerve roots that give rise to each sciatic nerve, or by compression or irritation of the left or right or both sciatic nerves. The pain is felt in the lower back, buttock, or...
). Lumbar artificial disc replacement is a newer surgical technique for treatment of degenerative disc disease
Degenerative disc disease
Degeneration of the intervertebral disc, often called "degenerative disc disease" of the spine, is a condition that can be painful and can greatly affect the quality of one's life...
, as are a variety of surgical procedures aimed at preserving motion in the spine. According to studies, benefits of spinal surgery are limited when dealing with degenerative discs.
A medical review in March 2009 found the following: Four randomised clinic trials showed that the benefits of spinal surgery are limited when treating degenerative discs with spinal pain (no sciatica). Between 1990 and 2001 there was a 220% increase in spinal surgery, despite the fact that during that period there were no changes, clarifications, or improvements in the indications for surgery or new evidence of improved effectiveness of spinal surgery. The review also found that higher spinal surgery rates are sometimes associated with worse outcomes and that the best surgical outcomes occurred where surgery rates were lower. It also found that use of surgical implants increased the risk of nerve injury, blood loss, overall complications, operating times and repeat surgery while it only slightly improved solid bone fusion rates. There was no added improvement in pain levels or function.
The logic behind spinal fusion is that by fusing two vertebrae together, they will act and function as a solid bone. Since lumbar pain may be caused by excessive motion of the vertebra the goal of spinal fusion surgery is to eliminate that extra motion in between the vertebrae, alleviating pain. If scoliosis or degenerative discs is the problem, the spinal fusion process may be recommended. There are several different ways of performing the spinal fusion procedure; however, none are proven to reduce pain better than the others.
Other
Additional treatments have been more recently reviewed by the Cochrane CollaborationCochrane Collaboration
The Cochrane Collaboration is a group of over 28,000 volunteers in more than 100 countries who review the effects of health care interventions tested in biomedical randomized controlled trials. A few more recent reviews have also studied the results of non-randomized, observational studies...
:
- MassageMassageMassage is the manipulation of superficial and deeper layers of muscle and connective tissue to enhance function, aid in the healing process, and promote relaxation and well-being. The word comes from the French massage "friction of kneading", or from Arabic massa meaning "to touch, feel or handle"...
therapy may benefit some patients. - Heat application may have a modest benefit. The evidence for cold therapy is limited.
- YogaYogaYoga is a physical, mental, and spiritual discipline, originating in ancient India. The goal of yoga, or of the person practicing yoga, is the attainment of a state of perfect spiritual insight and tranquility while meditating on Supersoul...
has been found beneficial. - Correcting leg length difference may help by inserting a heel lift or building up the shoe.
- The role of narcoticNarcoticThe term narcotic originally referred medically to any psychoactive compound with any sleep-inducing properties. In the United States of America it has since become associated with opioids, commonly morphine and heroin and their derivatives, such as hydrocodone. The term is, today, imprecisely...
s for chronic low back pain is uncertain. - A 2008 review found antidepressantAntidepressantAn antidepressant is a psychiatric medication used to alleviate mood disorders, such as major depression and dysthymia and anxiety disorders such as social anxiety disorder. According to Gelder, Mayou &*Geddes people with a depressive illness will experience a therapeutic effect to their mood;...
s ineffective in the treatment of chronic back pain even though some previous studies did find them helpful. - Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulationTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulationTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation is the use of electric current produced by a device to stimulate the nerves for therapeutic purposes...
(TENS) has not been found to be effective in chronic lower back pain.
Prognosis
Most people with acute lower back pain recover completely over a few weeks regardless of treatments. 60% of people recover after seven weeks, regardless of the treatments they receive. Consistent with these statistics, a recent study found that almost 30% of patients did not recover from the presenting episode of low back pain within a year. For those patients whose low back pain continues on to chronicity, it is rarely self limiting, as fewer than 10% of those patients whose low back pain becomes chronic report no pain five years later.Epidemiology
Over a lifetime 80% of people have lower back pain, with 26% of American adults reporting pain of at least one day in duration every three months. 41% of adults aged between 26 and 44 years reported having back pain in the previous 6 months. In the United States, estimates of the costs of low back pain range between $38 and $50 billion a year and there are 300,000 operations annually. Along with neck operations, back operations are the 3rd most common form of surgery in the United States.In pregnancy
50-70% of all pregnant women experience back pain.As one gets farther along in the pregnancy, due to the additional weight of the baby, one’s center of gravity will shift forward causing one’s posture
Posture
Posture or posturing may refer to:In humans* Posture * Neutral spine or good posture* Human position* Abnormal posturing, in neurotrauma* Posturography, in neurology* Posture and occupational healthIn biology...
to change. This change in posture leads to increasing lower back pain.
The increase in hormones during pregnancy is in preparation for birth. This increase of hormones softens the ligaments in the pelvic area and loosens joints. This change in ligaments and joints may alter the support in which one’s back is normally used to.

