Lithium amide
Encyclopedia
Lithium amide is an inorganic compound
with the chemical formula Li+NH2-, i.e. it is composed of a lithium
cation, and the conjugate base of ammonia
. It is a white solid with a tetragonal crystal structure.
(LDA), which is quite commonly used.
Lithium amide can be made by adding lithium
metal to liquid ammonia
:
Lithium amides in general can be similarly formed, substituting ammonia with the appropriate amine:
Lithium amides are very reactive compounds and can act as strong bases
. Unless the nitrogen atom is hindered, as in the case of LDA, they can also act as nucleophile
s.
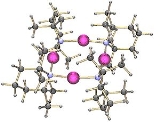
has been crystallised as a tetramer:
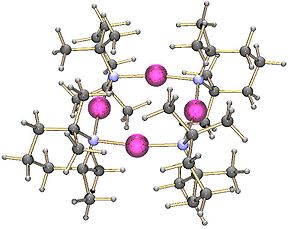 On the other hand, the lithium derivative of di-(1-phenylethyl)amine
On the other hand, the lithium derivative of di-(1-phenylethyl)amine
crystallises as a trimer:
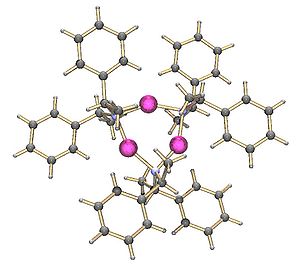 It is also possible to make mixed oligomers of metal alkoxide
It is also possible to make mixed oligomers of metal alkoxide
s and amides. These are related to the superbases which are mixtures of metal alkoxides and alkyls. The cyclic oligomers form when the nitrogen of the amide forms a sigma bond
to a lithium while the nitrogen lone pair
binds to another metal centre.
Other organolithium compounds (such as BuLi
) are generally considered to exist in and function via high-order, aggregated species.
Inorganic compound
Inorganic compounds have traditionally been considered to be of inanimate, non-biological origin. In contrast, organic compounds have an explicit biological origin. However, over the past century, the classification of inorganic vs organic compounds has become less important to scientists,...
with the chemical formula Li+NH2-, i.e. it is composed of a lithium
Lithium
Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly...
cation, and the conjugate base of ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
. It is a white solid with a tetragonal crystal structure.
Lithium amides
The anionic conjugate bases of amines are known as amides. Thus lithium amide may also refer to lithium salts of amines e.g. Li+NR2-. An example of a lithium amide is lithium diisopropylamideLithium diisopropylamide
Lithium diisopropylamide is the chemical compound with the formula [2CH]2NLi. Generally abbreviated LDA, it is a strong base used in organic chemistry for the deprotonation of weakly acidic compounds. The reagent has been widely accepted because it is soluble in non-polar organic solvents and it...
(LDA), which is quite commonly used.
Lithium amide can be made by adding lithium
Lithium
Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly...
metal to liquid ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
:
- 2Li + 2NH3 → 2LiNH2 + H2
Lithium amides in general can be similarly formed, substituting ammonia with the appropriate amine:
- 2Li + 2R2NH → 2LiNR2 + H2
Lithium amides are very reactive compounds and can act as strong bases
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
. Unless the nitrogen atom is hindered, as in the case of LDA, they can also act as nucleophile
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron-pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. All molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are by definition Lewis bases.Nucleophilic describes the...
s.
Examples
The lithium salt of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinePiperidine
Piperidine is an organic compound with the molecular formula 5NH. This heterocyclic amine consists of a six-membered ring containing five methylene units and one nitrogen atom...
has been crystallised as a tetramer:

Amine
Amines are organic compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines,...
crystallises as a trimer:

Alkoxide
An alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They can be written as RO−, where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands...
s and amides. These are related to the superbases which are mixtures of metal alkoxides and alkyls. The cyclic oligomers form when the nitrogen of the amide forms a sigma bond
Sigma bond
In chemistry, sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent chemical bond. They are formed by head-on overlapping between atomic orbitals. Sigma bonding is most clearly defined for diatomic molecules using the language and tools of symmetry groups. In this formal approach, a σ-bond is...
to a lithium while the nitrogen lone pair
Lone pair
In chemistry, a lone pair is a valence electron pair without bonding or sharing with other atoms. They are found in the outermost electron shell of an atom, so lone pairs are a subset of a molecule's valence electrons...
binds to another metal centre.
Other organolithium compounds (such as BuLi
Butyl lithium
Butyllithium may refer to one of three isomeric organolithium reagents used in chemical synthesis:*n-Butyllithium, abbreviated BuLi or nBuLi*sec-Butyllithium, abbreviated sec-BuLi or sBuLi...
) are generally considered to exist in and function via high-order, aggregated species.

