
Leaf Area Index
Encyclopedia
Leaf Area Index The Global Climate Observing System defines LAI as "one half the total green leaf area per unit ground
surface area. On sloping surfaces, the LAI should be projected to the normal to the slope. LAI is expressed in terms of square meters of leaf (half surface area) per square meter of ground. " (Law et al., 2010)
LAI ranges from 0 (bare ground) to over 10 (dense conifer forests).
.
In conifers, three different definitions have been used:
http://www.uni-giessen.de/~gh1461/plapada/lai/lai.html
, evapotranspiration and as a reference tool for crop
growth. As such, LAI plays an essential role in theoretical production ecology
. An inverse exponential relation between LAI and light interception, which is linearly proportional to the primary production rate, has been established:
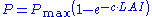
where Pmax designates the maximum primary production
and designates a crop-specific growth coefficient
designates a crop-specific growth coefficient
. This inverse exponential function is called the primary production function.
of foliage from a plant canopy, measuring the leaf area per sample plot and dividing it by the plot land surface area. Indirect methods measure canopy geometry or light extinction and relate it to LAI.
Traditional LAI meters require each plant leaf to be stripped and fed through the entrance of the machine, which can be likened to a kind of crude image scanner
.
 Indirect methods of estimating LAI in situ can be divided in two categories: (1) indirect contact LAI measurements such
Indirect methods of estimating LAI in situ can be divided in two categories: (1) indirect contact LAI measurements such
as plumb lines and inclined point quadrats; and (2) indirect non-contact measurements. Due to the subjectivity and labor involved with the first method, indirect non-contact measurements are typically preferred. Non-contact LAI tools, such as hemispherical photography
, the LAI-2000 http://www.licor.com/env/Products/AreaMeters/lai2000/2000_intro.jsp from LI-COR Biosciences
and the LP-80 LAI ceptometer http://www.decagon.com/ag_research/canopy/lp80.php from Decagon Devices
, measure LAI in a non-destructive way. Hemispherical photography
methods estimate LAI and other canopy structure attributes from analyzing upward-looking fisheye
photographs taken beneath the plant canopy. The LAI-2000 calculates LAI and other canopy structure attributes from solar radiation measurements made with a wide-angle optical sensor. Measurements made above and below the canopy are used to determine canopy light interception at five angles, from which LAI is computed using a model of radiative transfer in vegetative canopies. The LP-80 calculates LAI by means of measuring the difference between light levels above the canopy and at ground level, and factoring in the leaf angle distribution, solar zenith angle, and plant extinction coefficient. Such indirect methods, where LAI is calculated based upon observations of other variables (canopy geometry, light interception, leaf length and width, etc.) are generally faster, amenable to automation, and thereby allow for a larger number of spatial samples to be obtained. For reasons of convenience when compared to the direct (destructive) methods, these tools are becoming more and more important.
The disadvantage of the indirect method is that in some cases it can underestimate the value of LAI in very dense canopies, as it does not account for leaves that lie on each other, and essentially act as one leaf according to the theoretical LAI models.
surface area. On sloping surfaces, the LAI should be projected to the normal to the slope. LAI is expressed in terms of square meters of leaf (half surface area) per square meter of ground. " (Law et al., 2010)
LAI ranges from 0 (bare ground) to over 10 (dense conifer forests).
LAI in silviculture
Forestry scientists often define Leaf Area Index as the one-sided green leaf area per unit ground surface area in broadleaf canopiesCanopy (forest)
In biology, the canopy is the aboveground portion of a plant community or crop, formed by plant crowns.For forests, canopy also refers to the upper layer or habitat zone, formed by mature tree crowns and including other biological organisms .Sometimes the term canopy is used to refer to the extent...
.
In conifers, three different definitions have been used:
- Total needle surface area per unit ground area
- Half of the total needle surface area per unit horizontal ground area (Chen and Black, 1992)
- Projected needle area per unit ground area
http://www.uni-giessen.de/~gh1461/plapada/lai/lai.html
Interpretation and application of LAI
LAI is used to predict photosynthetic primary productionPrimary production
400px|thumb|Global oceanic and terrestrial photoautotroph abundance, from September [[1997]] to August 2000. As an estimate of autotroph biomass, it is only a rough indicator of primary production potential, and not an actual estimate of it...
, evapotranspiration and as a reference tool for crop
Crop
Crop may refer to:* Crop, a plant grown and harvested for agricultural use* Crop , part of the alimentary tract of some animals* Crop , a modified whip used in horseback riding or disciplining humans...
growth. As such, LAI plays an essential role in theoretical production ecology
Theoretical production ecology
Theoretical production ecology tries to quantitatively study the growth of crops.The plant is treated as a kind of biological factory, which processes light, carbon dioxide, water and nutrients into harvestable parts....
. An inverse exponential relation between LAI and light interception, which is linearly proportional to the primary production rate, has been established:
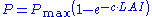
where Pmax designates the maximum primary production
Primary production
400px|thumb|Global oceanic and terrestrial photoautotroph abundance, from September [[1997]] to August 2000. As an estimate of autotroph biomass, it is only a rough indicator of primary production potential, and not an actual estimate of it...
and
 designates a crop-specific growth coefficient
designates a crop-specific growth coefficientCoefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
. This inverse exponential function is called the primary production function.
Determining LAI
LAI is determined directly by taking a statistically significant sampleSample (statistics)
In statistics, a sample is a subset of a population. Typically, the population is very large, making a census or a complete enumeration of all the values in the population impractical or impossible. The sample represents a subset of manageable size...
of foliage from a plant canopy, measuring the leaf area per sample plot and dividing it by the plot land surface area. Indirect methods measure canopy geometry or light extinction and relate it to LAI.
Direct methods
Direct methods require stripping and measuring the foliage of plant canopy samples. LAI for clip plots or individual plants is measured by hand or by using an LAI meter.Traditional LAI meters require each plant leaf to be stripped and fed through the entrance of the machine, which can be likened to a kind of crude image scanner
Image scanner
In computing, an image scanner—often abbreviated to just scanner—is a device that optically scans images, printed text, handwriting, or an object, and converts it to a digital image. Common examples found in offices are variations of the desktop scanner where the document is placed on a glass...
.
Indirect methods

as plumb lines and inclined point quadrats; and (2) indirect non-contact measurements. Due to the subjectivity and labor involved with the first method, indirect non-contact measurements are typically preferred. Non-contact LAI tools, such as hemispherical photography
Hemispherical photography
Hemispherical photography, also known as fisheye or canopy photography, is a technique to estimate solar radiation and characterize plant canopy geometry using photographs taken looking upward through an extreme wide-angle lens . Typically, the viewing angle approaches or equals 180-degrees, such...
, the LAI-2000 http://www.licor.com/env/Products/AreaMeters/lai2000/2000_intro.jsp from LI-COR Biosciences
LI-COR Biosciences
LI-COR Biosciences designs, manufactures, and markets instruments for biological and environmental research. It is ISO 9001 certified, meaning that it demonstrates "its ability to consistently provide products that enhance customer satisfaction and meet applicable statutory and regulatory...
and the LP-80 LAI ceptometer http://www.decagon.com/ag_research/canopy/lp80.php from Decagon Devices
Decagon Devices
Decagon Devices is an American corporation that designs and markets scientific instruments, sensors, data loggers and accessories. Decagon was founded in 1988 by Dr. Gaylon Campbell. Currently, Decagon designs and manufactures several different types of instruments that are used in both...
, measure LAI in a non-destructive way. Hemispherical photography
Hemispherical photography
Hemispherical photography, also known as fisheye or canopy photography, is a technique to estimate solar radiation and characterize plant canopy geometry using photographs taken looking upward through an extreme wide-angle lens . Typically, the viewing angle approaches or equals 180-degrees, such...
methods estimate LAI and other canopy structure attributes from analyzing upward-looking fisheye
Fisheye
Fisheye may refer to:* The eye of a fish or other aquatic creature resembling a fish* Fisheye lens, used in photography* Fisheye, a character from the anime Sailor Moon* FishEye , a revision control browser by Atlassian Software Systems...
photographs taken beneath the plant canopy. The LAI-2000 calculates LAI and other canopy structure attributes from solar radiation measurements made with a wide-angle optical sensor. Measurements made above and below the canopy are used to determine canopy light interception at five angles, from which LAI is computed using a model of radiative transfer in vegetative canopies. The LP-80 calculates LAI by means of measuring the difference between light levels above the canopy and at ground level, and factoring in the leaf angle distribution, solar zenith angle, and plant extinction coefficient. Such indirect methods, where LAI is calculated based upon observations of other variables (canopy geometry, light interception, leaf length and width, etc.) are generally faster, amenable to automation, and thereby allow for a larger number of spatial samples to be obtained. For reasons of convenience when compared to the direct (destructive) methods, these tools are becoming more and more important.
Disadvantages of methods
The disadvantage of the direct method is that it is destructive, time consuming and expensive, especially if the study area is very large.The disadvantage of the indirect method is that in some cases it can underestimate the value of LAI in very dense canopies, as it does not account for leaves that lie on each other, and essentially act as one leaf according to the theoretical LAI models.
See also
- Canopy (ecology)
- Hemispherical photographyHemispherical photographyHemispherical photography, also known as fisheye or canopy photography, is a technique to estimate solar radiation and characterize plant canopy geometry using photographs taken looking upward through an extreme wide-angle lens . Typically, the viewing angle approaches or equals 180-degrees, such...
- Normalized Difference Vegetation IndexNormalized Difference Vegetation IndexThe Normalized Difference Vegetation Index is a simple graphical indicator that can be used to analyze remote sensing measurements, typically but not necessarily from a space platform, and assess whether the target being observed contains live green vegetation or not.-Brief history:The exploration...
- Specific leaf areaSpecific leaf area-Application:Specific leaf area can be used to estimate the reproductive strategy of a particular plant based upon light and moisture levels, among other factors. Specific leaf area is one of the most widely accepted key leaf characteristics used during the study of leaf traits...

