
Lattice diffusion coefficient
Encyclopedia
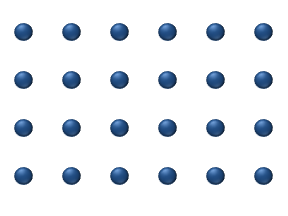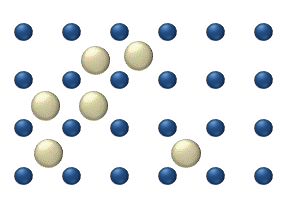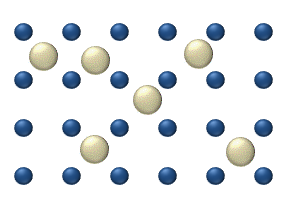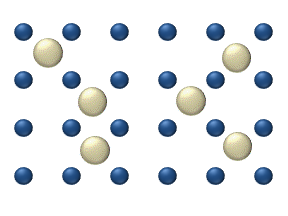
Atomic diffusion
Atomic diffusion is a diffusion process whereby the random thermally-activated movement of atoms in a solid results in the net transport of atoms. For example, helium atoms inside a balloon can diffuse through the wall of the balloon and escape, resulting in the balloon slowly deflating. Other air...
within a crystalline lattice . Diffusion within the crystal lattice occurs by either interstitial
Interstitial defect
Interstitials are a variety of crystallographic defects, i.e. atoms which occupy a site in the crystal structure at which there is usually not an atom, or two or more atoms sharing one or more lattice sites such that the number of atoms is larger than the number of lattice sites.They are generally...
or substitutional mechanisms and is referred to as lattice diffusion. In interstitial lattice diffusion, a diffusant (such as C in an iron alloy), will diffuse in between the lattice structure of another crystalline element. In substitutional lattice diffusion (self-diffusion for example), the atom can only move by substituting place with another atom. Substitutional lattice diffusion is often contingent upon the availability of point vacancies throughout the crystal lattice. Diffusing particles migrate from point vacancy to point vacancy by the rapid, essentially random jumping about (jump diffusion). Since the prevalence of point vacancies increases in accordance with the Arrhenius equation
Arrhenius equation
The Arrhenius equation is a simple, but remarkably accurate, formula for the temperature dependence of the reaction rate constant, and therefore, rate of a chemical reaction. The equation was first proposed by the Dutch chemist J. H. van 't Hoff in 1884; five years later in 1889, the Swedish...
, the rate of crystal solid state diffusion increases with temperature. For a single atom in a defect-free crystal, the movement can be described by the "random walk" model.

