Larsen syndrome
Encyclopedia
Larsen syndrome is a rare usually autosomal
dominant congenital disorder
that occurs in about every 1 in 100,000 people. Its symptoms include hypermobility
, congenital dislocations, brachycephaly
and cleft palate. It may rarely be recessive.
The condition was first described in a 1950 journal report by L. J. Larsen, et al.
It is caused by a resistance to Growth hormone (GH) secondary to a defect in GH receptors. Investigations reveal high levels of GH and low levels of Insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1).
Resources:
www.cleftsmile.org Cleft Lip and Palate Foundation of Smiles
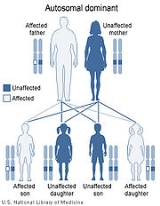
 Larsen syndrome is caused by mutation
Larsen syndrome is caused by mutation
s in the FLNB
(Filamin B) gene. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, which means the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome
, and only one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
dominant congenital disorder
Congenital disorder
A congenital disorder, or congenital disease, is a condition existing at birth and often before birth, or that develops during the first month of life , regardless of causation...
that occurs in about every 1 in 100,000 people. Its symptoms include hypermobility
Hypermobility
Hypermobility describes joints that stretch farther than is normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists, bend their knee joints backwards, put their leg behind the head or other contortionist performances...
, congenital dislocations, brachycephaly
Brachycephaly
Brachycephaly, also known as flat head syndrome, is a type of cephalic disorder. This can result from premature fusion of the coronal sutures or from external deformation . The coronal suture is the fibrous joint that unites the frontal bone with the two parietal bones of the skull. The parietal...
and cleft palate. It may rarely be recessive.
The condition was first described in a 1950 journal report by L. J. Larsen, et al.
It is caused by a resistance to Growth hormone (GH) secondary to a defect in GH receptors. Investigations reveal high levels of GH and low levels of Insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1).
Symptoms
A more complete list of symptoms includes:- Multiple joint dislocations
- Foot deformities
- Non-tapering, cylindrical shaped fingers
- Unusual facial appearance
- Less commonly occurring:
- Short stature
- Additional skeletal abnormalities
- Cleft palate
- Heart defects
- Hearing impairment
- Mental retardationMental retardationMental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
- Pulmonary hypoplasiaPulmonary hypoplasiaPulmonary hypoplasia is incomplete development of the lungs, resulting in an abnormally low number or size of bronchopulmonary segments or alveoli. A congenital malformation, it most often occurs secondary to other fetal abnormalities that interfere with normal development of the lungs...
Resources:
www.cleftsmile.org Cleft Lip and Palate Foundation of Smiles
Genetics

Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s in the FLNB
FLNB
Filamin B, beta , also known as FLNB, is a human cytoplasmic protein. It regulates intracellular communication and signalling by cross-linking the protein actin to allow direct communication between the cell membrane and cytoskeletal network, to control and guide proper skeletal...
(Filamin B) gene. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, which means the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
, and only one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.

