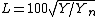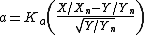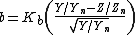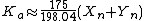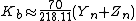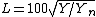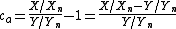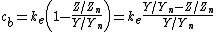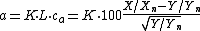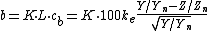
Lab color space
Encyclopedia
Opponent process
The color opponent process is a color theory that states that the human visual system interprets information about color by processing signals from cones and rods in an antagonistic manner...
space with dimension L for lightness
Lightness (color)
Lightness is a property of a color, or a dimension of a color space, that is defined in a way to reflect the subjective brightness perception of a color for humans along a lightness–darkness axis. A color's lightness also corresponds to its amplitude.Various color models have an explicit term for...
and a and b for the color-opponent dimensions, based on nonlinearly compressed CIE XYZ color space coordinates.
The coordinates of the Hunter 1948 L, a, b color space are L, a, and b. However, Lab is now more often used as an informal abbreviation for the CIE 1976 (L*, a*, b*) color space (also called CIELAB, whose coordinates are actually L*, a*, and b*). Thus the initials Lab by themselves are somewhat ambiguous. The color spaces are related in purpose, but differ in implementation.
Both spaces are derived from the "master" space CIE 1931 XYZ color space
CIE 1931 color space
In the study of color perception, one of the first mathematically defined color spaces is the CIE 1931 XYZ color space, created by the International Commission on Illumination in 1931....
, which can predict which spectral power distribution
Spectral power distribution
In color science and radiometry, a spectral power distribution describes the power per unit area per unit wavelength of an illumination , or more generally, the per-wavelength contribution to any radiometric quantity .Mathematically, for the spectral...
s will be perceived as the same color (see metamerism
Metamerism (color)
In colorimetry, metamerism is the matching of apparent color of objects with different spectral power distributions. Colors that match this way are called metamers....
), but which is not particularly perceptually uniform. Strongly influenced by the Munsell color system
Munsell color system
In colorimetry, the Munsell color system is a color space that specifies colors based on three color dimensions: hue, value , and chroma . It was created by Professor Albert H...
, the intention of both "Lab" color spaces is to create a space which can be computed via simple formulas from the XYZ space, but is more perceptually uniform than XYZ. Perceptually uniform means that a change of the same amount in a color value should produce a change of about the same visual importance. When storing colors in limited precision values, this can improve the reproduction of tones. Both Lab spaces are relative to the white point
White point
A white point is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending on the application, different definitions of white are needed to give acceptable results...
of the XYZ data they were converted from. Lab values do not define absolute colors unless the white point is also specified. Often, in practice, the white point is assumed to follow a standard and is not explicitly stated (e.g., for "absolute colorimetric" rendering intent ICC L*a*b* values are relative to CIE standard illuminant
Standard illuminant
A standard illuminant is a theoretical source of visible light with a profile which is published. Standard illuminants provide a basis for comparing images or colors recorded under different lighting.-CIE illuminants:...
D50, while they are relative to the unprinted substrate for other rendering intents).
The lightness correlate in CIELAB is calculated using the cube root of the relative luminance.
The L*a*b* color space includes all perceivable colors which means that its gamut exceeds those of the RGB and CMYK color models. One of the most important attributes of the L*a*b*-model is the device independency. This means that the colors are defined independent of their nature of creation or the device they are displayed on. The L*a*b* color space is used e.g. in Adobe Photoshop when graphics for print have to be converted from RGB to CMYK, as the L*a*b* gamut includes both the RGB and CMYK gamut. Also it is used as an interchange format between different devices as for its device independency.
Advantages of Lab
Unlike the RGBRGB color model
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which red, green, and blue light is added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors...
and CMYK
CMYK color model
The CMYK color model is a subtractive color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. CMYK refers to the four inks used in some color printing: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key...
color models, Lab color is designed to approximate human vision. It aspires to perceptual uniformity, and its L component closely matches human perception of lightness. It can thus be used to make accurate color balance corrections by modifying output curves
Curve (tonality)
In image editing, a curve is a remapping of image tonality, specified as a function from input level to output level, used as a way to emphasize colours or other elements in a picture....
in the a and b components, or to adjust the lightness contrast using the L component. In RGB or CMYK spaces, which model the output of physical devices rather than human visual perception, these transformations can only be done with the help of appropriate blend modes
Blend modes
Blend modes in digital image editing are used to determine how two Layers are blended into each other. The default blend mode in most applications is simply to hide the lower layer with whatever is present in the top layer...
in the editing application.
Because Lab space is much larger than the gamut
Gamut
In color reproduction, including computer graphics and photography, the gamut, or color gamut , is a certain complete subset of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors which can be accurately represented in a given circumstance, such as within a given color space or by a...
of computer displays, printers, or even human vision, a bitmap image represented as Lab requires more data per pixel to obtain the same precision as an RGB or CMYK bitmap. In the 1990s, when computer hardware and software was mostly limited to storing and manipulating 8 bit/channel bitmaps, converting an RGB image to Lab and back was a lossy operation. With 16 bit/channel support now common, this is no longer such a problem.
Additionally, many of the "colors" within Lab space fall outside the gamut of human vision, and are therefore purely imaginary; these "colors" cannot be reproduced in the physical world. Though color management software, such as that built in to image editing applications, will pick the closest in-gamut approximation, changing lightness, colorfulness, and sometimes hue in the process, author Dan Margulis
Dan Margulis
Dan Margulis is an expert on color correction and reproduction of photographs, using Adobe Photoshop or similar software.His Professional Photoshop series is widely viewed as an authoritative work in the field of digital color correction of photographs...
claims that this access to imaginary color
Imaginary color
Non-physical, unrealizable, or imaginary colors are points in a color space that correspond to combinations of cone cell responses that cannot be produced by any physical light spectrum. Thus, no object can have an imaginary color, and imaginary colors cannot be seen under normal circumstances...
s is useful, going between several steps in the manipulation of a picture.
Which "Lab"?
Some specific uses of the abbreviation in software, literature etc.- In Adobe PhotoshopAdobe PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop is a graphics editing program developed and published by Adobe Systems Incorporated.Adobe's 2003 "Creative Suite" rebranding led to Adobe Photoshop 8's renaming to Adobe Photoshop CS. Thus, Adobe Photoshop CS5 is the 12th major release of Adobe Photoshop...
, image editing using "Lab mode" is CIELAB D50. - In ICC profileICC profileIn color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium...
s, the "Lab color space" used as a profile connection space is CIELAB D50. - In TIFF files, the CIELAB color space may be used.
- In PDF documents, the "Lab color space" is CIELAB.
CIE 1976 (L*, a*, b*) color space (CIELAB)
CIE L*a*b* (CIELAB) is the most complete color spaceColor space
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components...
specified by the International Commission on Illumination
International Commission on Illumination
The International Commission on Illumination is the international authority on light, illumination, color, and color spaces...
(French Commission internationale de l'éclairage, hence its CIE initialism). It describes all the colors visible
Color vision
Color vision is the capacity of an organism or machine to distinguish objects based on the wavelengths of the light they reflect, emit, or transmit...
to the human eye and was created to serve as a device independent model to be used as a reference.
The three coordinates of CIELAB represent the lightness of the color (L* = 0 yields black and L* = 100 indicates diffuse white; specular white may be higher), its position between red/magenta and green (a*, negative values indicate green while positive values indicate magenta) and its position between yellow and blue (b*, negative values indicate blue and positive values indicate yellow). The asterisk (*) after L, a and b are part of the full name, since they represent L*, a* and b*, to distinguish them from Hunter's L, a, and b, described below.
Since the L*a*b* model is a three-dimensional model, it can only be represented properly in a three-dimensional space. Two-dimensional depictions include chromaticity diagrams: sections of the color solid
Color solid
A color solid is the three-dimensional representation of a color model, an analog of the two-dimensional color wheel. The added spatial dimension allows a color solid to depict an added dimension of color variation...
with a fixed lightness. It is crucial to realize that the visual representations of the full gamut
Gamut
In color reproduction, including computer graphics and photography, the gamut, or color gamut , is a certain complete subset of colors. The most common usage refers to the subset of colors which can be accurately represented in a given circumstance, such as within a given color space or by a...
of colors in this model are never accurate; they are there just to help in understanding the concept.
Because the red/green and yellow/blue opponent channels are computed as differences of lightness transformations of (putative) cone responses, CIELAB is a chromatic value color space.
A related color space, the CIE 1976 (L*, u*, v*) color space (a.k.a. CIELUV), preserves the same L* as L*a*b* but has a different representation of the chromaticity components. CIELUV can also be expressed in cylindrical form (CIELCH), with the chromaticity components replaced by correlates of chroma
Chrominance
Chrominance is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture, separately from the accompanying luma signal . Chrominance is usually represented as two color-difference components: U = B' − Y' and V = R' − Y'...
and hue
Hue
Hue is one of the main properties of a color, defined technically , as "the degree to which a stimulus can be describedas similar to or different from stimuli that are described as red, green, blue, and yellow,"...
.
Since CIELAB and CIELUV, the CIE has been incorporating an increasing number of color appearance phenomena into their models, to better model color vision. These color appearance models, of which CIELAB, although not designed as can be seen as a simple example, culminated with CIECAM02
CIECAM02
Published in 2002 by the CIE Technical Committee 8-01 , as of 2008 CIECAM02 is the most recent color appearance model ratified by the CIE, and the successor of CIECAM97s.| quote=The CIECAM97s model was adopted by the CIE in 1997 for color imaging applications. It includes forward and reverse modes...
.
Measuring differences
The nonlinear relations for L*, a*, and b* are intended to mimic the nonlinear response of the eye. Furthermore, uniform changes of components in the L*a*b* color space aim to correspond to uniform changes in perceived color, so the relative perceptual differences between any two colors in L*a*b* can be approximated by treating each color as a point in a three dimensional space (with three components: L*, a*, b*) and taking the Euclidean distanceEuclidean distance
In mathematics, the Euclidean distance or Euclidean metric is the "ordinary" distance between two points that one would measure with a ruler, and is given by the Pythagorean formula. By using this formula as distance, Euclidean space becomes a metric space...
between them.
RGB and CMYK conversions
There are no simple formulas for conversion between RGBRGB color model
The RGB color model is an additive color model in which red, green, and blue light is added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors...
or CMYK
CMYK color model
The CMYK color model is a subtractive color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. CMYK refers to the four inks used in some color printing: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key...
values and L*a*b*, because the RGB and CMYK color models are device dependent. The RGB or CMYK values first need to be transformed to a specific absolute color space
Absolute color space
In color science, there are two meanings of the term absolute color space:* A color space in which the perceptual difference between colors is directly related to distances between colors as represented by points in the color space....
, such as sRGB
SRGB color space
sRGB is a standard RGB color space created cooperatively by HP and Microsoft in 1996 for use on monitors, printers, and the Internet.sRGB uses the ITU-R BT.709 primaries, the same as are used in studio monitors and HDTV, and a transfer function typical of CRTs...
or Adobe RGB
Adobe RGB color space
The Adobe RGB color space is an RGB color space developed by Adobe Systems in 1998. It was designed to encompass most of the colors achievable on CMYK color printers, but by using RGB primary colors on a device such as the computer display...
. This adjustment will be device dependent, but the resulting data from the transform will be device independent, allowing data to be transformed to the CIE 1931 color space
CIE 1931 color space
In the study of color perception, one of the first mathematically defined color spaces is the CIE 1931 XYZ color space, created by the International Commission on Illumination in 1931....
and then transformed into L*a*b*.
Range of L*a*b* coordinates
As mentioned previously, the L* coordinate ranges from 0 to 100. The possible range of a* and b* coordinates is independent of the color space that one is converting from, since the conversion below uses X and Y which come from RGB.The forward transformation
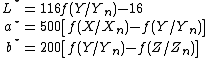
where
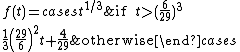
Here Xn, Yn and Zn are the CIE XYZ tristimulus values of the reference white point
White point
A white point is a set of tristimulus values or chromaticity coordinates that serve to define the color "white" in image capture, encoding, or reproduction. Depending on the application, different definitions of white are needed to give acceptable results...
(the subscript n suggests "normalized").
The division of the f(t) function into two domains was done to prevent an infinite slope at . f(t) was assumed to be linear below some , and was assumed to match the t1/3 part of the function at t0 in both value and slope. In other words:
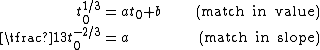
The slope was chosen to be . The above two equations can be solved for a and t0:
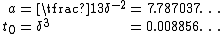
where . Note that the slope at the join is .
The reverse transformation
The reverse transformation is most easily expressed using the inverse of the function f above: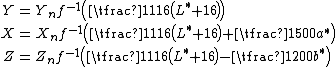
where
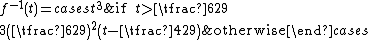
Hunter Lab Color Space
L is a correlate of lightnessLightness (color)
Lightness is a property of a color, or a dimension of a color space, that is defined in a way to reflect the subjective brightness perception of a color for humans along a lightness–darkness axis. A color's lightness also corresponds to its amplitude.Various color models have an explicit term for...
, and is computed from the Y tristimulus value using Priest's approximation to Munsell value:
where Yn is the Y tristimulus value of a specified white object. For surface-color applications, the specified white object is usually (though not always) a hypothetical material with unit reflectance and which follows Lambert's law. The resulting L will be scaled between 0 (black) and 100 (white); roughly ten times the Munsell value. Note that a medium lightness of 50 is produced by a luminance of 25, since
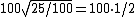
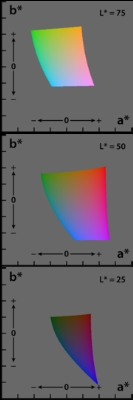
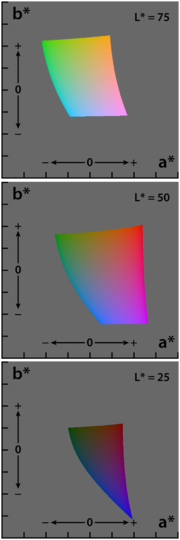
a and b are termed opponent color axes. a represents, roughly, Redness (positive) versus Greenness (negative). It is computed as:
where
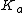 is a coefficient which depends upon the illuminant (for D65, Ka is 172.30; see approximate formula below) and
is a coefficient which depends upon the illuminant (for D65, Ka is 172.30; see approximate formula below) and 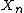 is the X tristimulus value of the specified white object.
is the X tristimulus value of the specified white object.The other opponent color axis, b, is positive for yellow colors and negative for blue colors. It is computed as:
where Kb is a coefficient which depends upon the illuminant (for D65, Kb is 67.20; see approximate formula below) and Zn is the Z tristimulus value of the specified white object.
Both a and b will be zero for objects which have the same chromaticity
Chromaticity
Chromaticity is an objective specification of the quality of a color regardless of its luminance, that is, as determined by its hue and colorfulness ....
coordinates as the specified white objects (i.e., achromatic, grey, objects).
Approximate formulas for Ka and Kb
In the previous version of the Hunter Lab color space, Ka was 175 and Kb was 70. Apparently, Hunter Associates Lab discovered that better agreement could be obtained with other color difference metrics, such as CIELAB (see above) by allowing these coefficients to depend upon the illuminants. Approximate formulæ are:which result in the original values for Illuminant C, the original illuminant with which the Lab color space was used.
The Hunter Lab Color Space as an Adams chromatic valence space
Adams chromatic valence color spaces are based on two elements: a (relatively) uniform lightness scale, and a (relatively) uniform chromaticityChromaticity
Chromaticity is an objective specification of the quality of a color regardless of its luminance, that is, as determined by its hue and colorfulness ....
scale. If we take as the uniform lightness scale Priest's approximation to the Munsell Value scale, which would be written in modern notation:
and, as the uniform chromaticity coordinates:
where ke is a tuning coefficient, we obtain the two chromatic axes:
and
which is identical to the Hunter Lab formulae given above if we select and . Therefore, the Hunter Lab color space is an Adams chromatic valence color space.
External links
- Demonstrative color conversion applet
- CIELAB Color Space by Gernot Hoffmann, includes explanations of L*a*b* conversion formulae, graphical depictions of various gamuts plotted in L*a*b* space, and PostScript code for performing the color transformations.
- Color Converter is an application for Windows, Linux and Mac OS X providing conversion between Hunter-Lab and several other color spaces including RGB and CMYK.