L2TP
Encyclopedia
In computer network
ing, Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol
used to support virtual private network
s (VPNs). It does not provide any encryption
or confidentiality
by itself; it relies on an encryption protocol that it passes within the tunnel to provide privacy.
(PPP): Cisco's Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol
(L2F) and US Robotics Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
(PPTP). A new version of this protocol, L2TPv3
, was published as proposed standard RFC 3931 in 2005. L2TPv3 provides additional security features, improved encapsulation, and the ability to carry data links other than simply PPP over an IP network (e.g., Frame Relay, Ethernet, ATM, etc).
(PPP) sessions within an L2TP tunnel. L2TP does not provide confidentiality or strong authentication by itself. IPsec
is often used to secure L2TP packets by providing confidentiality, authentication and integrity. The combination of these two protocols is generally known as L2TP/IPsec (discussed below).
The two endpoints of an L2TP tunnel are called the LAC (L2TP Access Concentrator) and the LNS (L2TP Network Server). The LAC is the initiator of the tunnel while the LNS is the server, which waits for new tunnels. Once a tunnel is established, the network traffic between the peers is bidirectional. To be useful for networking, higher-level protocols are then run through the L2TP tunnel. To facilitate this, an L2TP session (or call) is established within the tunnel for each higher-level protocol such as PPP. Either the LAC or LNS may initiate sessions. The traffic for each session is isolated by L2TP, so it is possible to set up multiple virtual networks across a single tunnel. MTU
should be considered when implementing L2TP.
The packets exchanged within an L2TP tunnel are categorised as either control packets or data packets. L2TP provides reliability features for the control packets, but no reliability for data packets. Reliability, if desired, must be provided by the nested protocols running within each session of the L2TP tunnel.
Field meanings:
Flags and version: control flags indicating data/control packet and presence of length, sequence, and offset fields.
Length (optional): Total length of the message in bytes, present only when length flag is set.
Tunnel ID: Indicates the identifier for the control connection.
Session ID: Indicates the identifier for a session within a tunnel.
Ns (optional): sequence number for this data or control message, beginning at zero and incrementing by one (modulo 216) for each message sent. Present only when sequence flag set.
Nr (optional): sequence number for expected message to be received. Nr is set to the Ns of the last in-order message received plus one (modulo 216). In data messages, Nr is reserved and, if present (as indicated by the S bit), MUST be ignored upon receipt..
Offset Size (optional): Specifies where payload data is located past the L2TP header. If the offset field is present, the L2TP header ends after the last byte of the offset padding. This field exists if the offset flag is set.
Offset Pad (optional): Variable length, as specified by the offset size. Contents of this field are undefined.
Payload data: Variable length (Max payload size = Max size of UDP packet − size of L2TP header)
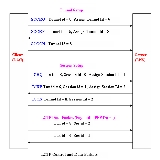
The list of L2TP Control messages exchanged between LAC and LNS, for handshaking before establishing a tunnel and session in voluntary tunneling method are

. This is referred to as L2TP/IPsec, and is standardized in IETF RFC 3193. The process of setting up an L2TP/IPsec VPN is as follows:
When the process is complete, L2TP packets between the endpoints are encapsulated by IPsec. Since the L2TP packet itself is wrapped and hidden within the IPsec packet, no information about the internal private network can be garnered from the encrypted packet. Also, it is not necessary to open UDP port 1701 on firewalls between the endpoints, since the inner packets are not acted upon until after IPsec data has been decrypted and stripped, which only takes place at the endpoints.
A potential point of confusion in L2TP/IPsec is the use of the terms 'tunnel' and 'secure channel'. The term 'tunnel' refers to a channel which allows untouched packets of one network to be transported over another network. In the case of L2TP/PPP, it allows L2TP/PPP packets to be transported over IP. A 'secure channel' refers to a connection within which the confidentiality of all data is guaranteed. In L2TP/IPsec, first IPsec provides a secure channel, then L2TP provides a tunnel.
provides two new configuration utilities that attempt to make using L2TP without IPsec easier, both described in sections that follow below:
Both these configuration utilities are not without their difficulties, and unfortunately, there is very little documentation about both "netsh advfirewall" and the IPsec client in WFwAS. One of the aforementioned difficulties is that it is not compatible with NAT
. Another problem is that servers must be specified only by IP address in the new Vista configuration utilities; the hostname of the server cannot be used, so if the IP address of the IPsec server changes, all clients will have to be informed of this new IP address (which also rules out servers that addressed by utilities such as DynDNS
).
. Again, the reselling cable provider doesn't appear as doing the transport.
Computer network
A computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
ing, Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol
Tunneling protocol
Computer networks use a tunneling protocol when one network protocol encapsulates a different payload protocol...
used to support virtual private network
Virtual private network
A virtual private network is a network that uses primarily public telecommunication infrastructure, such as the Internet, to provide remote offices or traveling users access to a central organizational network....
s (VPNs). It does not provide any encryption
Encryption
In cryptography, encryption is the process of transforming information using an algorithm to make it unreadable to anyone except those possessing special knowledge, usually referred to as a key. The result of the process is encrypted information...
or confidentiality
Confidentiality
Confidentiality is an ethical principle associated with several professions . In ethics, and in law and alternative forms of legal resolution such as mediation, some types of communication between a person and one of these professionals are "privileged" and may not be discussed or divulged to...
by itself; it relies on an encryption protocol that it passes within the tunnel to provide privacy.
History
Published in 1999 as proposed standard RFC 2661, L2TP has its origins primarily in two older tunneling protocols for Point-to-Point ProtocolPoint-to-Point Protocol
In networking, the Point-to-Point Protocol is a data link protocol commonly used in establishing a direct connection between two networking nodes...
(PPP): Cisco's Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol
Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol
L2F, or Layer 2 Forwarding, is a tunneling protocol developed by Cisco Systems, Inc. to establish virtual private network connections over the Internet. L2F does not provide encryption or confidentiality by itself; It relies on the protocol being tunneled to provide privacy...
(L2F) and US Robotics Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
Point-to-point tunneling protocol
The Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol is a method for implementing virtual private networks. PPTP uses a control channel over TCP and a GRE tunnel operating to encapsulate PPP packets....
(PPTP). A new version of this protocol, L2TPv3
L2TPv3
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol Version 3 is an IETF standard related to L2TP that can be used as an alternative protocol to Multiprotocol Label Switching for encapsulation of multiprotocol Layer 2 communications traffic over IP networks...
, was published as proposed standard RFC 3931 in 2005. L2TPv3 provides additional security features, improved encapsulation, and the ability to carry data links other than simply PPP over an IP network (e.g., Frame Relay, Ethernet, ATM, etc).
Description
The entire L2TP packet, including payload and L2TP header, is sent within a UDP datagram. It is common to carry Point-to-Point ProtocolPoint-to-Point Protocol
In networking, the Point-to-Point Protocol is a data link protocol commonly used in establishing a direct connection between two networking nodes...
(PPP) sessions within an L2TP tunnel. L2TP does not provide confidentiality or strong authentication by itself. IPsec
IPsec
Internet Protocol Security is a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session...
is often used to secure L2TP packets by providing confidentiality, authentication and integrity. The combination of these two protocols is generally known as L2TP/IPsec (discussed below).
The two endpoints of an L2TP tunnel are called the LAC (L2TP Access Concentrator) and the LNS (L2TP Network Server). The LAC is the initiator of the tunnel while the LNS is the server, which waits for new tunnels. Once a tunnel is established, the network traffic between the peers is bidirectional. To be useful for networking, higher-level protocols are then run through the L2TP tunnel. To facilitate this, an L2TP session (or call) is established within the tunnel for each higher-level protocol such as PPP. Either the LAC or LNS may initiate sessions. The traffic for each session is isolated by L2TP, so it is possible to set up multiple virtual networks across a single tunnel. MTU
Maximum transmission unit
In computer networking, the maximum transmission unit of a communications protocol of a layer is the size of the largest protocol data unit that the layer can pass onwards. MTU parameters usually appear in association with a communications interface...
should be considered when implementing L2TP.
The packets exchanged within an L2TP tunnel are categorised as either control packets or data packets. L2TP provides reliability features for the control packets, but no reliability for data packets. Reliability, if desired, must be provided by the nested protocols running within each session of the L2TP tunnel.
Tunneling models
An L2TP tunnel can extend across an entire PPP session or only across one segment of a two-segment session. This can be represented by four different tunneling models, namely http://publib.boulder.ibm.com/infocenter/iseries/v5r3/index.jsp?topic=/rzaiy/rzaiymultihop.htm http://www.cisco.com/en/US/tech/tk827/tk369/tk388/tsd_technology_support_sub-protocol_home.html http://technet2.microsoft.com/WindowsServer/en/library/04bd5817-0e41-46b7-9dda-d6340fce514f1033.mspx- voluntary tunnel
- compulsory tunnel — incoming call
- compulsory tunnel — remote dial
- L2TP multi-hop connection
L2TP packet structure
An L2TP packet consists of :| Bits 0–15 | Bits 16–31 |
|---|---|
| Flags and Version Info | Length (opt) |
| Tunnel ID | Session ID |
| Ns (opt) | Nr (opt) |
| Offset Size (opt) | Offset Pad (opt)...... |
| Payload data | |
Field meanings:
Flags and version: control flags indicating data/control packet and presence of length, sequence, and offset fields.
Length (optional): Total length of the message in bytes, present only when length flag is set.
Tunnel ID: Indicates the identifier for the control connection.
Session ID: Indicates the identifier for a session within a tunnel.
Ns (optional): sequence number for this data or control message, beginning at zero and incrementing by one (modulo 216) for each message sent. Present only when sequence flag set.
Nr (optional): sequence number for expected message to be received. Nr is set to the Ns of the last in-order message received plus one (modulo 216). In data messages, Nr is reserved and, if present (as indicated by the S bit), MUST be ignored upon receipt..
Offset Size (optional): Specifies where payload data is located past the L2TP header. If the offset field is present, the L2TP header ends after the last byte of the offset padding. This field exists if the offset flag is set.
Offset Pad (optional): Variable length, as specified by the offset size. Contents of this field are undefined.
Payload data: Variable length (Max payload size = Max size of UDP packet − size of L2TP header)
L2TP packet exchange
At the time of setup of L2TP connection, many control packets are exchanged between server and client to establish tunnel and session for each direction. One peer requests the other peer to assign a specific tunnel and session id through these control packets. Then using this tunnel and session id, data packets are exchanged with the compressed PPP frames as payload.The list of L2TP Control messages exchanged between LAC and LNS, for handshaking before establishing a tunnel and session in voluntary tunneling method are

L2TP/IPsec
Because of the lack of confidentiality inherent in the L2TP protocol, it is often implemented along with IPsecIPsec
Internet Protocol Security is a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session...
. This is referred to as L2TP/IPsec, and is standardized in IETF RFC 3193. The process of setting up an L2TP/IPsec VPN is as follows:
-
- Negotiation of IPsec security associationSecurity associationA Security Association is the establishment of shared security attributes between two network entities to support secure communication. An SA may include attributes such as: cryptographic algorithm and mode; traffic encryption key; and parameters for the network data to be passed over the...
(SA), typically through Internet key exchangeInternet key exchangeInternet Key Exchange is the protocol used to set up a security association in the IPsec protocol suite. IKE builds upon the Oakley protocol and ISAKMP...
(IKE). This is carried out over UDP port 500, and commonly uses either a shared password (so-called "pre-shared keys"), public keys, or X.509X.509In cryptography, X.509 is an ITU-T standard for a public key infrastructure and Privilege Management Infrastructure . X.509 specifies, amongst other things, standard formats for public key certificates, certificate revocation lists, attribute certificates, and a certification path validation...
certificates on both ends, although other keying methods exist. - Establishment of Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) communication in transport mode. The IP protocol number for ESP is 50 (compare TCP's 6 and UDP's 17). At this point, a secure channel has been established, but no tunneling is taking place.
- Negotiation and establishment of L2TP tunnel between the SA endpoints. The actual negotiation of parameters takes place over the SA's secure channel, within the IPsec encryption. L2TP uses UDP port 1701.
- Negotiation of IPsec security association
When the process is complete, L2TP packets between the endpoints are encapsulated by IPsec. Since the L2TP packet itself is wrapped and hidden within the IPsec packet, no information about the internal private network can be garnered from the encrypted packet. Also, it is not necessary to open UDP port 1701 on firewalls between the endpoints, since the inner packets are not acted upon until after IPsec data has been decrypted and stripped, which only takes place at the endpoints.
A potential point of confusion in L2TP/IPsec is the use of the terms 'tunnel' and 'secure channel'. The term 'tunnel' refers to a channel which allows untouched packets of one network to be transported over another network. In the case of L2TP/PPP, it allows L2TP/PPP packets to be transported over IP. A 'secure channel' refers to a connection within which the confidentiality of all data is guaranteed. In L2TP/IPsec, first IPsec provides a secure channel, then L2TP provides a tunnel.
Windows implementation
Windows VistaWindows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
provides two new configuration utilities that attempt to make using L2TP without IPsec easier, both described in sections that follow below:
- an MMCMicrosoft Management ConsoleMicrosoft Management Console is a component of Windows 2000 and its successors that provides system administrators and advanced users an interface for configuring and monitoring the system.- Snap-ins and consoles :...
snap-in called "Windows Firewall with Advanced Security" (WFwAS), located in Control Panel → Administrative Tools - the "netshNetshIn software, netsh, or network shell, is a utility included in Microsoft's Windows NT line of operating systems beginning with Windows 2000. It allows local or remote configuration of network devices such as the interface....
advfirewall" command-line tool
Both these configuration utilities are not without their difficulties, and unfortunately, there is very little documentation about both "netsh advfirewall" and the IPsec client in WFwAS. One of the aforementioned difficulties is that it is not compatible with NAT
Network address translation
In computer networking, network address translation is the process of modifying IP address information in IP packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device....
. Another problem is that servers must be specified only by IP address in the new Vista configuration utilities; the hostname of the server cannot be used, so if the IP address of the IPsec server changes, all clients will have to be informed of this new IP address (which also rules out servers that addressed by utilities such as DynDNS
DynDNS
Dyn is an infrastructure as a service company that provides Internet DNS and email delivery services for commercial and private users. It originally provided a free dynamic DNS service, which allowed users to have a subdomain that points to a computer with regularly changing IP addresses, such as...
).
L2TP in ADSL networks
L2TP is often used as a tunneling mechanism to resell ADSL endpoint connectivity at layer 2. An L2TP tunnel would sit between the user and the ISP the connection would be resold to, so the reselling ISP would not appear as doing the transport.L2TP in cable networks
L2TP is used by the cable Internet provider as a tunnelling mechanism to sell endpoint connectivity. The L2TP tunnel sits between the user and the ISPInternet service provider
An Internet service provider is a company that provides access to the Internet. Access ISPs directly connect customers to the Internet using copper wires, wireless or fiber-optic connections. Hosting ISPs lease server space for smaller businesses and host other people servers...
. Again, the reselling cable provider doesn't appear as doing the transport.
See also
- IPsecIPsecInternet Protocol Security is a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session...
- Layer 2 Forwarding ProtocolLayer 2 Forwarding ProtocolL2F, or Layer 2 Forwarding, is a tunneling protocol developed by Cisco Systems, Inc. to establish virtual private network connections over the Internet. L2F does not provide encryption or confidentiality by itself; It relies on the protocol being tunneled to provide privacy...
- Point-to-Point Tunneling ProtocolPoint-to-point tunneling protocolThe Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol is a method for implementing virtual private networks. PPTP uses a control channel over TCP and a GRE tunnel operating to encapsulate PPP packets....
- Point-to-Point ProtocolPoint-to-Point ProtocolIn networking, the Point-to-Point Protocol is a data link protocol commonly used in establishing a direct connection between two networking nodes...
Implementations
- Cisco: Cisco L2TP documentation, also read Technology brief from Cisco
- Open source and Linux: xl2tpd, Linux RP-L2TP, OpenL2TP, l2tpns, l2tpd (inactive), Linux L2TP/IPsec server, FreeBSD multi-link PPP daemon
- Microsoft: built-in client included with Windows 2000 and higher; Microsoft L2TP/IPsec VPN Client for Windows 98/Windows Me/Windows NT 4.0
- Apple: built-in client included with Mac OS X 10.3 and higher.
Internet standards and extensions
- RFC 2341 Cisco Layer Two Forwarding (Protocol) "L2F" (a predecessor to L2TP)
- RFC 2637 Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) (a predecessor to L2TP)
- RFC 2661 Layer Two Tunneling Protocol "L2TP"
- RFC 2809 Implementation of L2TP Compulsory Tunneling via RADIUS
- RFC 2888 Secure Remote Access with L2TP
- RFC 3070 Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) over Frame Relay
- RFC 3145 L2TP Disconnect Cause Information
- RFC 3193 Securing L2TP using IPsecIPsecInternet Protocol Security is a protocol suite for securing Internet Protocol communications by authenticating and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session...
- RFC 3301 Layer Two Tunnelling Protocol (L2TP): ATM access network
- RFC 3308 Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Differentiated Services
- RFC 3355 Layer Two Tunnelling Protocol (L2TP) Over ATM Adaptation Layer 5 (AAL5)
- RFC 3371 Layer Two Tunneling Protocol "L2TP" Management Information Base
- RFC 3437 Layer Two Tunneling Protocol Extensions for PPP Link Control Protocol Negotiation
- RFC 3438 Layer Two Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Internet Assigned Numbers: Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) Considerations Update
- RFC 3573 Signaling of Modem-On-Hold status in Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
- RFC 3817 Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) Active Discovery Relay for PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
- RFC 3931 Layer Two Tunneling Protocol - Version 3 (L2TPv3)
- RFC 4045 Extensions to Support Efficient Carrying of Multicast Traffic in Layer-2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
- RFC 4951 Fail Over Extensions for Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) "failover"
Other
- IANA assigned numbers for L2TP
- L2TP Extensions Working Group (l2tpext) - (where future standardization work is being coordinated)
- Using Linux as an L2TP/IPsec VPN client
- Configuring L2TP VPN in Windows

