
L-estimator
Encyclopedia
In robust statistics
, an L-estimator is an estimator
which equals a linear combination of order statistics of the measurements.
Consider, for example, the median
. Given n measurements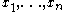 , where n is odd, the median equals
, where n is odd, the median equals 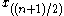 , the
, the 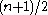 th order statistic (for
th order statistic (for 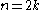 even, it is the average of two order statistics:
even, it is the average of two order statistics: 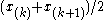 ). The median is therefore a simple example of an L-estimator. Other examples include the trimean
). The median is therefore a simple example of an L-estimator. Other examples include the trimean
, the trimmed mean, and the Winsorized mean
.
Not all L-estimators are robust: the minimum, maximum, mean
, and mid-range are all L-estimators, but have a breakdown point of 0. The breakdown point is defined as the fraction of the measurements which can be arbitrarily changed without causing the resulting estimate to tend to infinity (i.e., to "break down"). The breakdown point of an L-estimator is given by the closest order statistic to the minimum or maximum: for instance, the median has a breakdown point of 50% (the highest possible), and a n% trimmed or Winsorized mean has a breakdown point of n%.
Robust statistics
Robust statistics provides an alternative approach to classical statistical methods. The motivation is to produce estimators that are not unduly affected by small departures from model assumptions.- Introduction :...
, an L-estimator is an estimator
Estimator
In statistics, an estimator is a rule for calculating an estimate of a given quantity based on observed data: thus the rule and its result are distinguished....
which equals a linear combination of order statistics of the measurements.
Consider, for example, the median
Median
In probability theory and statistics, a median is described as the numerical value separating the higher half of a sample, a population, or a probability distribution, from the lower half. The median of a finite list of numbers can be found by arranging all the observations from lowest value to...
. Given n measurements
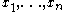 , where n is odd, the median equals
, where n is odd, the median equals 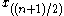 , the
, the 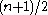 th order statistic (for
th order statistic (for 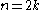 even, it is the average of two order statistics:
even, it is the average of two order statistics: 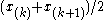 ). The median is therefore a simple example of an L-estimator. Other examples include the trimean
). The median is therefore a simple example of an L-estimator. Other examples include the trimeanTrimean
In statistics the trimean , or Tukey's trimean, is a measure of a probability distribution's location defined as a weighted average of the distribution's median and its two quartiles:This is equivalent to the average of the median and the midhinge:...
, the trimmed mean, and the Winsorized mean
Winsorized mean
A Winsorized mean is a Winsorized statistical measure of central tendency, much like the mean and median, and even more similar to the truncated mean...
.
Not all L-estimators are robust: the minimum, maximum, mean
Mean
In statistics, mean has two related meanings:* the arithmetic mean .* the expected value of a random variable, which is also called the population mean....
, and mid-range are all L-estimators, but have a breakdown point of 0. The breakdown point is defined as the fraction of the measurements which can be arbitrarily changed without causing the resulting estimate to tend to infinity (i.e., to "break down"). The breakdown point of an L-estimator is given by the closest order statistic to the minimum or maximum: for instance, the median has a breakdown point of 50% (the highest possible), and a n% trimmed or Winsorized mean has a breakdown point of n%.

