
Kutrigurs
Encyclopedia
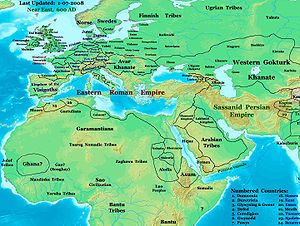
Bulgars
The Bulgars were a semi-nomadic who flourished in the Pontic Steppe and the Volga basin in the 7th century.The Bulgars emerge after the collapse of the Hunnic Empire in the 5th century....
that inhabited the Eurasian plains during the Dark Ages
Dark Ages
The "Dark Ages" is a historical periodization emphasizing the cultural and economic deterioration that supposedly occurred in Europe following the decline of the Roman Empire. The label employs traditional light-versus-darkness imagery to contrast the "darkness" of the period with earlier and later...
. They came into existence when the Eurasian Avars
Eurasian Avars
The Eurasian Avars or Ancient Avars were a highly organized nomadic confederacy of mixed origins. They were ruled by a khagan, who was surrounded by a tight-knit entourage of nomad warriors, an organization characteristic of Turko-Mongol groups...
conquered half of the Hunno-Bulgars, whilst the remaining group, who were free (led by Sandilch
Sandilch
Sandilch , 555, was promoted by the Gokturks in 569 as Khan of the Utigur Bulgars in Patria Onoguria and an ally to the Byzantines who through him played the Utigurs off against their Pseudo-Avar controlled relatives....
in the east) were called Utigurs. The conquest of the easternmost Kutrigurs by Gokturk arrivals led by three brothers from the Imaon Mountains in the 6th century is mentioned by Bar Hebraeus, as well as in the Chronicle of the late 12th century Jacobite patriarch
Patriarch
Originally a patriarch was a man who exercised autocratic authority as a pater familias over an extended family. The system of such rule of families by senior males is called patriarchy. This is a Greek word, a compound of πατριά , "lineage, descent", esp...
of Antioch
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes was an ancient city on the eastern side of the Orontes River. It is near the modern city of Antakya, Turkey.Founded near the end of the 4th century BC by Seleucus I Nicator, one of Alexander the Great's generals, Antioch eventually rivaled Alexandria as the chief city of the...
Michael the Syrian
Michael the Syrian
Michael the Syrian , also known as Michael the Great or Michael Syrus or Michael the Elder, to distinguish him from his nephew, was a patriarch of the Syriac Orthodox Church from 1166 to 1199. He is best known today as the author of the largest medieval Chronicle, which he composed in Syriac...
. At this time they came to be dominated by clans related to the Göktürks
Göktürks
The Göktürks or Kök Türks, were a nomadic confederation of peoples in medieval Inner Asia. Known in Chinese sources as 突厥 , the Göktürks under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan The Göktürks or Kök Türks, (Old Turkic: Türük or Kök Türük or Türük; Celestial Turks) were a nomadic confederation of...
.
In 632, Kubrat
Kubrat
Kubrat or Kurt was a Bulgar ruler credited with establishing the confederation of Old Great Bulgaria in 632. He is said to have achieved this by conquering the Avars and uniting all the Bulgar tribes under one rule....
united the Kutrigur and Utigur tribes who lived in Scythia
Scythia
In antiquity, Scythian or Scyths were terms used by the Greeks to refer to certain Iranian groups of horse-riding nomadic pastoralists who dwelt on the Pontic-Caspian steppe...
. Upon their unification, the state which East Roman scholars referred to as Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria or Great Bulgaria was а term used by Byzantine historians to refer to Onoguria during the reign of the Bulgar ruler Kubrat in the 7th century north of the Caucasus mountains in the steppe between the Dniester and Lower...
was established.
When the Khazar state expanded, it challenged the dominance of Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria
Old Great Bulgaria or Great Bulgaria was а term used by Byzantine historians to refer to Onoguria during the reign of the Bulgar ruler Kubrat in the 7th century north of the Caucasus mountains in the steppe between the Dniester and Lower...
. The Khazars
Khazars
The Khazars were semi-nomadic Turkic people who established one of the largest polities of medieval Eurasia, with the capital of Atil and territory comprising much of modern-day European Russia, western Kazakhstan, eastern Ukraine, Azerbaijan, large portions of the northern Caucasus , parts of...
were able to obtain tribute from Batbayan, Kubrat's eldest son, and so came the downfall of Great Bulgaria. In the mid 7th century, a dissenting faction of Kutrigurs seems to have traveled to the upper Volga where, along with part of the Utigurs, they founded the state of Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria
Volga Bulgaria, or Volga–Kama Bolghar, is a historic Bulgar state that existed between the seventh and thirteenth centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama rivers in what is now Russia.-Origin:...
with Kotrag
Kotrag
Khan Kotrag was the founder of Volga Bulgaria. He was the son of Kubrat who left Great Bulgaria after the death of his father. His successors reached the lands of modern Tatarstan and established a state during 7-9 centuries and recognised Islam as the official religion in 922 AD during the visit...
as its ruler.
Under the leadership of Kuber
Kuber
Khan Kuber was a Bulgar leader, brother of Khan Asparukh and member of the Dulo clan, who according to the Miracles of St Demetrius, in the 670s was the leader of a mixed Christian population of Bulgars, ‘Romans’, Slavs and Germanic people that had been transferred to the Syrmia region in Pannonia...
, another part of the Kutrigur tribe seems to have moved to Sirmium
Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in ancient Roman Pannonia. Firstly mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by the Illyrians and Celts, it was conquered by the Romans in the 1st century BC and subsequently became the capital of the Roman province of Lower Pannonia. In 294 AD, Sirmium was...
(Pannonia
Pannonia
Pannonia was an ancient province of the Roman Empire bounded north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia....
) and from there south to the Pelagonia
Pelagonia
This is about the geographical plain between Greece and the Republic of Macedonia. For the political unit in Macedonia, go to Pelagonia Statistical Region....
n plain. Thereafter they disappear from history as a separate Bulgar group. Kuber
Kuber
Khan Kuber was a Bulgar leader, brother of Khan Asparukh and member of the Dulo clan, who according to the Miracles of St Demetrius, in the 670s was the leader of a mixed Christian population of Bulgars, ‘Romans’, Slavs and Germanic people that had been transferred to the Syrmia region in Pannonia...
's Kutrigur Bulgars displaced some of the populations that had already settled in the region of Macedonia, and intermingled with the populations that remained. In the 8th century, the Kuber Bulgars merged with Asparuh's Bulgars who had already settled on both sides of the Danube River in the late 7th century.

