
Kilauea Iki
Encyclopedia
Kīlauea Iki is a pit crater
which is next to the main summit caldera of Kīlauea
.

s was detected by the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory
. In October it was indicated by seismographs that Kilauea summit was filling with magma. This formed a new cinder cone
, named Puu Puai (gushing hill).
s that flowed from Puu Puai. By November 17, the fountain was reaching 60–80 meters tall with occasional bursts as high as 180 meters. The fountain grew to over 320 meters on November 18. On November 21, the lava lake was over a meter deep over the vent causing ripples across the surface of the lava lake causing lava on the shores to break like waves on a beach. At 7:25 p.m. local time on November 21, the fountain went from 210 meters tall to a few gas bubbles in less than 40 seconds. Some of the fountains were extraordinarily high, reaching nearly 580 m (1,900 ft), among the highest ever recorded.
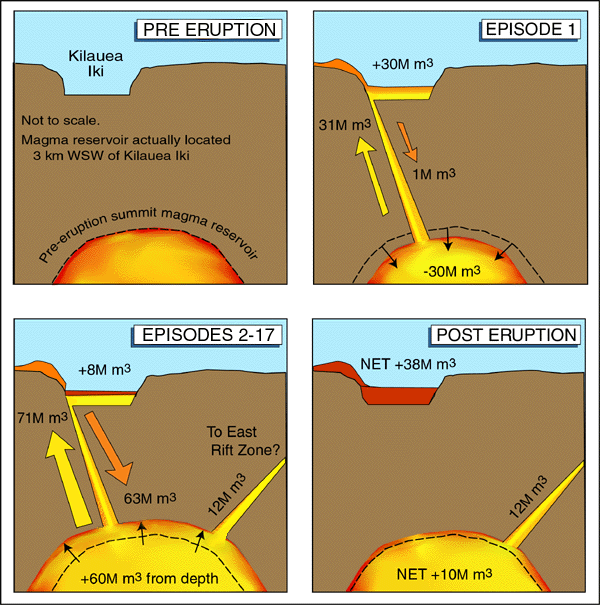
 The first episode had 31 million cubic meters of lava flow into Kīlauea Iki with 1 million cubic meters draining back. During the following episodes, a total of 71 million cubic meters of lava was ejected during a month long eruption that stopped on December 20, 1959. Only 8 million cubic meters of lava remained, 63 million cubic meters of lava drained back into Kīlauea magma reservoir. Often the lava drainback had a higher rate of flow than the eruptions.
The first episode had 31 million cubic meters of lava flow into Kīlauea Iki with 1 million cubic meters draining back. During the following episodes, a total of 71 million cubic meters of lava was ejected during a month long eruption that stopped on December 20, 1959. Only 8 million cubic meters of lava remained, 63 million cubic meters of lava drained back into Kīlauea magma reservoir. Often the lava drainback had a higher rate of flow than the eruptions.
On December 15, the highest flow of lava was measured at 1.45 million cubic meters per hour. With every filling and draining of the lava lake, a 'black ledge' was formed along the rim of the crater which is now 15–60 meters wide and 15 meters tall. During lava drainbacks, a giant counter-clockwise whirlpool would form.
as well as walking along the crater floor on what once was a lake of lava
. Even after 50 years, the surface is still warm to the touch. Rainwater seeps into the cracks and makes contact with the extremely hot rock below and steam is emitted from various surface cracks. The steam and some rocks are hot enough to cause serious burns.
Pit crater
A pit crater is a depression formed by a sinking of the ground surface lying above a void or empty chamber, rather than by the eruption of a volcano or lava vent. It is often found in chains or troughs. Several craters may merge into a linear alignment...
which is next to the main summit caldera of Kīlauea
Kilauea
Kīlauea is a volcano in the Hawaiian Islands, and one of five shield volcanoes that together form the island of Hawaii. Kīlauea means "spewing" or "much spreading" in the Hawaiian language, referring to its frequent outpouring of lava. The Puu Ōō cone has been continuously erupting in the eastern...
.

Kilauea volcano eruption
In August 1959, a swarm of deep earthquakeEarthquake
An earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s was detected by the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory
Hawaiian Volcano Observatory
The Hawaiian Volcano Observatory is a volcano observatory located at Uwekahuna Bluff on the rim of Kīlauea Caldera on the Island of Hawaii. The observatory monitors four active Hawaiian volcanoes: Kīlauea, Mauna Loa, Hualālai, and Haleakalā...
. In October it was indicated by seismographs that Kilauea summit was filling with magma. This formed a new cinder cone
Cinder cone
According to the , Cinder Cone is the proper name of 1 cinder cone in Canada and 7 cinder cones in the United States:In Canada: Cinder Cone In the United States:...
, named Puu Puai (gushing hill).
Lava fountain
Some of the most impressive parts of the eruption were the lava fountainLava fountain
A lava fountain is a volcanic phenomenon in which lava is forcefully but non-explosively ejected from a crater, vent, or fissure. Lava fountains may reach heights of up to . They may occur as a series of short pulses, or a continuous jet of lava. They are commonly seen in Hawaiian eruptions.-See...
s that flowed from Puu Puai. By November 17, the fountain was reaching 60–80 meters tall with occasional bursts as high as 180 meters. The fountain grew to over 320 meters on November 18. On November 21, the lava lake was over a meter deep over the vent causing ripples across the surface of the lava lake causing lava on the shores to break like waves on a beach. At 7:25 p.m. local time on November 21, the fountain went from 210 meters tall to a few gas bubbles in less than 40 seconds. Some of the fountains were extraordinarily high, reaching nearly 580 m (1,900 ft), among the highest ever recorded.

Lava drainback

On December 15, the highest flow of lava was measured at 1.45 million cubic meters per hour. With every filling and draining of the lava lake, a 'black ledge' was formed along the rim of the crater which is now 15–60 meters wide and 15 meters tall. During lava drainbacks, a giant counter-clockwise whirlpool would form.
Tourism
Drivers may view Kīlauea Iki from either a lookout point or the trailhead parking lot. Currently guests can hike across Kīlauea Iki from Byron Ledge which overlooks the craterVolcanic crater
A volcanic crater is a circular depression in the ground caused by volcanic activity. It is typically a basin, circular in form within which occurs a vent from which magma erupts as gases, lava, and ejecta. A crater can be of large dimensions, and sometimes of great depth...
as well as walking along the crater floor on what once was a lake of lava
Lava
Lava refers both to molten rock expelled by a volcano during an eruption and the resulting rock after solidification and cooling. This molten rock is formed in the interior of some planets, including Earth, and some of their satellites. When first erupted from a volcanic vent, lava is a liquid at...
. Even after 50 years, the surface is still warm to the touch. Rainwater seeps into the cracks and makes contact with the extremely hot rock below and steam is emitted from various surface cracks. The steam and some rocks are hot enough to cause serious burns.

