
Joule second
Encyclopedia
The joule-second is a unit equal to a joule
multiplied by a second
, used to measure action
or angular momentum
. The joule-second is the unit used for Planck's constant.
In SI
base units, the joule-second is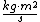 .
.
of a system has the dimensions of energy
integrated over time
; it is therefore measured in joule-seconds.
of an object is the integral with respect to time of the torque
on the object. Torque in the SI system has the unit N·m
, so angular momentum has the unit N·m·s, or J·s.
Joule
The joule ; symbol J) is a derived unit of energy or work in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy expended in applying a force of one newton through a distance of one metre , or in passing an electric current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm for one second...
multiplied by a second
Second
The second is a unit of measurement of time, and is the International System of Units base unit of time. It may be measured using a clock....
, used to measure action
Action (physics)
In physics, action is an attribute of the dynamics of a physical system. It is a mathematical functional which takes the trajectory, also called path or history, of the system as its argument and has a real number as its result. Action has the dimension of energy × time, and its unit is...
or angular momentum
Angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
. The joule-second is the unit used for Planck's constant.
In SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
base units, the joule-second is
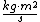 .
.Action
The actionAction (physics)
In physics, action is an attribute of the dynamics of a physical system. It is a mathematical functional which takes the trajectory, also called path or history, of the system as its argument and has a real number as its result. Action has the dimension of energy × time, and its unit is...
of a system has the dimensions of energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
integrated over time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
; it is therefore measured in joule-seconds.
Angular momentum
The angular momentumAngular momentum
In physics, angular momentum, moment of momentum, or rotational momentum is a conserved vector quantity that can be used to describe the overall state of a physical system...
of an object is the integral with respect to time of the torque
Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
on the object. Torque in the SI system has the unit N·m
Metre
The metre , symbol m, is the base unit of length in the International System of Units . Originally intended to be one ten-millionth of the distance from the Earth's equator to the North Pole , its definition has been periodically refined to reflect growing knowledge of metrology...
, so angular momentum has the unit N·m·s, or J·s.

