Joint
Encyclopedia
A joint is the location at which two or more bone
s make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.
 Joints are mainly classified structurally and functionally. Structural classification is determined by how the bones connect to each other, while functional classification is determined by the degree of movement between the articulating bones. In practice, there is significant overlap between the two types of classifications.
Joints are mainly classified structurally and functionally. Structural classification is determined by how the bones connect to each other, while functional classification is determined by the degree of movement between the articulating bones. In practice, there is significant overlap between the two types of classifications.
Terms ending in the suffix
-sis are singular and refer to just one joint, while -ses is the suffix for pluralization.
The joints may be classified anatomically into the following groups:
, and when involving inflammation
of one or more joints the disorder is called an arthritis
. Most joint disorders involve arthritis, but joint damage by external physical trauma
is typically not termed arthritis.
Arthropathies are called polyarticular when involving many joints and monoarticular when involving only one single joint.
Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in people over the age of 55. There are many different forms of arthritis, each of which has a different cause. The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis
(also known as degenerative joint disease) occurs following trauma to the joint, following an infection of the joint or simply as a result of aging. Furthermore, there is emerging evidence that abnormal anatomy may contribute to early development of osteoarthritis. Other forms of arthritis are rheumatoid arthritis
and psoriatic arthritis
, which are autoimmune diseases in which the body is attacking itself. Septic arthritis
is caused by joint infection
. Gouty arthritis
is caused by deposition of uric acid
crystals in the joint that results in subsequent inflammation. Additionally, there is a less common form of gout that is caused by the formation of rhomboidal shaped crystals of calcium pyrophosphate. This form of gout is known as pseudogout.
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
s make contact. They are constructed to allow movement and provide mechanical support, and are classified structurally and functionally.
Classification


Terms ending in the suffix
Suffix
In linguistics, a suffix is an affix which is placed after the stem of a word. Common examples are case endings, which indicate the grammatical case of nouns or adjectives, and verb endings, which form the conjugation of verbs...
-sis are singular and refer to just one joint, while -ses is the suffix for pluralization.
Structural classification
Structural classification names and divides joints according to how the bones are connected to each other. There are three structural classifications of joints:- fibrous jointFibrous jointFibrous joints are connected by dense connective tissue, consisting mainly of collagen.-Types:These joints are also called "fixed" or "immoveable" joints, because they do not move. These joints have no joint cavity and are connected via fibrous connective tissue. The skull bones are connected by...
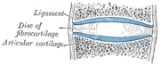
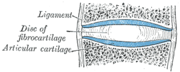
- joined by dense irregular connective tissue that is rich in collagen fibers - cartilaginous jointCartilaginous jointCartilaginous joints are connected entirely by cartilage . Cartilaginous joints allow more movement between bones than a fibrous joint but less than the highly mobile synovial joint. An example would be the joint between the manubrium and the sternum...
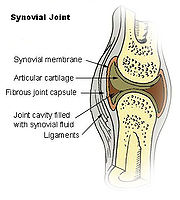
- joined by cartilageCartilageCartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in many areas in the bodies of humans and other animals, including the joints between bones, the rib cage, the ear, the nose, the elbow, the knee, the ankle, the bronchial tubes and the intervertebral discs... - synovial jointSynovial jointA Synovial joint, also known as a diarthrosis, is the most common and most movable type of joint in the body of a mammal. As with most other joints, synovial joints achieve movement at the point of contact of the articulating bones....
- not directly joined - the bones have a synovial cavity and are united by the dense irregular connective tissue that forms the articular capsule that is normally associated with accessory ligaments.
Functional classification
Joints can also be classified functionally, by the degree of mobility they allow:- synarthrosisSynarthrosisA synarthrosis is a type of joint which permits very little or no movement under normal conditions. Most synarthrosis joints are fibrous.Suture joints and Gomphosis joint are synarthroses.-Types:...
- permits little or no mobility. Most synarthrosis joints are fibrous jointFibrous jointFibrous joints are connected by dense connective tissue, consisting mainly of collagen.-Types:These joints are also called "fixed" or "immoveable" joints, because they do not move. These joints have no joint cavity and are connected via fibrous connective tissue. The skull bones are connected by...
s (e.g., skull sutures). - amphiarthrosis - permits slight mobility. Most amphiarthrosis joints are cartilaginous jointCartilaginous jointCartilaginous joints are connected entirely by cartilage . Cartilaginous joints allow more movement between bones than a fibrous joint but less than the highly mobile synovial joint. An example would be the joint between the manubrium and the sternum...
s (e.g., vertebrae). - diarthrosis - permits a variety of movements. All diarthrosis joints are synovial jointSynovial jointA Synovial joint, also known as a diarthrosis, is the most common and most movable type of joint in the body of a mammal. As with most other joints, synovial joints achieve movement at the point of contact of the articulating bones....
s (e.g., shoulder, hip, elbow, knee, etc.), and the terms "diarthrosis" and "synovial joint" are considered equivalent by Terminologia AnatomicaTerminologia AnatomicaTerminologia Anatomica is the international standard on human anatomic terminology. It was developed by the Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology and the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists and was released in 1998. It supersedes the previous standard, Nomina...
.
Biomechanical classification
Joints can also be classified based on their anatomy or on their biomechanical properties. According to the anatomic classification, joints are subdivided into simple and compound, depending on the number of bones involved, and into complex and combination joints:- Simple Joint: 2 articulation surfaces (e.g. shoulder joint, hip joint)
- Compound Joint: 3 or more articulation surfaces (e.g. radiocarpal joint)
- Complex Joint: 2 or more articulation surfaces and an articular disc or meniscusMeniscus (anatomy)In anatomy, a meniscus is a crescent-shaped fibrocartilaginous structure that, in contrast to articular disks, only partly divides a joint cavity. In humans it is present in the knee, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular, and temporomandibular joints; in other organisms they may be present in other...
(e.g. knee jointKneeThe knee joint joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two articulations: one between the fibula and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body and is very complicated. The knee is a mobile trocho-ginglymus , which permits flexion and extension as...
)
Anatomical
The joints may be classified anatomically into the following groups:
- Articulations of hand
- Elbow jointsElbowThe human elbow is the region surrounding the elbow-joint—the ginglymus or hinge joint in the middle of the arm. Three bones form the elbow joint: the humerus of the upper arm, and the paired radius and ulna of the forearm....
- Wrist jointsWristIn human anatomy, the wrist is variously defined as 1) the carpus or carpal bones, the complex of eight bones forming the proximal skeletal segment of the hand;...
- Axillary articulationsAxillary articulationsAxillary articulations refers to these joints in the shoulder:*Glenohumeral joint*acromioclavicular joint...
- Sternoclavicular joints
- Vertebral articulations
- Temporomandibular jointTemporomandibular jointThe temporomandibular joint is the joint of the jaw and is frequently referred to as TMJ. There are two TMJs, one on either side, working in unison. The name is derived from the two bones which form the joint: the upper temporal bone which is part of the cranium , and the lower jaw bone called the...
s - Sacroiliac jointSacroiliac jointThe sacroiliac joint or SI joint is the joint in the bony pelvis between the sacrum and the ilium of the pelvis, which are joined together by strong ligaments. In humans, the sacrum supports the spine and is supported in turn by an ilium on each side...
s - Hip joints
- Knee jointKneeThe knee joint joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two articulations: one between the fibula and tibia, and one between the femur and patella. It is the largest joint in the human body and is very complicated. The knee is a mobile trocho-ginglymus , which permits flexion and extension as...
s - Articulations of foot
Joint disorders
A joint disorder is termed an arthropathyArthropathy
-Scope:Arthritis is a form of arthropathy that involves inflammation of one or more joints, while the term arthropathy may be used regardless of whether there is inflammation or not.Spondylarthropathy is any form of arthropathy of the vertebral column....
, and when involving inflammation
Inflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
of one or more joints the disorder is called an arthritis
Arthritis
Arthritis is a form of joint disorder that involves inflammation of one or more joints....
. Most joint disorders involve arthritis, but joint damage by external physical trauma
Physical trauma
Trauma refers to "a body wound or shock produced by sudden physical injury, as from violence or accident." It can also be described as "a physical wound or injury, such as a fracture or blow." Major trauma can result in secondary complications such as circulatory shock, respiratory failure and death...
is typically not termed arthritis.
Arthropathies are called polyarticular when involving many joints and monoarticular when involving only one single joint.
Arthritis is the leading cause of disability in people over the age of 55. There are many different forms of arthritis, each of which has a different cause. The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis also known as degenerative arthritis or degenerative joint disease, is a group of mechanical abnormalities involving degradation of joints, including articular cartilage and subchondral bone. Symptoms may include joint pain, tenderness, stiffness, locking, and sometimes an effusion...
(also known as degenerative joint disease) occurs following trauma to the joint, following an infection of the joint or simply as a result of aging. Furthermore, there is emerging evidence that abnormal anatomy may contribute to early development of osteoarthritis. Other forms of arthritis are rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. The process produces an inflammatory response of the synovium secondary to hyperplasia of synovial cells, excess synovial fluid, and the development...
and psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a type of inflammatory arthritis that, according to the National Psoriasis Foundation, will develop in up to 30 percent of people who have the chronic skin condition psoriasis...
, which are autoimmune diseases in which the body is attacking itself. Septic arthritis
Septic arthritis
Septic arthritis is the purulent invasion of a joint by an infectious agent which produces arthritis. People with artificial joints are more at risk than the general population but have slightly different symptoms, are infected with different organisms and require different treatment. Septic...
is caused by joint infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
. Gouty arthritis
Gout
Gout is a medical condition usually characterized by recurrent attacks of acute inflammatory arthritis—a red, tender, hot, swollen joint. The metatarsal-phalangeal joint at the base of the big toe is the most commonly affected . However, it may also present as tophi, kidney stones, or urate...
is caused by deposition of uric acid
Uric acid
Uric acid is a heterocyclic compound of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen with the formula C5H4N4O3. It forms ions and salts known as urates and acid urates such as ammonium acid urate. Uric acid is created when the body breaks down purine nucleotides. High blood concentrations of uric acid...
crystals in the joint that results in subsequent inflammation. Additionally, there is a less common form of gout that is caused by the formation of rhomboidal shaped crystals of calcium pyrophosphate. This form of gout is known as pseudogout.

