
Jet engine performance
Encyclopedia
In fixed-wing aircraft
driven by one or more jet engines, the performance of the jet engine is important to the operation of the aircraft and includes measurement of thrust
, fuel consumption, noise
and engine emissions
.
The thrust, noise and emission elements of the performance of a jet engine are of vital importance in the takeoff
phase of operation of the aircraft. The thrust and fuel consumption elements, and their variation with altitude and airspeed
, are of vital importance in the climb
and cruise
phases of operation of the aircraft.
The velocity of the exhaust gas as it leaves a jet engine is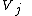 :
: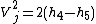
where
Alternatively,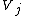 is related to the temperatures of the exhaust gas:
is related to the temperatures of the exhaust gas: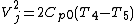
where
Fixed-wing aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is an aircraft capable of flight using wings that generate lift due to the vehicle's forward airspeed. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct from rotary-wing aircraft in which wings rotate about a fixed mast and ornithopters in which lift is generated by flapping wings.A powered...
driven by one or more jet engines, the performance of the jet engine is important to the operation of the aircraft and includes measurement of thrust
Thrust
Thrust is a reaction force described quantitatively by Newton's second and third laws. When a system expels or accelerates mass in one direction the accelerated mass will cause a force of equal magnitude but opposite direction on that system....
, fuel consumption, noise
Noise pollution
Noise pollution is excessive, displeasing human, animal or machine-created environmental noise that disrupts the activity or balance of human or animal life...
and engine emissions
Emission standard
Emission standards are requirements that set specific limits to the amount of pollutants that can be released into the environment. Many emissions standards focus on regulating pollutants released by automobiles and other powered vehicles but they can also regulate emissions from industry, power...
.
The thrust, noise and emission elements of the performance of a jet engine are of vital importance in the takeoff
Takeoff
Takeoff is the phase of flight in which an aerospace vehicle goes from the ground to flying in the air.For horizontal takeoff aircraft this usually involves starting with a transition from moving along the ground on a runway. For balloons, helicopters and some specialized fixed-wing aircraft , no...
phase of operation of the aircraft. The thrust and fuel consumption elements, and their variation with altitude and airspeed
Airspeed
Airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are: indicated airspeed , calibrated airspeed , true airspeed , equivalent airspeed and density airspeed....
, are of vital importance in the climb
Climb
thumb|right|An [[Embraer ERJ 145]] climbingIn aviation, the term climb refers both to the actual operation of increasing the altitude of an aircraft and to the logical phase of a typical flight following take-off and preceding the cruise, during which an increase in altitude to a predetermined...
and cruise
Cruise (flight)
Cruise is the level portion of aircraft travel where flight is most fuel efficient. It occurs between ascent and descent phases and is usually the majority of a journey. Technically, cruising consists of heading changes only at a constant airspeed and altitude...
phases of operation of the aircraft.
Thrust
The thrust from a jet engine is determined by the velocity of exhaust gases measured relative to the engine.The velocity of the exhaust gas as it leaves a jet engine is
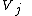 :
: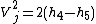
where
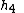 |
is the specific enthalpy Enthalpy Enthalpy is a measure of the total energy of a thermodynamic system. It includes the internal energy, which is the energy required to create a system, and the amount of energy required to make room for it by displacing its environment and establishing its volume and pressure.Enthalpy is a... of the gas leaving the turbine and entering the propelling nozzle Propelling nozzle A propelling nozzle is the component of a jet engine that operates to constrict the flow, to form an exhaust jet and to maximise the velocity of propelling gases from the engine.... |
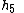 |
is the specific enthalpy of the gas after it has left the propelling nozzle |
Alternatively,
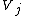 is related to the temperatures of the exhaust gas:
is related to the temperatures of the exhaust gas: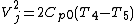
where
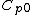 |
is the specific heat of exhaust gas at constant pressure |
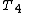 |
is the temperature of the gas leaving the turbine and entering the propelling nozzle |
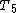 |
is the temperature of the gas after it has left the propelling nozzle |

